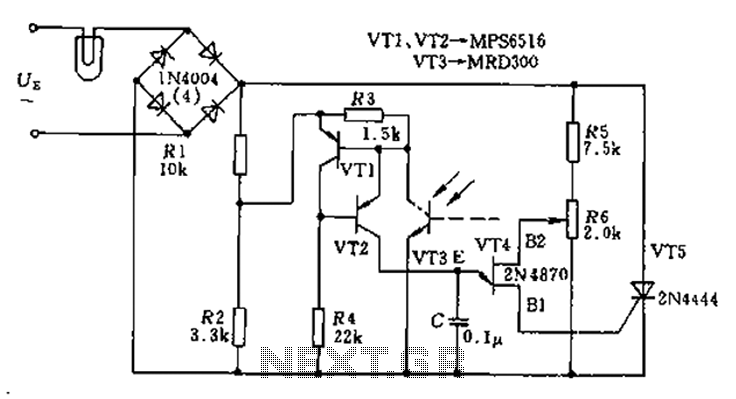
900 MHz Radio Amplifier Circuit
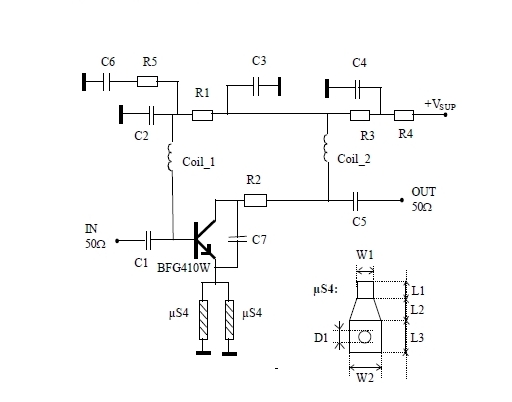
This 900 MHz amplifier circuit is constructed using the BFG480W transistor, which exhibits excellent linearity performance. As a result, the BFG480W is highly suitable for low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) that require high linearity.
The 900 MHz amplifier circuit utilizing the BFG480W transistor is designed to operate efficiently within the specified frequency range, making it ideal for applications in communication systems where signal integrity is paramount. The BFG480W is a high-frequency NPN transistor known for its low noise figure and high gain, which are essential characteristics for low-noise amplification.
In this circuit, the BFG480W is typically configured in a common-emitter configuration to maximize voltage gain while maintaining stability. The input stage may include impedance matching networks to ensure optimal power transfer from the source to the amplifier. This can involve the use of inductors and capacitors to create a tuned circuit that resonates at 900 MHz.
Biasing is a critical aspect of the design to ensure the transistor operates in the linear region. Resistors are used to set the appropriate DC operating point, taking into account the supply voltage and the desired quiescent current. Capacitors may be employed for AC coupling at the input and output to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through.
The amplifier's output stage can also include a matching network to minimize reflections and maximize power transfer to the load. This is particularly important in RF applications, where mismatches can lead to signal degradation and reduced performance.
Overall, the design of a 900 MHz amplifier circuit using the BFG480W requires careful consideration of component values, layout, and thermal management to ensure reliable operation and optimal performance in various applications, including wireless communication and broadcasting.This 900 MHz Amplifier Circuit is built with BFG480W which has a good linearity performance. Therefore the BFG480W is well suited for LNAs with high linear.. 🔗 External reference
The 900 MHz amplifier circuit utilizing the BFG480W transistor is designed to operate efficiently within the specified frequency range, making it ideal for applications in communication systems where signal integrity is paramount. The BFG480W is a high-frequency NPN transistor known for its low noise figure and high gain, which are essential characteristics for low-noise amplification.
In this circuit, the BFG480W is typically configured in a common-emitter configuration to maximize voltage gain while maintaining stability. The input stage may include impedance matching networks to ensure optimal power transfer from the source to the amplifier. This can involve the use of inductors and capacitors to create a tuned circuit that resonates at 900 MHz.
Biasing is a critical aspect of the design to ensure the transistor operates in the linear region. Resistors are used to set the appropriate DC operating point, taking into account the supply voltage and the desired quiescent current. Capacitors may be employed for AC coupling at the input and output to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through.
The amplifier's output stage can also include a matching network to minimize reflections and maximize power transfer to the load. This is particularly important in RF applications, where mismatches can lead to signal degradation and reduced performance.
Overall, the design of a 900 MHz amplifier circuit using the BFG480W requires careful consideration of component values, layout, and thermal management to ensure reliable operation and optimal performance in various applications, including wireless communication and broadcasting.This 900 MHz Amplifier Circuit is built with BFG480W which has a good linearity performance. Therefore the BFG480W is well suited for LNAs with high linear.. 🔗 External reference