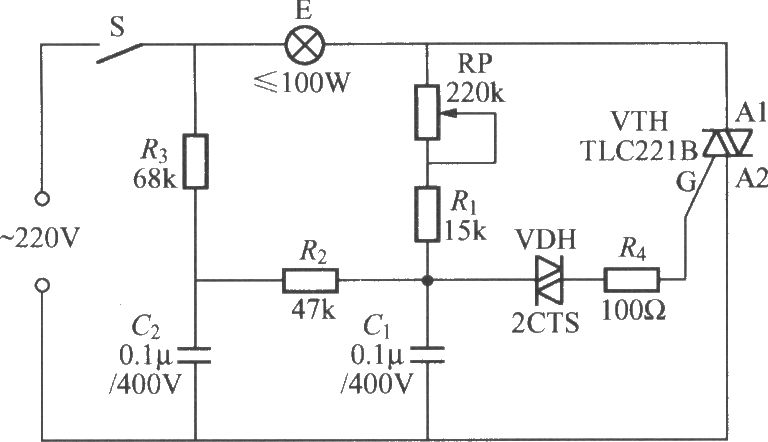
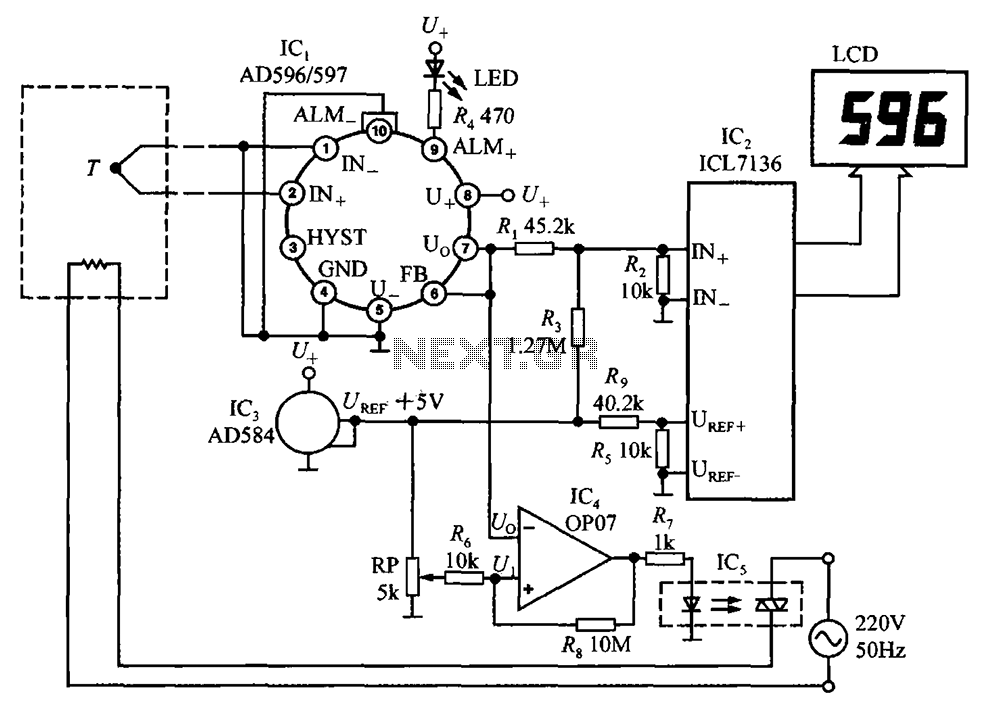
cheap emergency light circuit diagram

Although LEDs dominate the lighting market today, a standard flashlight bulb can still be a viable light-emitting option, particularly due to its simpler configuration compared to an LED. When the AC mains supply fails, transistor T1 becomes forward-biased, allowing it to conduct and enabling battery power to flow through it, which activates the bulb and powers the emergency light.
In this circuit, the flashlight bulb serves as the primary light source, while the battery acts as a backup power supply. The operation of the circuit is dependent on the behavior of transistor T1, which is typically configured as a switch. During normal operation, when AC mains power is available, the transistor remains off, preventing current from flowing from the battery to the bulb.
Upon detection of a power failure, the voltage at the base of T1 rises due to the absence of the AC signal, leading to its forward biasing. This allows current to flow from the battery through T1, illuminating the flashlight bulb. The circuit may also include a diode in parallel with the bulb to prevent reverse current flow, thus protecting the transistor and ensuring reliable operation.
In addition, a resistor may be placed in series with the base of T1 to limit the base current and prevent damage to the transistor. The choice of the flashlight bulb rating should correspond to the battery voltage to ensure optimal performance and brightness.
Overall, this simple yet effective circuit design provides an emergency lighting solution that leverages the reliability of traditional flashlight bulbs while offering a straightforward implementation that can be easily configured and maintained.Though it`s the world LEDs today, an ordinary flashlight bulb can also be considered a useful light emitting candidate especially because it`s much to configure than an LED. However, the moment AC mains fails, T1 is instantly forward biased, it conducts and allows the battery power to pass through it, which ultimately turns ON the bulb and the emergency light.
🔗 External reference
In this circuit, the flashlight bulb serves as the primary light source, while the battery acts as a backup power supply. The operation of the circuit is dependent on the behavior of transistor T1, which is typically configured as a switch. During normal operation, when AC mains power is available, the transistor remains off, preventing current from flowing from the battery to the bulb.
Upon detection of a power failure, the voltage at the base of T1 rises due to the absence of the AC signal, leading to its forward biasing. This allows current to flow from the battery through T1, illuminating the flashlight bulb. The circuit may also include a diode in parallel with the bulb to prevent reverse current flow, thus protecting the transistor and ensuring reliable operation.
In addition, a resistor may be placed in series with the base of T1 to limit the base current and prevent damage to the transistor. The choice of the flashlight bulb rating should correspond to the battery voltage to ensure optimal performance and brightness.
Overall, this simple yet effective circuit design provides an emergency lighting solution that leverages the reliability of traditional flashlight bulbs while offering a straightforward implementation that can be easily configured and maintained.Though it`s the world LEDs today, an ordinary flashlight bulb can also be considered a useful light emitting candidate especially because it`s much to configure than an LED. However, the moment AC mains fails, T1 is instantly forward biased, it conducts and allows the battery power to pass through it, which ultimately turns ON the bulb and the emergency light.
🔗 External reference