TRIAC dimmer light circuit with dual time constant
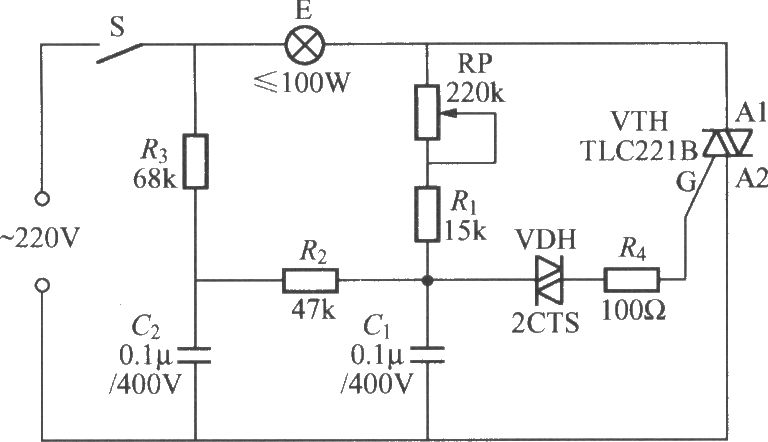
To address the lag and light transition issues, a Triac dimming light circuit featuring a dual time constant can be employed. This circuit enhances the resistor-capacitor network formed by R3 and C2. The reduced charge on capacitor C1 can be quickly replenished through the circuit comprising C2, R2, and R3, effectively minimizing lag and lighting transitions.
The Triac dimming light circuit utilizes a Triac as the main switching element, allowing for the control of the power delivered to a load, typically an incandescent bulb. The dual time constant behavior is achieved through the strategic selection of resistor and capacitor values, specifically R3 and C2. This arrangement allows for a rapid response to changes in the control signal, thereby reducing the lag time associated with the dimming process.
In this configuration, capacitor C1 charges and discharges through the resistors R2 and R3, alongside capacitor C2. The charge time of C2 is crucial as it influences the timing of the Triac's triggering point. By increasing the value of R3 and C2, the circuit can effectively manage the charge and discharge cycles, allowing for smoother transitions in light intensity. This is particularly beneficial in applications where precise control over lighting conditions is necessary, such as in theater lighting or mood lighting environments.
The circuit can be further optimized by selecting components that minimize thermal drift and ensure stable operation across varying temperatures. Additionally, incorporating snubber circuits may protect the Triac from voltage spikes, enhancing the reliability of the dimming function. Overall, this Triac dimming light circuit design presents an effective solution for mitigating lag and improving light transition performance in dimmable lighting applications.In order to solve the lag and light transition phenomena, it can use the Triac dimming light circuit shown in the figure with dual time constant. The circuit increases R3, C2 resistor-capacitor network, and the reducing charge on capacitor C1 can get promptly complement through C2, R2, R3 circuit, it can effectively reduce the lag and lighting transitions a..
🔗 External reference
The Triac dimming light circuit utilizes a Triac as the main switching element, allowing for the control of the power delivered to a load, typically an incandescent bulb. The dual time constant behavior is achieved through the strategic selection of resistor and capacitor values, specifically R3 and C2. This arrangement allows for a rapid response to changes in the control signal, thereby reducing the lag time associated with the dimming process.
In this configuration, capacitor C1 charges and discharges through the resistors R2 and R3, alongside capacitor C2. The charge time of C2 is crucial as it influences the timing of the Triac's triggering point. By increasing the value of R3 and C2, the circuit can effectively manage the charge and discharge cycles, allowing for smoother transitions in light intensity. This is particularly beneficial in applications where precise control over lighting conditions is necessary, such as in theater lighting or mood lighting environments.
The circuit can be further optimized by selecting components that minimize thermal drift and ensure stable operation across varying temperatures. Additionally, incorporating snubber circuits may protect the Triac from voltage spikes, enhancing the reliability of the dimming function. Overall, this Triac dimming light circuit design presents an effective solution for mitigating lag and improving light transition performance in dimmable lighting applications.In order to solve the lag and light transition phenomena, it can use the Triac dimming light circuit shown in the figure with dual time constant. The circuit increases R3, C2 resistor-capacitor network, and the reducing charge on capacitor C1 can get promptly complement through C2, R2, R3 circuit, it can effectively reduce the lag and lighting transitions a..
🔗 External reference