Colpitts Crystal Oscillator
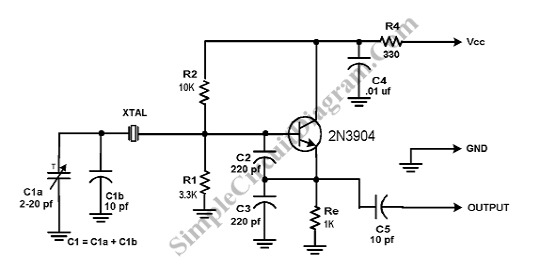
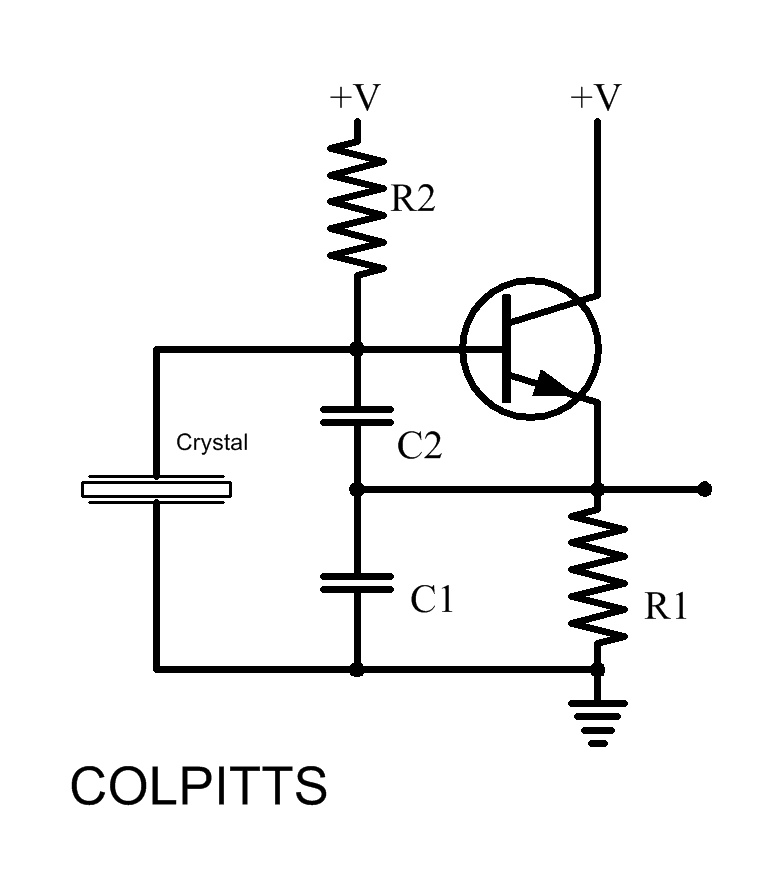
A Crystal Colpitts oscillator can be constructed using a parallel mode crystal and a transistor. The circuit is depicted in the accompanying figure. In this configuration, an inductance is utilized.
The Crystal Colpitts oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sinusoidal waveforms. It employs a crystal to stabilize the frequency of oscillation, ensuring that the output signal remains consistent and precise. The fundamental components of this oscillator include a transistor, a parallel mode crystal, and a feedback network formed by capacitors and inductors.
In the typical configuration, the transistor operates in the active region, allowing it to amplify the signal. The crystal is connected in parallel with two capacitors, which are part of the feedback network. This arrangement creates a resonant circuit that determines the oscillation frequency. The inductance used in the circuit can be either a physical inductor or the inherent inductance of the transistor's leads and connections, depending on the design requirements.
The output of the oscillator can be taken from the collector of the transistor, where the amplified oscillating signal can be further processed or utilized in various applications, such as radio frequency transmission or signal generation in communication systems. The stability and frequency accuracy provided by the crystal make the Colpitts oscillator suitable for applications requiring precise frequency control.
Overall, the Crystal Colpitts oscillator is a versatile and widely used circuit in electronics, offering reliable performance in generating oscillatory signals.We can create Crystal Colpitts oscillator using a parallel mode crystal and a transistor. The circuit shown by the following figure As an inductance, this.. 🔗 External reference
The Crystal Colpitts oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sinusoidal waveforms. It employs a crystal to stabilize the frequency of oscillation, ensuring that the output signal remains consistent and precise. The fundamental components of this oscillator include a transistor, a parallel mode crystal, and a feedback network formed by capacitors and inductors.
In the typical configuration, the transistor operates in the active region, allowing it to amplify the signal. The crystal is connected in parallel with two capacitors, which are part of the feedback network. This arrangement creates a resonant circuit that determines the oscillation frequency. The inductance used in the circuit can be either a physical inductor or the inherent inductance of the transistor's leads and connections, depending on the design requirements.
The output of the oscillator can be taken from the collector of the transistor, where the amplified oscillating signal can be further processed or utilized in various applications, such as radio frequency transmission or signal generation in communication systems. The stability and frequency accuracy provided by the crystal make the Colpitts oscillator suitable for applications requiring precise frequency control.
Overall, the Crystal Colpitts oscillator is a versatile and widely used circuit in electronics, offering reliable performance in generating oscillatory signals.We can create Crystal Colpitts oscillator using a parallel mode crystal and a transistor. The circuit shown by the following figure As an inductance, this.. 🔗 External reference