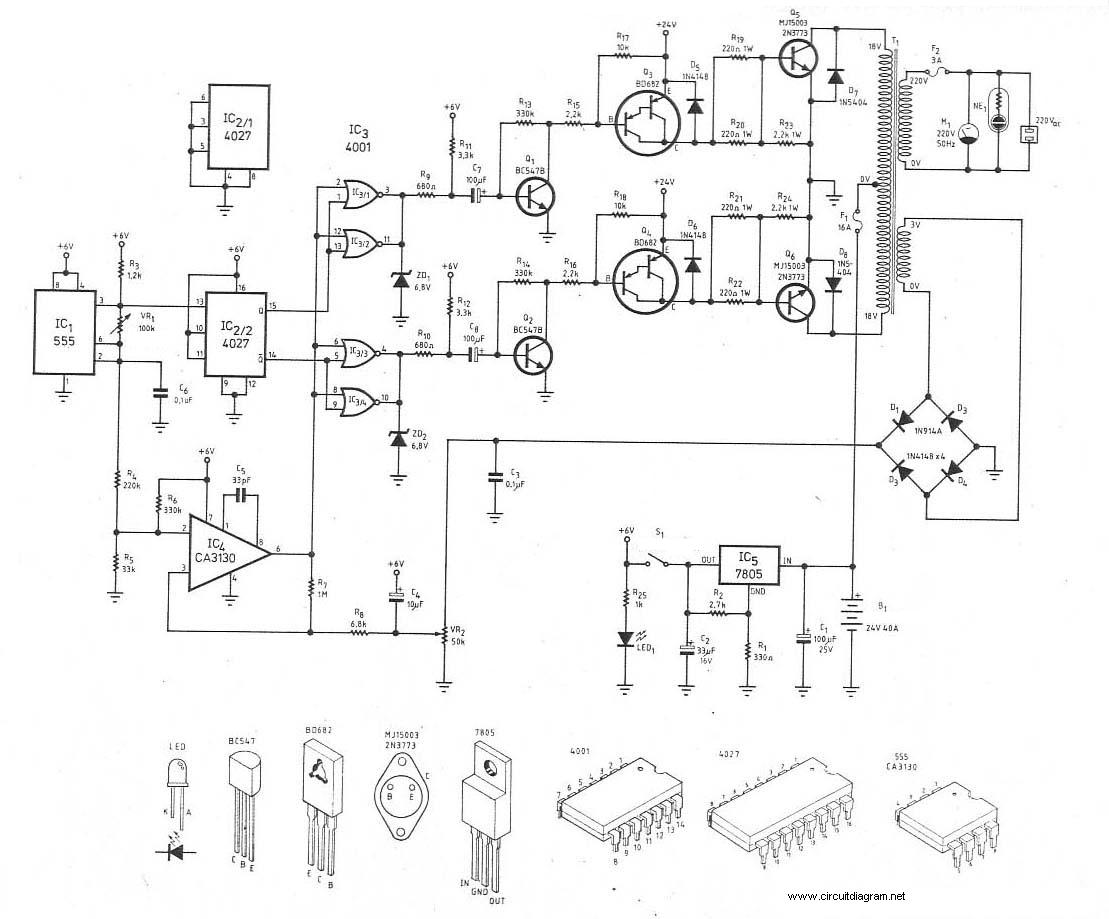
cheap 12v to 220v inverter
Although modern electrical appliances are increasingly self-powered, particularly portable devices used during camping or summer vacations, there are still occasions when a 230 V AC source is necessary. Additionally, it is beneficial for this source to operate at a frequency similar to that of the mains supply. When the power requirement from such a source is relatively low—specifically, 30 VA—it is straightforward to construct an inverter using simple, inexpensive components that many electronics hobbyists may already possess.
