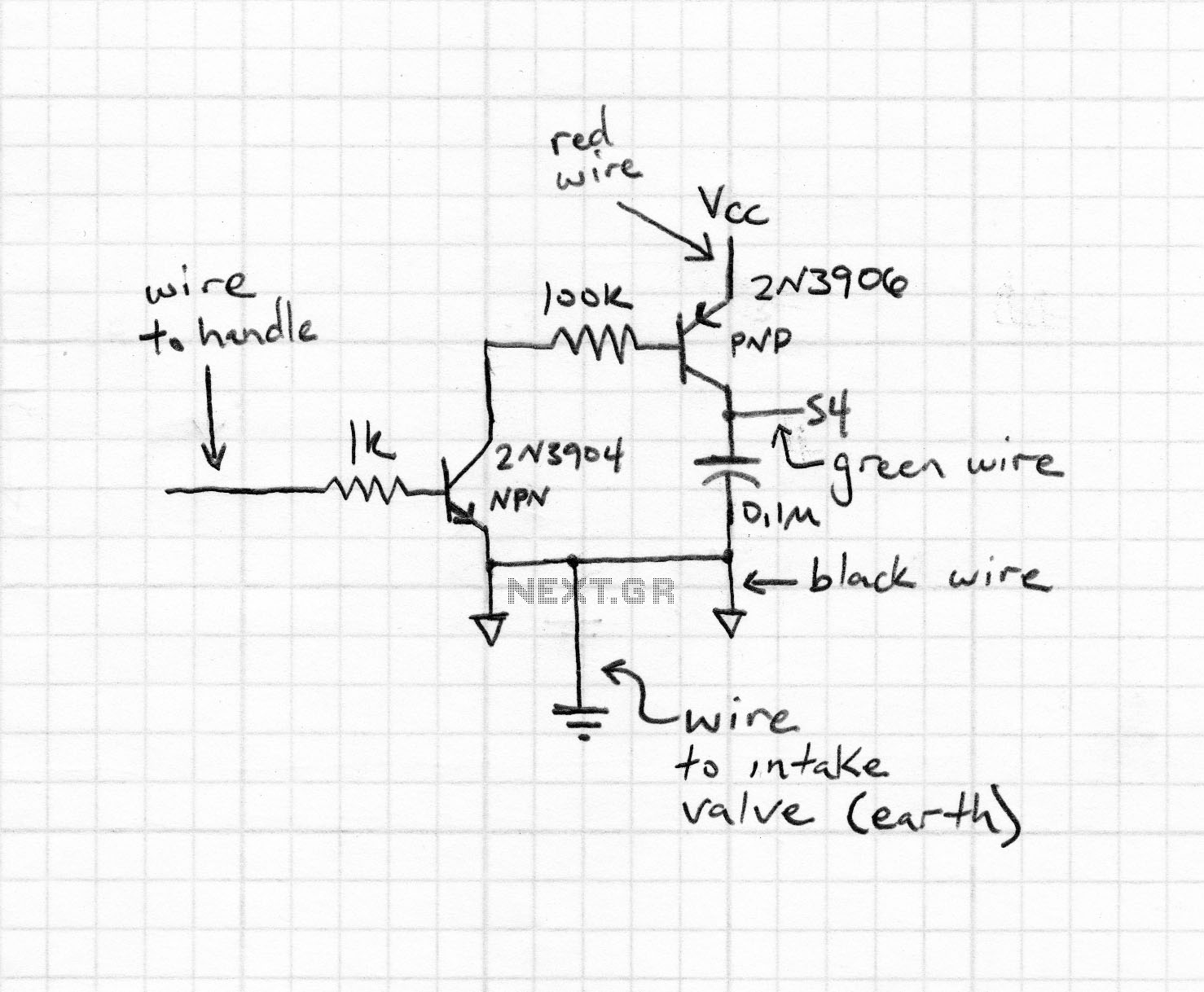
CENTER TAPPED TRANSFORMER AUDIO OSCILLATOR

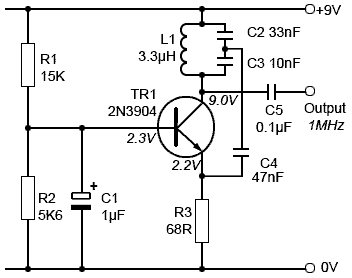
The oscillator circuit employs a center-tapped transistor output transformer that functions as a load for the collector of Q1, provides a feedback signal to the base, and acts as the output winding to drive the speaker. Resistor R1 supplies DC bias, while capacitor C1 completes the AC path from the transformer to the base of Q1. Adjusting the values of C1 and R1 allows for modifications to the oscillator's output level and tone; however, caution should be exercised not to decrease the value of R1 excessively, as this may lead to excessive collector current drawn by the transistor.
