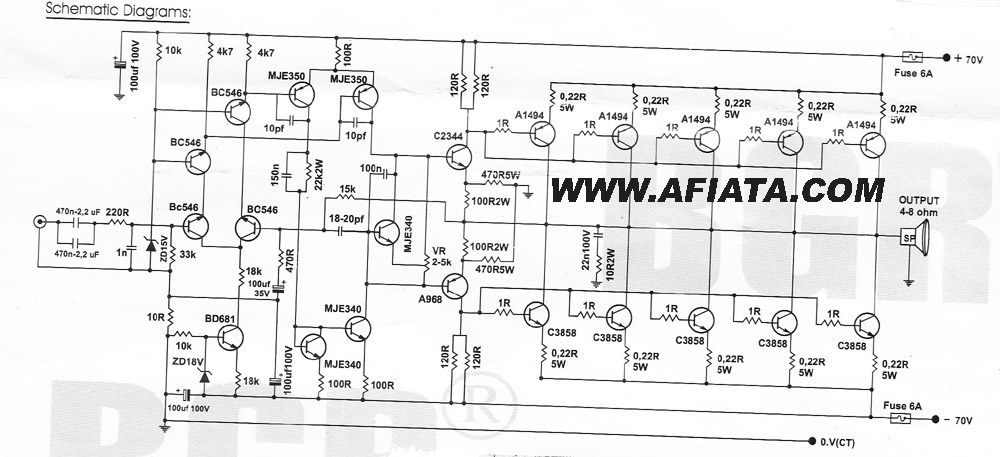
Common low-pass filter circuit b
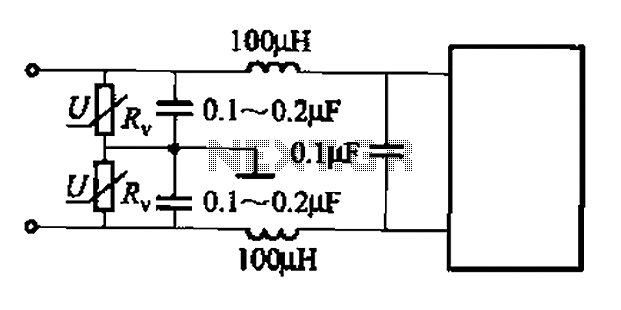
A common low-pass filter circuit is illustrated. Figures (a) to (c) demonstrate its ability to suppress high-frequency interference, while Figure (b) shows a varistor that can absorb lightning surge voltage. Figure (d) indicates the circuit's capability to suppress low interference, and Figure (f) is utilized for power supply decoupling. The selection of components can be made based on specific circumstances.
The low-pass filter circuit serves as an essential component in various electronic applications where it is necessary to eliminate high-frequency noise while allowing low-frequency signals to pass through. The circuit typically consists of passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are arranged in a configuration that defines the cutoff frequency.
In the configurations shown in Figures (a) to (c), the filter effectively attenuates frequencies above a certain threshold, thereby protecting sensitive components from high-frequency interference. This feature is particularly beneficial in audio processing, radio frequency applications, and digital signal processing, where signal integrity is paramount.
Figure (b) introduces a varistor, which is a voltage-dependent resistor that provides transient voltage suppression. This is particularly useful in applications exposed to lightning strikes or other high-voltage transients, as the varistor can shunt excessive voltage away from sensitive components, thus preventing damage.
Figure (d) highlights the circuit's capability to suppress low-frequency interference, which may arise from power supply fluctuations or other sources of noise. This suppression is crucial in maintaining the stability and reliability of electronic systems.
Figure (f) illustrates the application of the low-pass filter for power supply decoupling. In this context, the filter helps to smooth out voltage fluctuations and reduce ripple in the power supply line, ensuring that downstream components receive a clean and stable voltage.
The choice of components and configuration in a low-pass filter circuit should be tailored to the specific requirements of the application, including the desired cutoff frequency, the level of attenuation needed, and the nature of the interference to be suppressed. Common low-pass filter circuit commonly used low-pass filter circuit is shown. Figure (a) ~ (c) suppress high-frequency interference; Figure (b) of the varistor foot can absorb lightning surge voltage; Fig. (D) suppress low interference; FIG. (F) for the power supply decoupling. You can choose to use depending on the circumstances.
The low-pass filter circuit serves as an essential component in various electronic applications where it is necessary to eliminate high-frequency noise while allowing low-frequency signals to pass through. The circuit typically consists of passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are arranged in a configuration that defines the cutoff frequency.
In the configurations shown in Figures (a) to (c), the filter effectively attenuates frequencies above a certain threshold, thereby protecting sensitive components from high-frequency interference. This feature is particularly beneficial in audio processing, radio frequency applications, and digital signal processing, where signal integrity is paramount.
Figure (b) introduces a varistor, which is a voltage-dependent resistor that provides transient voltage suppression. This is particularly useful in applications exposed to lightning strikes or other high-voltage transients, as the varistor can shunt excessive voltage away from sensitive components, thus preventing damage.
Figure (d) highlights the circuit's capability to suppress low-frequency interference, which may arise from power supply fluctuations or other sources of noise. This suppression is crucial in maintaining the stability and reliability of electronic systems.
Figure (f) illustrates the application of the low-pass filter for power supply decoupling. In this context, the filter helps to smooth out voltage fluctuations and reduce ripple in the power supply line, ensuring that downstream components receive a clean and stable voltage.
The choice of components and configuration in a low-pass filter circuit should be tailored to the specific requirements of the application, including the desired cutoff frequency, the level of attenuation needed, and the nature of the interference to be suppressed. Common low-pass filter circuit commonly used low-pass filter circuit is shown. Figure (a) ~ (c) suppress high-frequency interference; Figure (b) of the varistor foot can absorb lightning surge voltage; Fig. (D) suppress low interference; FIG. (F) for the power supply decoupling. You can choose to use depending on the circumstances.