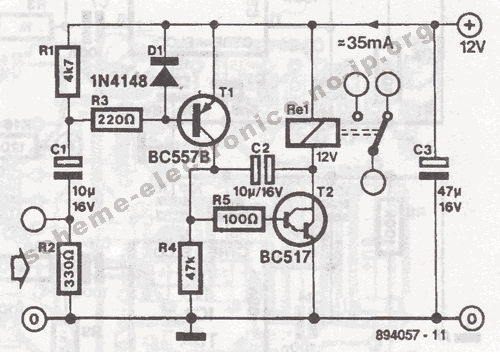
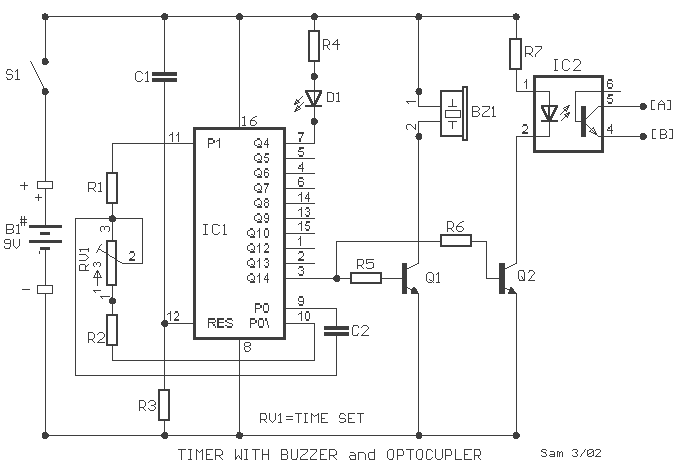
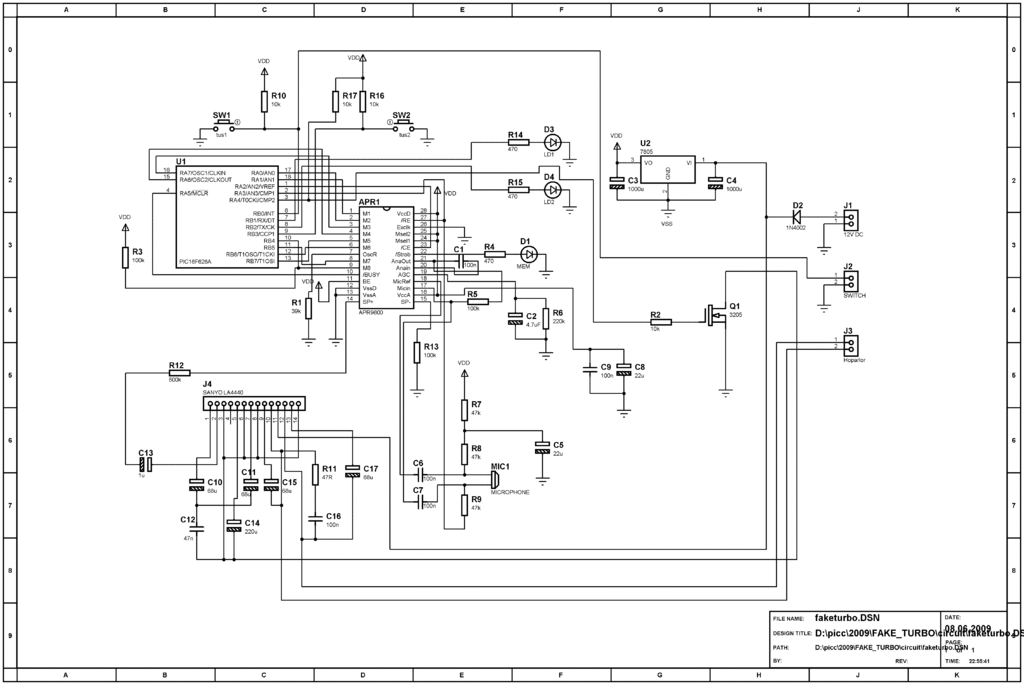
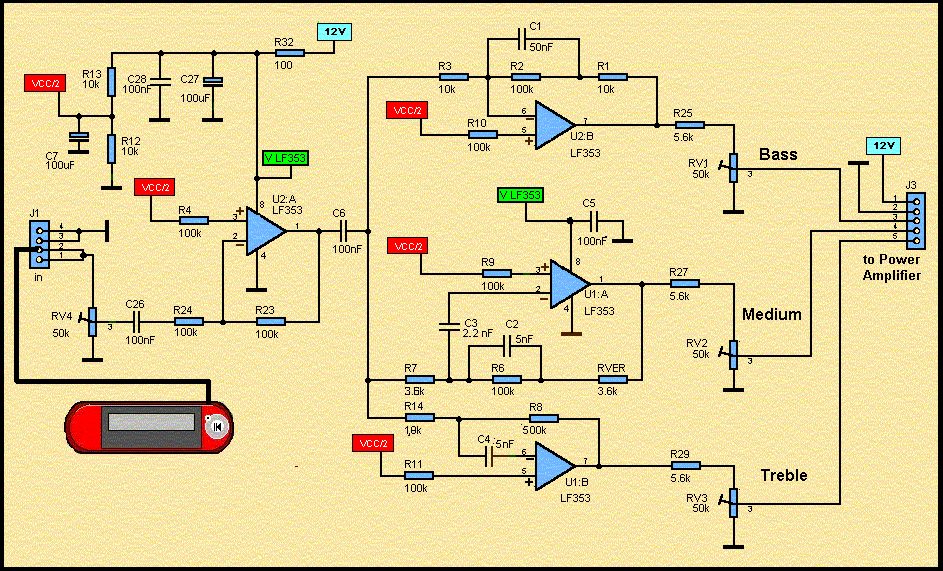
Coffee thermometer circuit
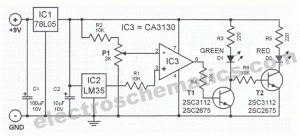
Measuring the temperature of coffee is important because the taste of coffee relies on two main factors: the strength of the coffee and its temperature.
