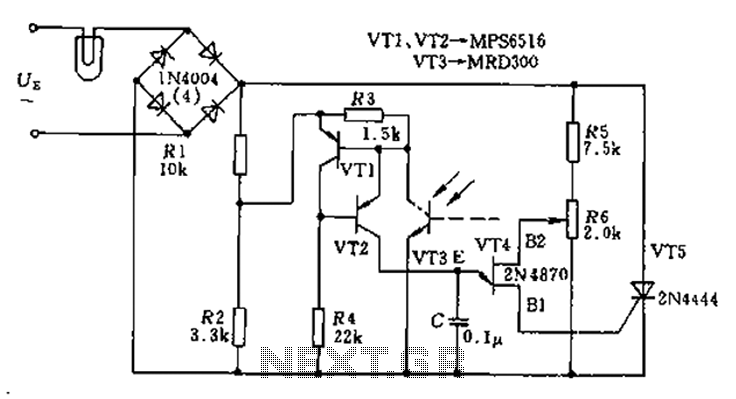
Cellular phone detector circuit schematic
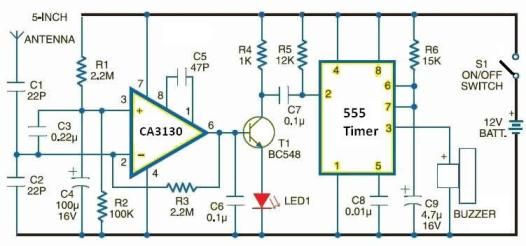
Cellular phone detector circuit schematic using common electronic parts
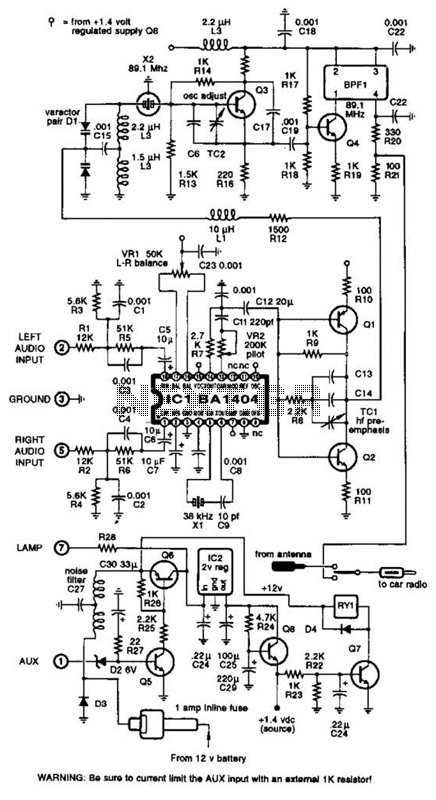
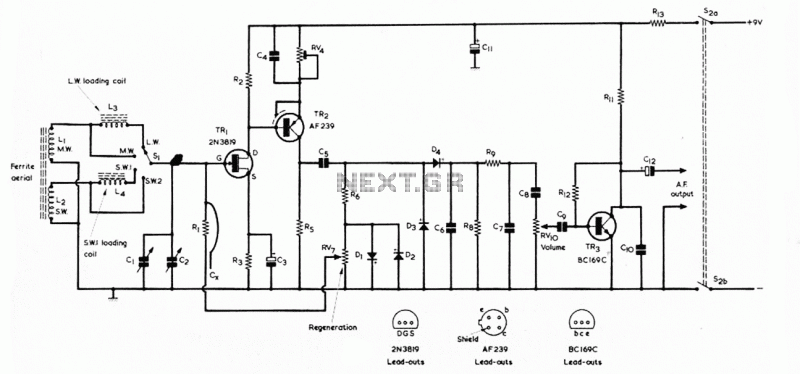
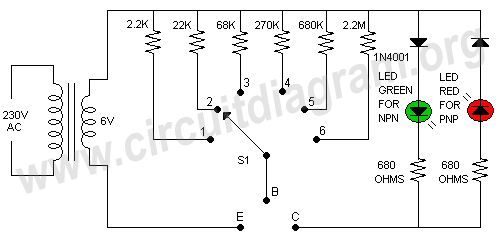
The cellular phone detector circuit is designed to identify the presence of a cellular phone within a specified range. This circuit utilizes basic electronic components, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. The primary components typically include a radio frequency (RF) receiver, an operational amplifier, and a series of passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
The RF receiver is crucial for detecting the signals emitted by cellular phones. It is tuned to the specific frequency bands used by mobile phones, allowing it to pick up incoming signals effectively. The output of the RF receiver is then fed into an operational amplifier, which amplifies the signal for further processing.
Additional components, such as diodes, may be included to rectify the output signal, converting it from AC to DC. A visual indicator, such as an LED, can be incorporated into the circuit to provide a clear indication when a cellular phone is detected. The LED will illuminate when the circuit receives a sufficient signal strength, indicating the presence of a phone.
This circuit can be powered by a standard battery or a DC power supply, making it versatile for various applications. Overall, the cellular phone detector circuit serves as a practical tool for monitoring cellular phone activity in specific environments, such as classrooms or meeting rooms. Its simplicity and reliance on commonly available electronic parts make it an excellent project for those interested in RF technology and circuit design.Cellular phone detector circuit schematic using common electronic parts 🔗 External reference
The cellular phone detector circuit is designed to identify the presence of a cellular phone within a specified range. This circuit utilizes basic electronic components, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. The primary components typically include a radio frequency (RF) receiver, an operational amplifier, and a series of passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
The RF receiver is crucial for detecting the signals emitted by cellular phones. It is tuned to the specific frequency bands used by mobile phones, allowing it to pick up incoming signals effectively. The output of the RF receiver is then fed into an operational amplifier, which amplifies the signal for further processing.
Additional components, such as diodes, may be included to rectify the output signal, converting it from AC to DC. A visual indicator, such as an LED, can be incorporated into the circuit to provide a clear indication when a cellular phone is detected. The LED will illuminate when the circuit receives a sufficient signal strength, indicating the presence of a phone.
This circuit can be powered by a standard battery or a DC power supply, making it versatile for various applications. Overall, the cellular phone detector circuit serves as a practical tool for monitoring cellular phone activity in specific environments, such as classrooms or meeting rooms. Its simplicity and reliance on commonly available electronic parts make it an excellent project for those interested in RF technology and circuit design.Cellular phone detector circuit schematic using common electronic parts 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713