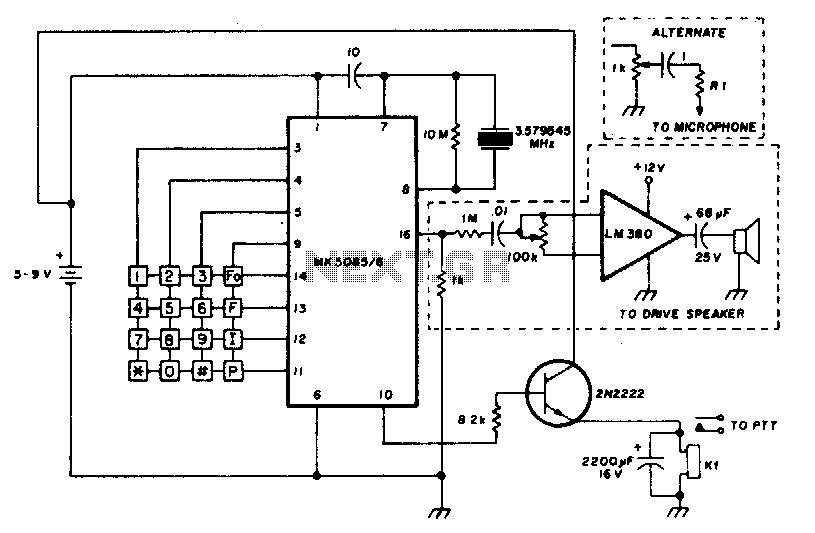
Color-Bar Generator
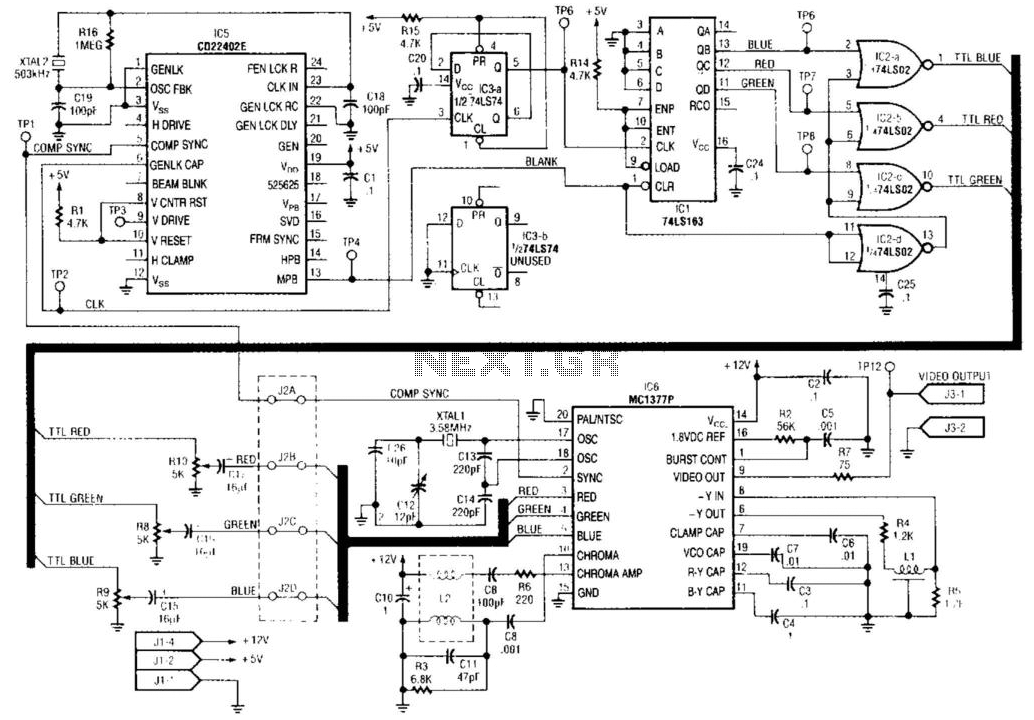
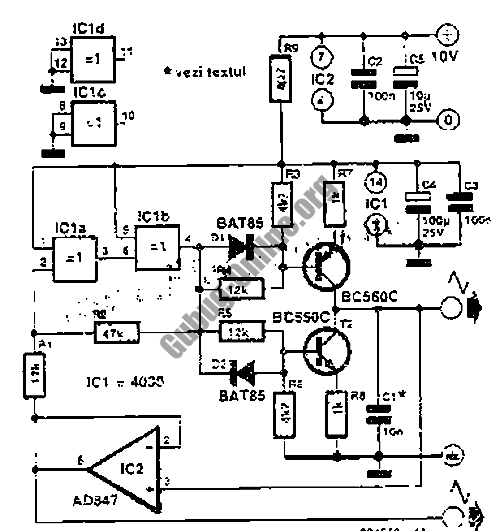
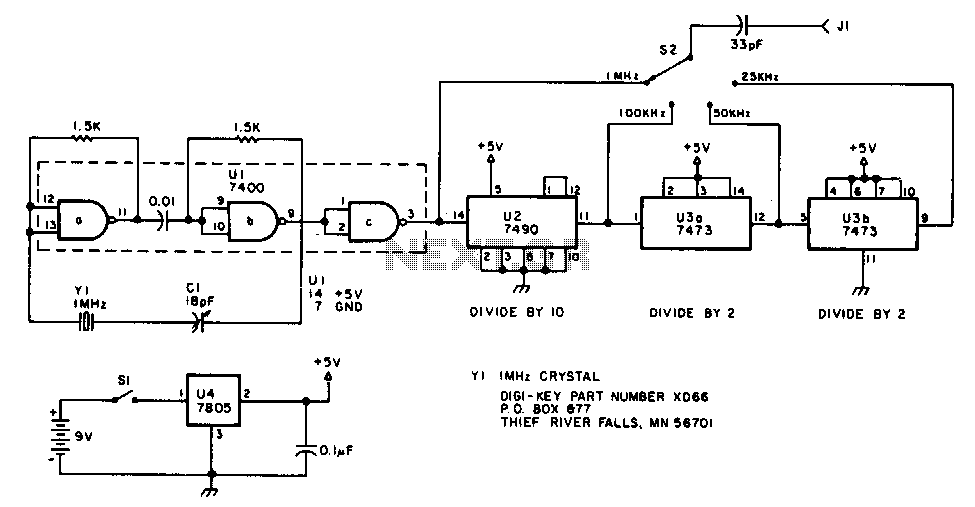
IC5 generates RS-170 NTSC synchronization signals. IC1, IC2, and IC3 are responsible for producing the red, green, and blue video signals that feed into the encoder section of IC6 to create color bars. IC3 functions as a 2-counter that drives the 4-bit counter IC1. Gates IC2a through IC2b are utilized to form the red, blue, and green video signals. IC6 encodes these signals, along with synchronization, to generate an NTSC video output signal, which is available at TP12.
The circuit comprises several integrated circuits (ICs) that work collaboratively to generate an NTSC video output signal conforming to the RS-170 standard. IC5 is designated as the synchronization generator, producing the necessary timing signals that ensure proper synchronization of the video output. This synchronization is essential for maintaining the integrity of the video signal during transmission.
The color video signals are produced by IC1, IC2, and IC3. Each of these ICs is dedicated to generating one of the primary colors: red, green, and blue (RGB). The output from these ICs is essential for creating a full-color video signal. Specifically, IC3 operates as a 2-counter, which serves to drive the 4-bit counter IC1. This configuration allows for precise control over the timing and sequencing of the color signals.
Gates IC2a and IC2b are critical components in forming the RGB video signals. These gates process the outputs from the respective color ICs to ensure that the signals are properly combined and formatted for encoding. The output from these gates is then fed into the encoder section of IC6.
IC6 plays a pivotal role in the overall circuit by encoding the RGB signals along with the synchronization signals generated by IC5. This encoding process is crucial for converting the individual color signals into a composite NTSC video signal. The final output is made available at test point TP12, where it can be monitored or utilized in further applications.
The design of this circuit emphasizes the importance of each component in the video signal generation process, ensuring that the output adheres to the required standards for NTSC video. Proper functioning of the synchronization, color generation, and encoding stages is vital for achieving high-quality video output. IC5 generates RS-170 NTSC synch. IC1, IC2, and IC3 make up the red, green, and blue video signals that drive the video encoder section of IC6 to make up the color bars. IC3 is an a 2 counter that drives 4-bit counter IC1. Gates IC2a through IC2b form the R, B, and G, video signals. IC6 encodes these, plus synch, to form an NTSC video output signal, which appears at TP12.