The described oscillator circuit is a fundamental design often used in audio applications, where modulation of sound frequencies is required. The center-tapped transformer plays a critical role in this configuration, as it not only provides the necessary load for the transistor but also facilitates the feedback loop essential for sustaining oscillation. The feedback signal is vital for maintaining the oscillation frequency and stability of the circuit.
In this setup, the transistor Q1 acts as the primary amplifying element. The DC bias provided by R1 ensures that Q1 operates in the active region, allowing it to amplify the AC signals effectively. The value of R1 is crucial; if it is too low, it risks pushing Q1 into saturation, leading to distortion or complete cutoff of the output signal. Conversely, if R1 is too high, the transistor may not turn on sufficiently, resulting in weak oscillation.
Capacitor C1 serves to couple the AC signal from the transformer to the base of Q1. The capacitance value of C1 can be adjusted to fine-tune the frequency response of the oscillator. A larger capacitance will allow lower frequencies to pass through, potentially lowering the tone, while a smaller capacitance will restrict lower frequencies and allow higher frequencies to dominate.
The transformer’s output is connected to the speaker, which converts the electrical oscillations into audible sound waves. By modifying the values of R1 and C1, the user can experiment with different sound characteristics, such as volume and tonal quality, making this circuit versatile for various audio applications.
In summary, the oscillator circuit's design, with its center-tapped transformer, biasing resistor, and coupling capacitor, allows for a range of sound modulation possibilities, while careful consideration of component values ensures reliable operation without risking damage to the transistor.The oscillator circuit uses a center-tapped transistor output transformer to serve as a load for the collector of Q1, supply a feedback signal for the base, and serve as the output winding for driving the speaker. R1 supplies dc bias and C1 completes the ac path from the transformer to Q1`s base. You can play around with the values of C1 and R1 to change the oscillator`s output level and tone, but don`t reduce R1`s value too much or the transistor will draw excessive collector current. 🔗 External reference
The described oscillator circuit is a fundamental design often used in audio applications, where modulation of sound frequencies is required. The center-tapped transformer plays a critical role in this configuration, as it not only provides the necessary load for the transistor but also facilitates the feedback loop essential for sustaining oscillation. The feedback signal is vital for maintaining the oscillation frequency and stability of the circuit.
In this setup, the transistor Q1 acts as the primary amplifying element. The DC bias provided by R1 ensures that Q1 operates in the active region, allowing it to amplify the AC signals effectively. The value of R1 is crucial; if it is too low, it risks pushing Q1 into saturation, leading to distortion or complete cutoff of the output signal. Conversely, if R1 is too high, the transistor may not turn on sufficiently, resulting in weak oscillation.
Capacitor C1 serves to couple the AC signal from the transformer to the base of Q1. The capacitance value of C1 can be adjusted to fine-tune the frequency response of the oscillator. A larger capacitance will allow lower frequencies to pass through, potentially lowering the tone, while a smaller capacitance will restrict lower frequencies and allow higher frequencies to dominate.
The transformer’s output is connected to the speaker, which converts the electrical oscillations into audible sound waves. By modifying the values of R1 and C1, the user can experiment with different sound characteristics, such as volume and tonal quality, making this circuit versatile for various audio applications.
In summary, the oscillator circuit's design, with its center-tapped transformer, biasing resistor, and coupling capacitor, allows for a range of sound modulation possibilities, while careful consideration of component values ensures reliable operation without risking damage to the transistor.The oscillator circuit uses a center-tapped transistor output transformer to serve as a load for the collector of Q1, supply a feedback signal for the base, and serve as the output winding for driving the speaker. R1 supplies dc bias and C1 completes the ac path from the transformer to Q1`s base. You can play around with the values of C1 and R1 to change the oscillator`s output level and tone, but don`t reduce R1`s value too much or the transistor will draw excessive collector current. 🔗 External reference