Code Collection
CrustCrawler develops and manufactures advanced walking robots and robotic accessories.
CrustCrawler specializes in the design and production of innovative walking robots, which incorporate advanced technologies and engineering principles to achieve improved mobility and functionality. These robots are typically characterized by their unique legged locomotion systems, allowing them to traverse a variety of terrains that may be challenging for traditional wheeled robots.
The walking robots developed by CrustCrawler often feature modular designs, enabling customization and the integration of various robotic accessories. This adaptability allows users to tailor the robots for specific applications, such as research, exploration, or industrial tasks. The robotic accessories may include sensors, cameras, or manipulation tools, enhancing the robots' capabilities and making them suitable for a wide range of scenarios.
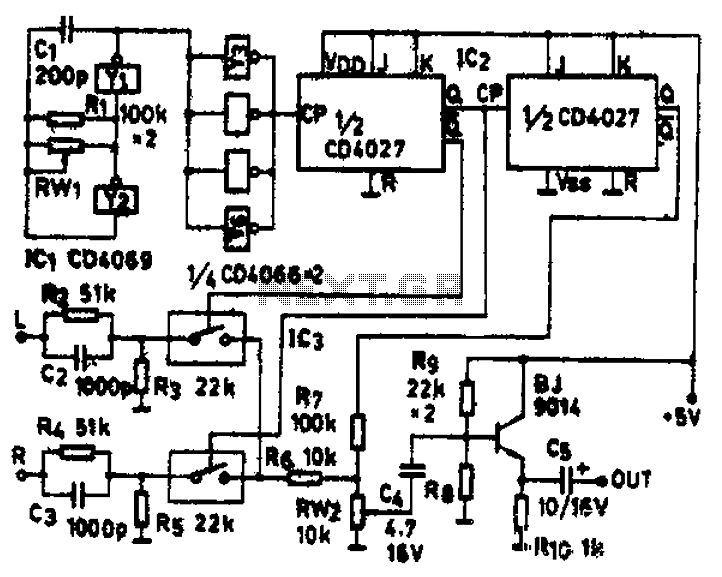
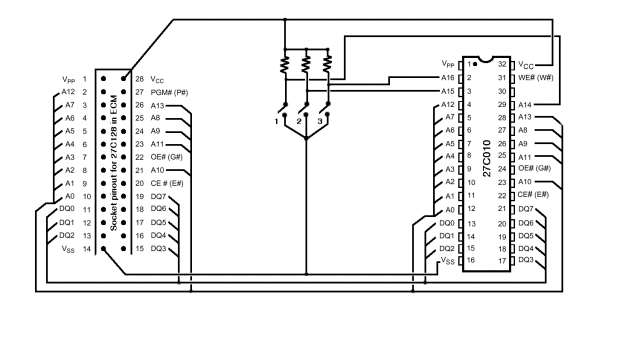
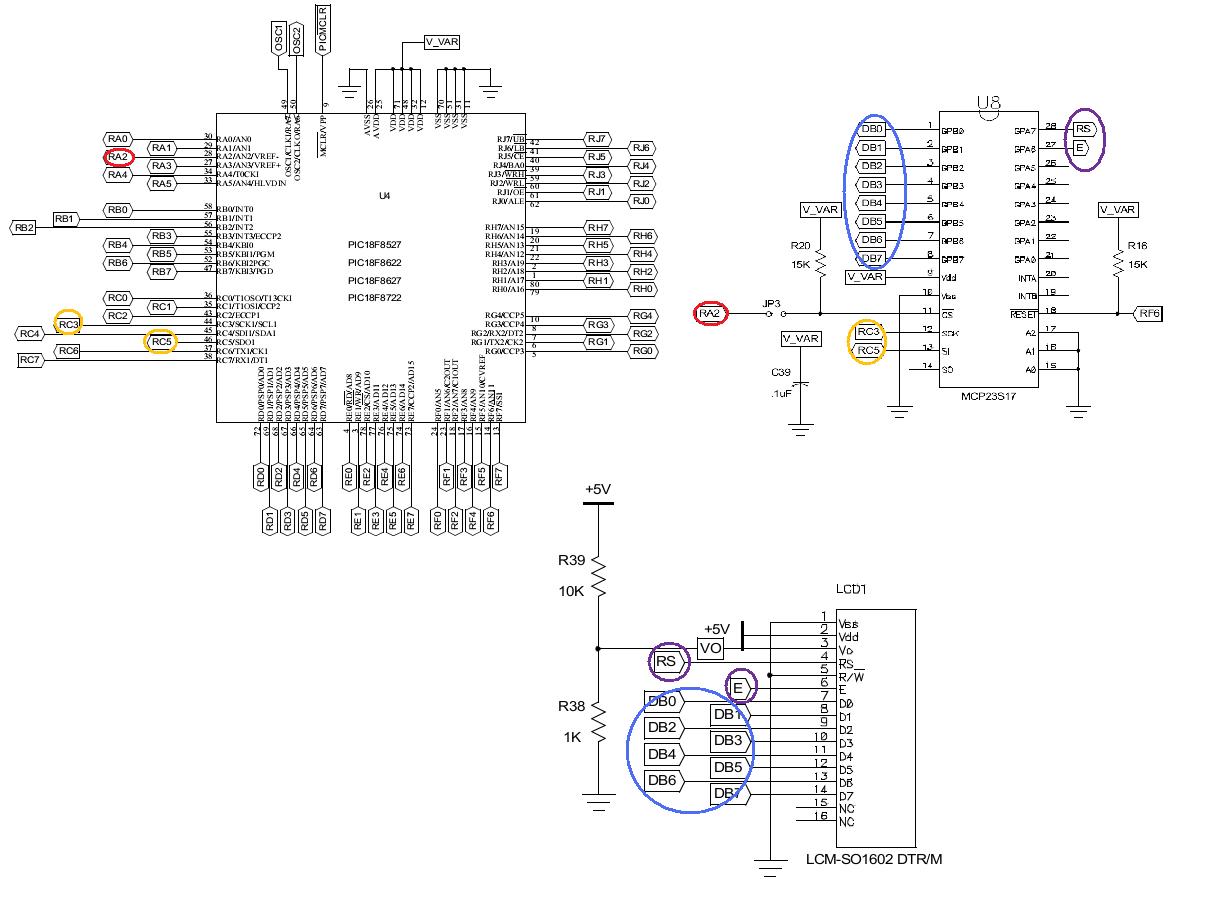
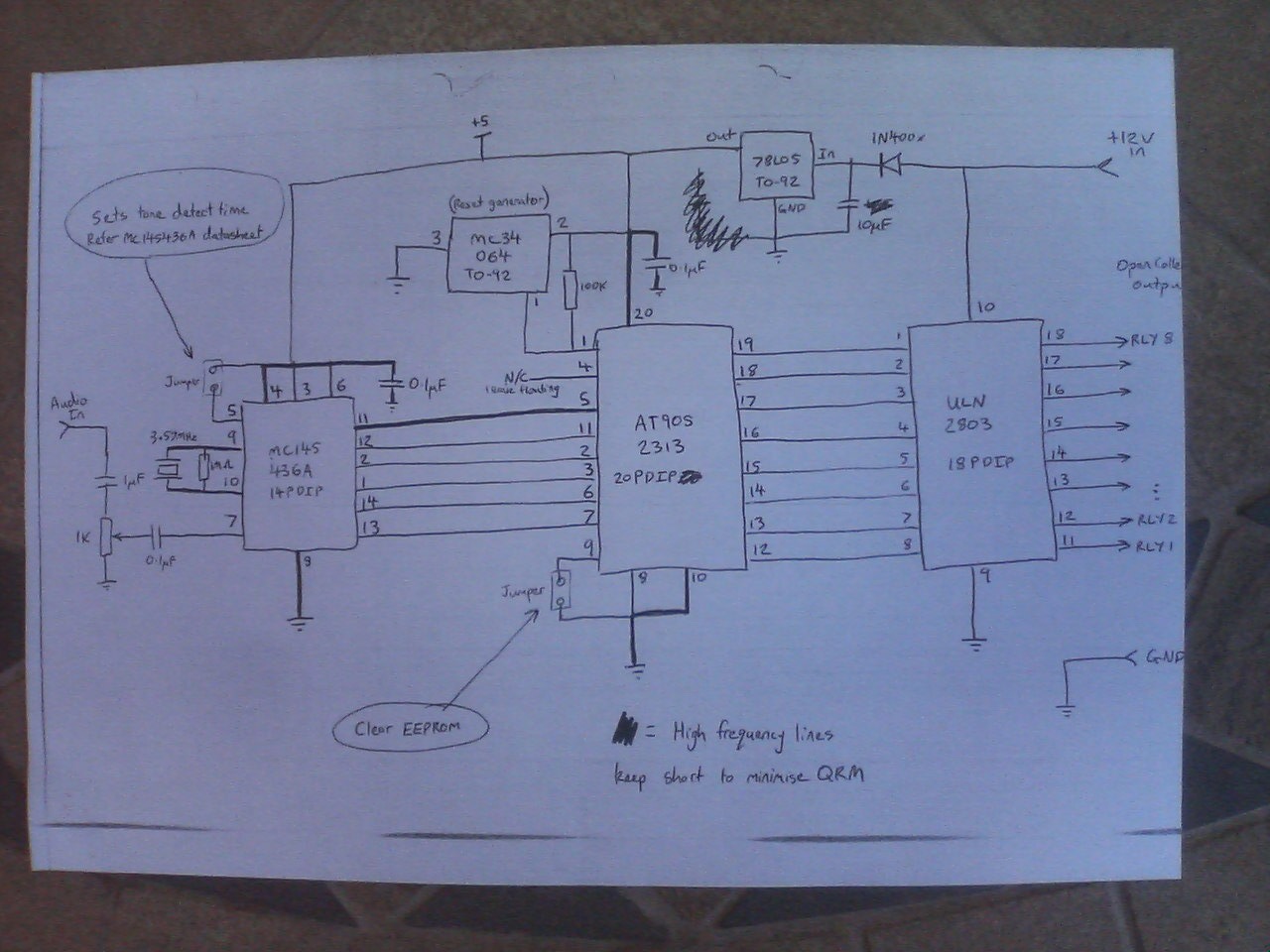
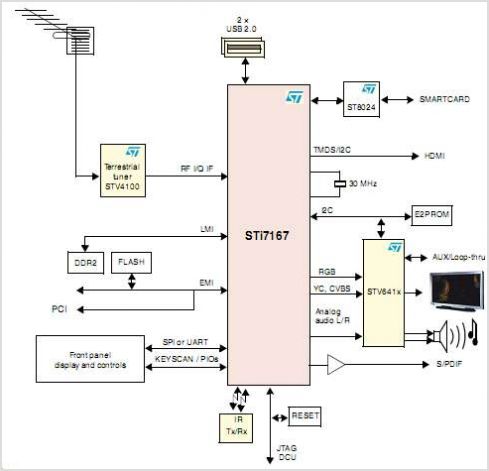
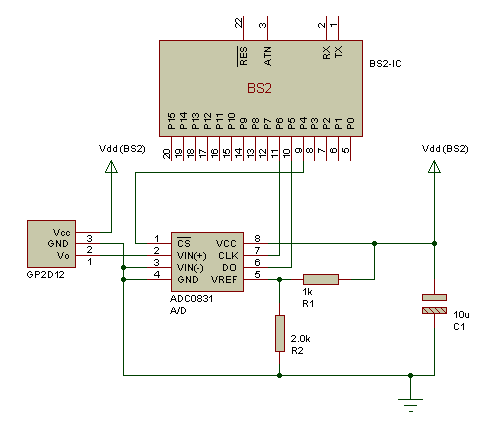
In terms of electronic schematics, the walking robots likely utilize a combination of microcontrollers and motor drivers to control the movement of the legs. The microcontroller would process input from various sensors, such as gyroscopes and accelerometers, to maintain balance and navigate obstacles. The motor drivers would be responsible for powering the servos or stepper motors that actuate the legs, ensuring precise movement and coordination.
