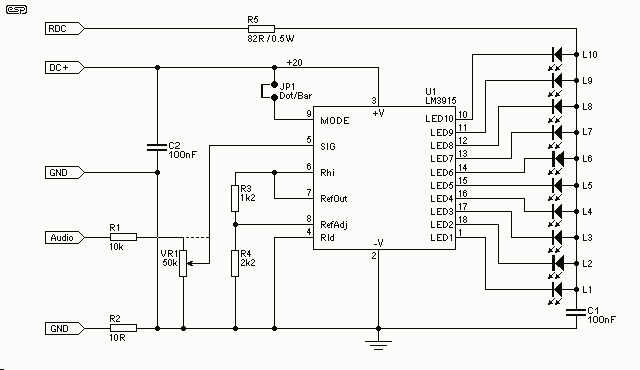
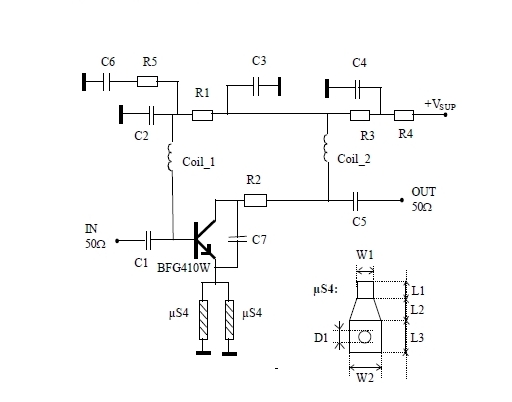
Class D Audio Amplifier Matches Class AB With Higher Efficiency

Class D audio amplifiers are now prepared to replace Class AB amplifiers. An integrated high-voltage audio driver simplifies the design and construction of high-power audio systems.
Class D audio amplifiers, also known as switching amplifiers, utilize pulse-width modulation (PWM) to convert input audio signals into high-frequency square waves. This method allows for greater efficiency compared to traditional Class AB amplifiers, which dissipate more heat during operation. The primary advantage of Class D amplifiers is their ability to deliver high power output while maintaining low thermal losses, making them ideal for applications requiring compact designs and high performance.
The integrated high-voltage audio driver plays a crucial role in the functionality of Class D amplifiers. It is responsible for driving the output stage of the amplifier, which usually consists of MOSFETs or IGBTs that switch on and off rapidly to modulate the audio signal. This driver is designed to handle high voltage levels, allowing the amplifier to produce significant output power suitable for driving speakers in various audio applications, from home theaters to professional sound systems.
In terms of design considerations, the layout of a Class D amplifier circuit is critical for minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensuring stable operation. Careful attention should be paid to the placement of components, especially the power supply, output stage, and feedback loops. Additionally, the choice of passive components, such as inductors and capacitors, must be optimized to ensure the desired frequency response and minimize distortion.
Overall, the transition from Class AB to Class D amplifiers represents a significant advancement in audio amplification technology, providing higher efficiency, reduced heat generation, and the ability to drive larger loads without compromising audio quality.Class D audio amplifiers are now geared up to replace class AB An integrated high voltage audio driver facilitates the design and construction of a high power.. 🔗 External reference
Class D audio amplifiers, also known as switching amplifiers, utilize pulse-width modulation (PWM) to convert input audio signals into high-frequency square waves. This method allows for greater efficiency compared to traditional Class AB amplifiers, which dissipate more heat during operation. The primary advantage of Class D amplifiers is their ability to deliver high power output while maintaining low thermal losses, making them ideal for applications requiring compact designs and high performance.
The integrated high-voltage audio driver plays a crucial role in the functionality of Class D amplifiers. It is responsible for driving the output stage of the amplifier, which usually consists of MOSFETs or IGBTs that switch on and off rapidly to modulate the audio signal. This driver is designed to handle high voltage levels, allowing the amplifier to produce significant output power suitable for driving speakers in various audio applications, from home theaters to professional sound systems.
In terms of design considerations, the layout of a Class D amplifier circuit is critical for minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensuring stable operation. Careful attention should be paid to the placement of components, especially the power supply, output stage, and feedback loops. Additionally, the choice of passive components, such as inductors and capacitors, must be optimized to ensure the desired frequency response and minimize distortion.
Overall, the transition from Class AB to Class D amplifiers represents a significant advancement in audio amplification technology, providing higher efficiency, reduced heat generation, and the ability to drive larger loads without compromising audio quality.Class D audio amplifiers are now geared up to replace class AB An integrated high voltage audio driver facilitates the design and construction of a high power.. 🔗 External reference