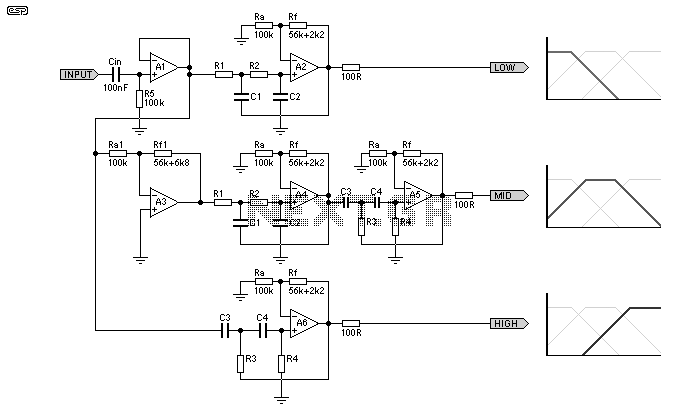
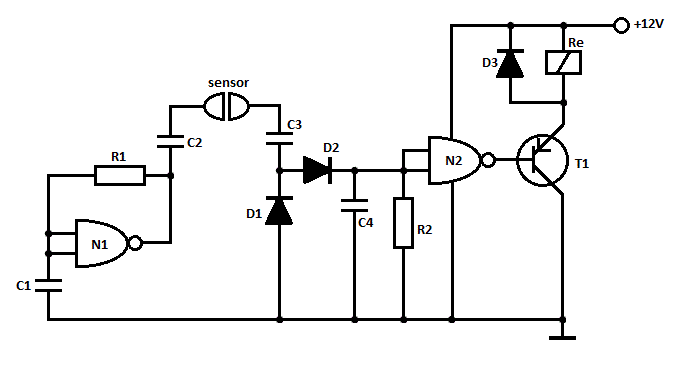
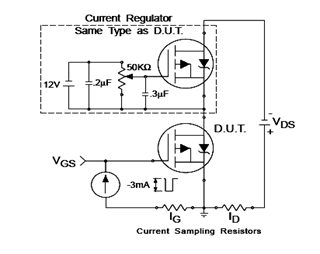
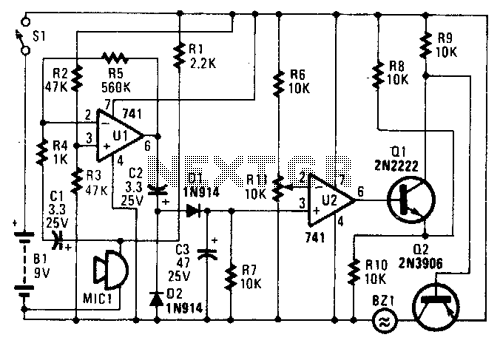
TV preamplifier circuit
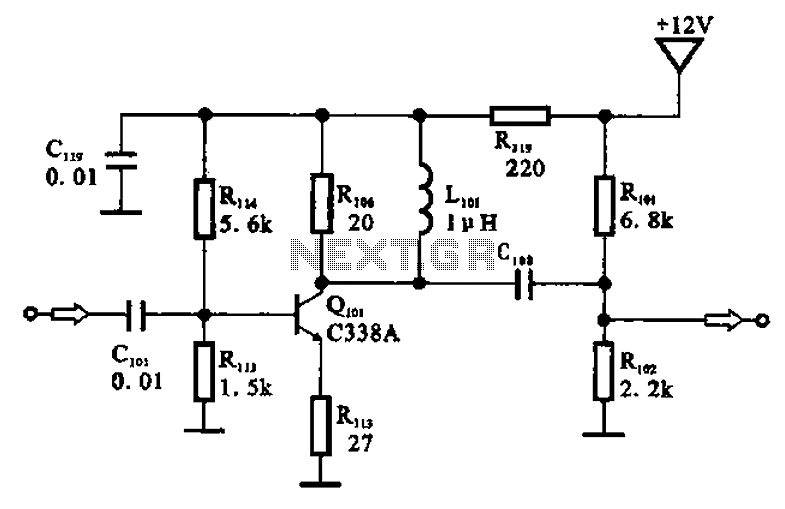
The amplifier circuit is designed as a pre-amplifier configuration. It utilizes transistor Q101 and other components such as inductor L101 and biasing elements. The transistor operates as a common emitter intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier. The IF signal is coupled through capacitor C101 to the base of Q101, where it is amplified at the collector output. The amplified signal is then passed through coupling capacitor C103, which serves to block DC, before being directed to a surface acoustic wave (SAW) filter X101. In addition, inductor L101 and collector load resistor R106 are arranged in parallel with Q101 to enhance the high-frequency response of the pre-amplifier, leveraging the high impedance characteristics of L101.
