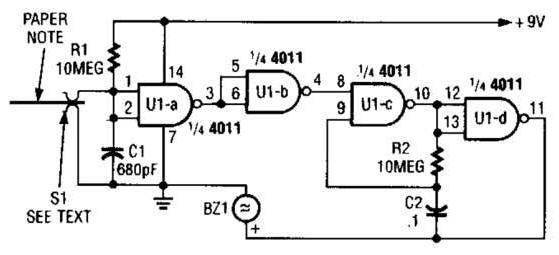
TYPICAL TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT
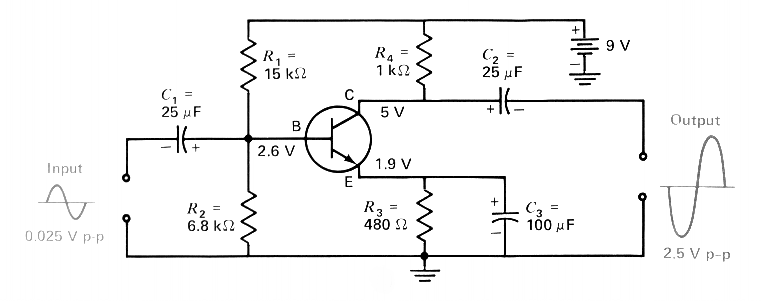
This is a silicon transistor circuit showing typical voltage values. When the forward base/emitter voltage is 0.6 to 0.7 V, the transistor is silicon. Germanium transistors will have a forward base/emitter bias voltage of 0.2 to 0.3 V. This is a silicon transistor because 2.6 base volts minus 1.9 emitter volts equal a forward bias of 0.7 volts, indicating a silicon transistor.
The described circuit utilizes a silicon transistor, characterized by its forward base/emitter voltage range of 0.6 to 0.7 volts. This voltage range is crucial for identifying the type of transistor in use. In this instance, the calculation of the forward bias voltage is conducted by subtracting the emitter voltage (1.9 V) from the base voltage (2.6 V), resulting in a forward bias of 0.7 V. This confirms that the transistor is indeed a silicon type, as opposed to a germanium transistor, which typically operates with a forward bias voltage of 0.2 to 0.3 V.
In practical applications, understanding the operating characteristics of silicon transistors is essential for designing reliable electronic circuits. Silicon transistors are favored in many applications due to their higher thermal stability and better performance in high-frequency environments compared to germanium transistors.
When designing circuits that incorporate silicon transistors, it is important to consider parameters such as the transistor's current gain, maximum collector current, and the thermal resistance. Additionally, biasing arrangements must be carefully designed to ensure that the transistor operates within its optimal range, preventing distortion and signal loss. Proper impedance matching is also vital to maximize power transfer and minimize reflections in RF applications.
Further exploration into transistor amplifier bias arrangements, specifications, and parameters will enhance the understanding of transistor functionality and design principles, allowing for the creation of more complex and efficient electronic equipment.This is a silicon transistor circuit showing typical voltage values. When the forward base/emitter voltage is 0.6 to 0.7 V, the transistor is silicon. Germanium transistors will have a forward base/emitter bias voltage of 0.2 to 0.3 V This is a silicon transistor because 2.6 base volts minus 1.9 emitter volts equal a forward bias of 0.7 volts indicating a silicon transistor.
The described circuit utilizes a silicon transistor, characterized by its forward base/emitter voltage range of 0.6 to 0.7 volts. This voltage range is crucial for identifying the type of transistor in use. In this instance, the calculation of the forward bias voltage is conducted by subtracting the emitter voltage (1.9 V) from the base voltage (2.6 V), resulting in a forward bias of 0.7 V. This confirms that the transistor is indeed a silicon type, as opposed to a germanium transistor, which typically operates with a forward bias voltage of 0.2 to 0.3 V.
In practical applications, understanding the operating characteristics of silicon transistors is essential for designing reliable electronic circuits. Silicon transistors are favored in many applications due to their higher thermal stability and better performance in high-frequency environments compared to germanium transistors.
When designing circuits that incorporate silicon transistors, it is important to consider parameters such as the transistor's current gain, maximum collector current, and the thermal resistance. Additionally, biasing arrangements must be carefully designed to ensure that the transistor operates within its optimal range, preventing distortion and signal loss. Proper impedance matching is also vital to maximize power transfer and minimize reflections in RF applications.
Further exploration into transistor amplifier bias arrangements, specifications, and parameters will enhance the understanding of transistor functionality and design principles, allowing for the creation of more complex and efficient electronic equipment.This is a silicon transistor circuit showing typical voltage values. When the forward base/emitter voltage is 0.6 to 0.7 V, the transistor is silicon. Germanium transistors will have a forward base/emitter bias voltage of 0.2 to 0.3 V This is a silicon transistor because 2.6 base volts minus 1.9 emitter volts equal a forward bias of 0.7 volts indicating a silicon transistor.
At this point you should have more questions and want to learn more about how transistor circuits work, how to design your own transistor circuits and build electronic equipment. Therefore; the next step would be to study the material in the following links. From this study you will be on your way to learning more about transistor amplifier bias arrangements, the importance of impedance matching, transistor specifications, and transistor parameters.
🔗 External reference