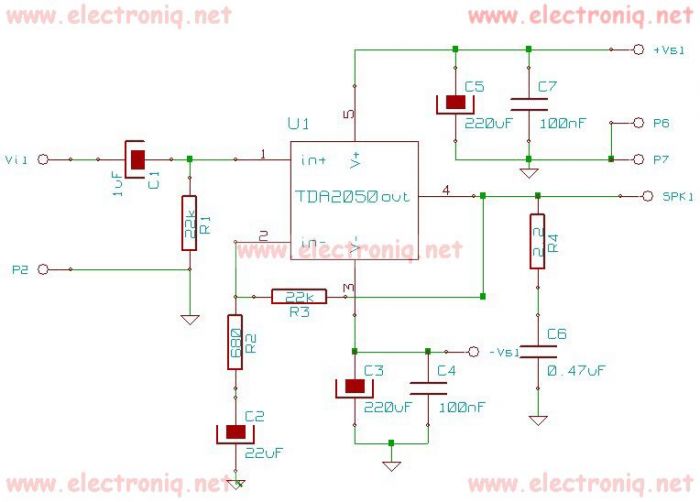
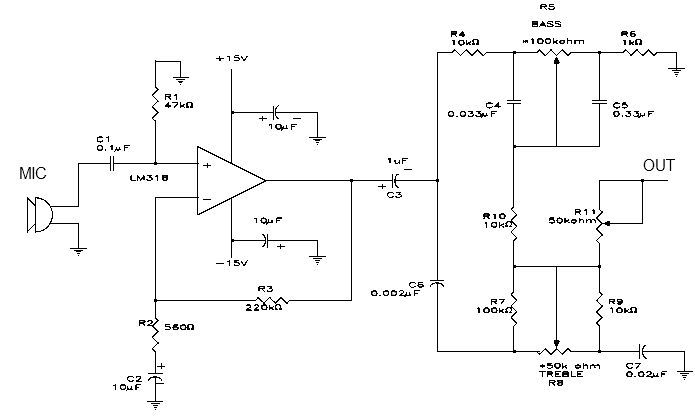
Measuring the temperature of coffee can be accomplished using a simple electronic circuit designed to provide accurate readings. A typical setup may include a thermistor or a thermocouple as the temperature sensor, which converts the temperature into an electrical signal. This signal can be processed by an operational amplifier (op-amp) to enhance its strength and accuracy.
The circuit can be designed to include an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital output, allowing for easy integration with microcontrollers or digital displays. The microcontroller can be programmed to interpret the ADC readings and display the temperature on an LCD screen or send it to a smartphone via Bluetooth for remote monitoring.
Power management is also a crucial aspect of the design. A power supply circuit, which may include a voltage regulator, ensures that the sensor and microcontroller receive a stable voltage. Additionally, incorporating a battery management system can extend the operational life of the device.
To enhance user experience, the circuit can include features such as temperature alerts or the ability to log temperature data over time, providing insights into how temperature variations affect coffee flavor profiles. Overall, the electronic schematic for measuring coffee temperature consists of a temperature sensor, signal processing components, a microcontroller, and a display or communication module, all working together to ensure precise temperature measurement and data management.Why measure the temperature of the coffee? Well, coffee taste depends on two things. First, how strong the coffee is and second, how hot it is. The second. 🔗 External reference
Measuring the temperature of coffee can be accomplished using a simple electronic circuit designed to provide accurate readings. A typical setup may include a thermistor or a thermocouple as the temperature sensor, which converts the temperature into an electrical signal. This signal can be processed by an operational amplifier (op-amp) to enhance its strength and accuracy.
The circuit can be designed to include an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital output, allowing for easy integration with microcontrollers or digital displays. The microcontroller can be programmed to interpret the ADC readings and display the temperature on an LCD screen or send it to a smartphone via Bluetooth for remote monitoring.
Power management is also a crucial aspect of the design. A power supply circuit, which may include a voltage regulator, ensures that the sensor and microcontroller receive a stable voltage. Additionally, incorporating a battery management system can extend the operational life of the device.
To enhance user experience, the circuit can include features such as temperature alerts or the ability to log temperature data over time, providing insights into how temperature variations affect coffee flavor profiles. Overall, the electronic schematic for measuring coffee temperature consists of a temperature sensor, signal processing components, a microcontroller, and a display or communication module, all working together to ensure precise temperature measurement and data management.Why measure the temperature of the coffee? Well, coffee taste depends on two things. First, how strong the coffee is and second, how hot it is. The second. 🔗 External reference