The described amplifier circuit configuration is essential for processing weak signals in various communication applications. The common emitter configuration of transistor Q101 provides significant voltage gain, making it suitable for amplifying low-level IF signals. The coupling capacitors C101 and C103 are critical components in this design, ensuring that DC bias levels do not interfere with the AC signal amplification process.
Capacitor C101 is responsible for coupling the input IF signal to the base of the transistor while blocking any DC offset that might be present. This allows the transistor to operate in its active region, where it can effectively amplify the signal. Similarly, capacitor C103 performs a vital function by preventing any DC component of the amplified output from reaching the SAW filter X101, which is designed to process only the AC components of the signal.
Inductor L101 plays a dual role in this circuit. It not only serves as a part of the collector load but also enhances the overall high-frequency performance of the amplifier. By providing a high impedance path for high-frequency signals, L101 ensures that the amplifier can respond effectively to rapid changes in the input signal, thereby preserving the integrity of the amplified output.
Resistor R106, placed in parallel with the inductor, helps to stabilize the operating point of the transistor and sets the load for the collector, ensuring efficient power transfer and minimizing distortion. The combination of these components creates a robust pre-amplifier circuit capable of handling a wide range of frequencies while maintaining signal fidelity, making it ideal for use in television and other RF applications.Amp circuit as shown in the pre-television. The pre-amplifier circuit is Qioi and other parts of xlol. Q [ol and biasing element is configured as a common emitter IF amplifier, IF signal through a coupling capacitor c] ol Qioi added to the base, is amplified by the collector output, and then through a coupling capacitor C103 is applied to a surface acoustic wave filter XjoJ input device (the coupling capacitor has a DC blocking effect). Inductor Lioi and collector load resistor R106 in parallel Qioi, the use of high-frequency signal L10l high impedance characteristics in the pre-amp to compensate for high-frequency characteristics.
The described amplifier circuit configuration is essential for processing weak signals in various communication applications. The common emitter configuration of transistor Q101 provides significant voltage gain, making it suitable for amplifying low-level IF signals. The coupling capacitors C101 and C103 are critical components in this design, ensuring that DC bias levels do not interfere with the AC signal amplification process.
Capacitor C101 is responsible for coupling the input IF signal to the base of the transistor while blocking any DC offset that might be present. This allows the transistor to operate in its active region, where it can effectively amplify the signal. Similarly, capacitor C103 performs a vital function by preventing any DC component of the amplified output from reaching the SAW filter X101, which is designed to process only the AC components of the signal.
Inductor L101 plays a dual role in this circuit. It not only serves as a part of the collector load but also enhances the overall high-frequency performance of the amplifier. By providing a high impedance path for high-frequency signals, L101 ensures that the amplifier can respond effectively to rapid changes in the input signal, thereby preserving the integrity of the amplified output.
Resistor R106, placed in parallel with the inductor, helps to stabilize the operating point of the transistor and sets the load for the collector, ensuring efficient power transfer and minimizing distortion. The combination of these components creates a robust pre-amplifier circuit capable of handling a wide range of frequencies while maintaining signal fidelity, making it ideal for use in television and other RF applications.Amp circuit as shown in the pre-television. The pre-amplifier circuit is Qioi and other parts of xlol. Q [ol and biasing element is configured as a common emitter IF amplifier, IF signal through a coupling capacitor c] ol Qioi added to the base, is amplified by the collector output, and then through a coupling capacitor C103 is applied to a surface acoustic wave filter XjoJ input device (the coupling capacitor has a DC blocking effect). Inductor Lioi and collector load resistor R106 in parallel Qioi, the use of high-frequency signal L10l high impedance characteristics in the pre-amp to compensate for high-frequency characteristics.