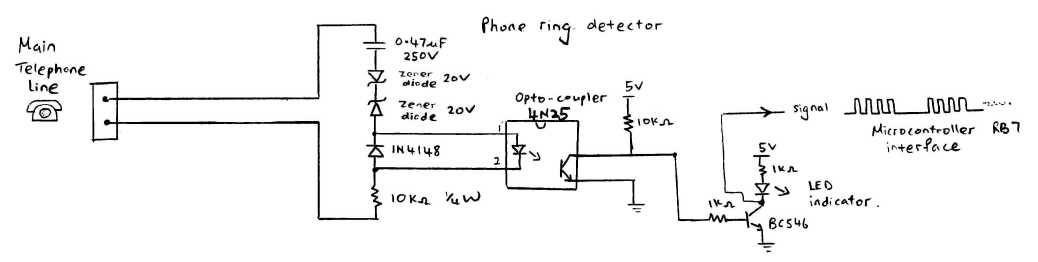
The power supply system is also a critical component, providing the necessary voltage and current for the motors and onboard electronics. Battery management systems may be integrated to monitor battery health and optimize performance. Communication protocols, such as I2C or SPI, may be employed for inter-module communication, enabling seamless operation of the robotic system.
Overall, the development of walking robots by CrustCrawler represents a significant advancement in robotics, combining cutting-edge technology with practical applications in various fields.CrustCrawler develops and manufactures cutting edge walking robots and robotic accessories.. 🔗 External reference
CrustCrawler specializes in the design and production of innovative walking robots, which incorporate advanced technologies and engineering principles to achieve improved mobility and functionality. These robots are typically characterized by their unique legged locomotion systems, allowing them to traverse a variety of terrains that may be challenging for traditional wheeled robots.
The walking robots developed by CrustCrawler often feature modular designs, enabling customization and the integration of various robotic accessories. This adaptability allows users to tailor the robots for specific applications, such as research, exploration, or industrial tasks. The robotic accessories may include sensors, cameras, or manipulation tools, enhancing the robots' capabilities and making them suitable for a wide range of scenarios.
In terms of electronic schematics, the walking robots likely utilize a combination of microcontrollers and motor drivers to control the movement of the legs. The microcontroller would process input from various sensors, such as gyroscopes and accelerometers, to maintain balance and navigate obstacles. The motor drivers would be responsible for powering the servos or stepper motors that actuate the legs, ensuring precise movement and coordination.
The power supply system is also a critical component, providing the necessary voltage and current for the motors and onboard electronics. Battery management systems may be integrated to monitor battery health and optimize performance. Communication protocols, such as I2C or SPI, may be employed for inter-module communication, enabling seamless operation of the robotic system.
Overall, the development of walking robots by CrustCrawler represents a significant advancement in robotics, combining cutting-edge technology with practical applications in various fields.CrustCrawler develops and manufactures cutting edge walking robots and robotic accessories.. 🔗 External reference