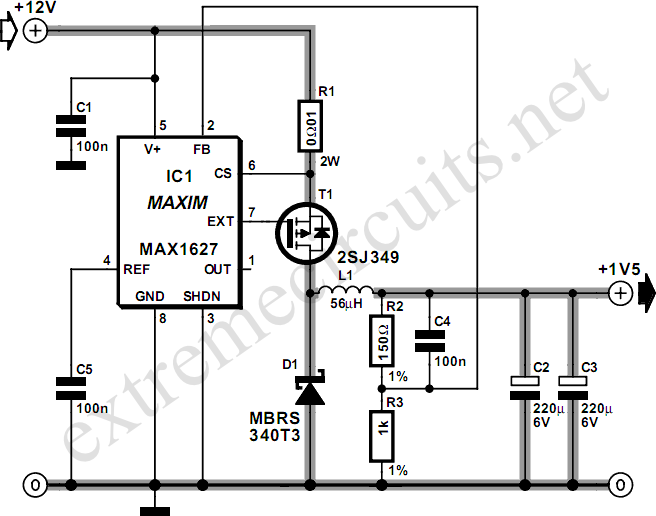
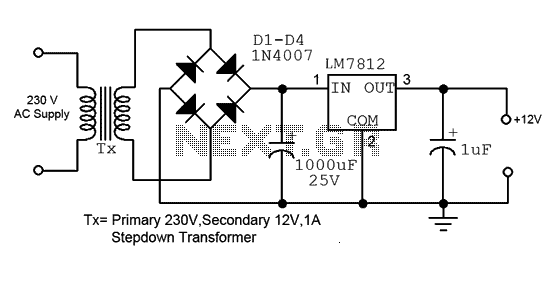
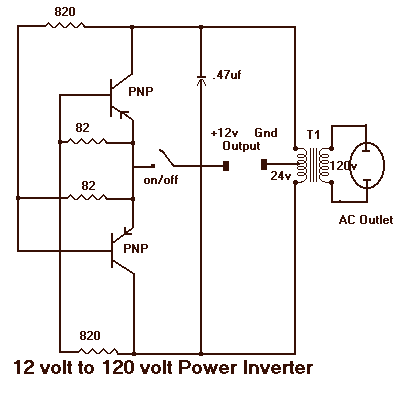
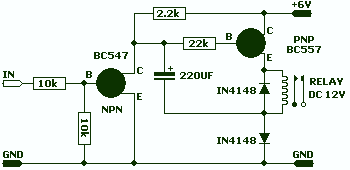
To create a low-power inverter capable of converting DC voltage to 230 V AC at a frequency close to the mains supply, a basic understanding of circuit design and component selection is essential. The inverter circuit typically consists of several key components: a DC power source (such as a battery), an oscillator circuit, a transformer, and a switching mechanism.
The oscillator circuit generates a square wave signal that alternates between high and low states, effectively simulating the AC waveform. Commonly used oscillators include the astable multivibrator configuration using transistors or integrated circuits such as the 555 timer. The frequency of the oscillator can be adjusted to match the desired output frequency, typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the regional standards.
The switching mechanism, often implemented with transistors or MOSFETs, is responsible for controlling the flow of current through the transformer. When the oscillator activates the switches, current flows through the primary winding of the transformer, inducing a voltage in the secondary winding. The transformer steps up the voltage to the required 230 V AC level.
To ensure the inverter operates efficiently and safely, it is crucial to incorporate protective components such as fuses and diodes. Fuses can prevent overcurrent situations, while diodes can protect against reverse voltage spikes, which could damage sensitive components.
Finally, the output of the inverter should be filtered to smooth the waveform, as the square wave produced by the oscillator may not be suitable for all appliances. This can be achieved using capacitors and inductors to create a low-pass filter, effectively converting the square wave into a more sinusoidal waveform.
Overall, constructing a low-power inverter is an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts, providing a practical solution for powering 230 V AC appliances in off-grid scenarios.Even though today s electrical appliances are increasingly often self-powered, especially the portable ones you carry around when camping or holidaying in summer, you do still sometimes need a source of 230 V AC - and while we re about it, why not at a frequency close to that of the mains? As long as the power required from such a source remains relatively low - here we ve chosen 30 VA - it s very easy to build an inverter with simple, cheap components that many electronics hobbyists may even already have..
🔗 External reference
To create a low-power inverter capable of converting DC voltage to 230 V AC at a frequency close to the mains supply, a basic understanding of circuit design and component selection is essential. The inverter circuit typically consists of several key components: a DC power source (such as a battery), an oscillator circuit, a transformer, and a switching mechanism.
The oscillator circuit generates a square wave signal that alternates between high and low states, effectively simulating the AC waveform. Commonly used oscillators include the astable multivibrator configuration using transistors or integrated circuits such as the 555 timer. The frequency of the oscillator can be adjusted to match the desired output frequency, typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the regional standards.
The switching mechanism, often implemented with transistors or MOSFETs, is responsible for controlling the flow of current through the transformer. When the oscillator activates the switches, current flows through the primary winding of the transformer, inducing a voltage in the secondary winding. The transformer steps up the voltage to the required 230 V AC level.
To ensure the inverter operates efficiently and safely, it is crucial to incorporate protective components such as fuses and diodes. Fuses can prevent overcurrent situations, while diodes can protect against reverse voltage spikes, which could damage sensitive components.
Finally, the output of the inverter should be filtered to smooth the waveform, as the square wave produced by the oscillator may not be suitable for all appliances. This can be achieved using capacitors and inductors to create a low-pass filter, effectively converting the square wave into a more sinusoidal waveform.
Overall, constructing a low-power inverter is an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts, providing a practical solution for powering 230 V AC appliances in off-grid scenarios.Even though today s electrical appliances are increasingly often self-powered, especially the portable ones you carry around when camping or holidaying in summer, you do still sometimes need a source of 230 V AC - and while we re about it, why not at a frequency close to that of the mains? As long as the power required from such a source remains relatively low - here we ve chosen 30 VA - it s very easy to build an inverter with simple, cheap components that many electronics hobbyists may even already have..
🔗 External reference