The circuit comprises several integrated circuits (ICs) that work collaboratively to generate an NTSC video output signal conforming to the RS-170 standard. IC5 is designated as the synchronization generator, producing the necessary timing signals that ensure proper synchronization of the video output. This synchronization is essential for maintaining the integrity of the video signal during transmission.
The color video signals are produced by IC1, IC2, and IC3. Each of these ICs is dedicated to generating one of the primary colors: red, green, and blue (RGB). The output from these ICs is essential for creating a full-color video signal. Specifically, IC3 operates as a 2-counter, which serves to drive the 4-bit counter IC1. This configuration allows for precise control over the timing and sequencing of the color signals.
Gates IC2a and IC2b are critical components in forming the RGB video signals. These gates process the outputs from the respective color ICs to ensure that the signals are properly combined and formatted for encoding. The output from these gates is then fed into the encoder section of IC6.
IC6 plays a pivotal role in the overall circuit by encoding the RGB signals along with the synchronization signals generated by IC5. This encoding process is crucial for converting the individual color signals into a composite NTSC video signal. The final output is made available at test point TP12, where it can be monitored or utilized in further applications.
The design of this circuit emphasizes the importance of each component in the video signal generation process, ensuring that the output adheres to the required standards for NTSC video. Proper functioning of the synchronization, color generation, and encoding stages is vital for achieving high-quality video output. IC5 generates RS-170 NTSC synch. IC1, IC2, and IC3 make up the red, green, and blue video signals that drive the video encoder section of IC6 to make up the color bars. IC3 is an a 2 counter that drives 4-bit counter IC1. Gates IC2a through IC2b form the R, B, and G, video signals. IC6 encodes these, plus synch, to form an NTSC video output signal, which appears at TP12.