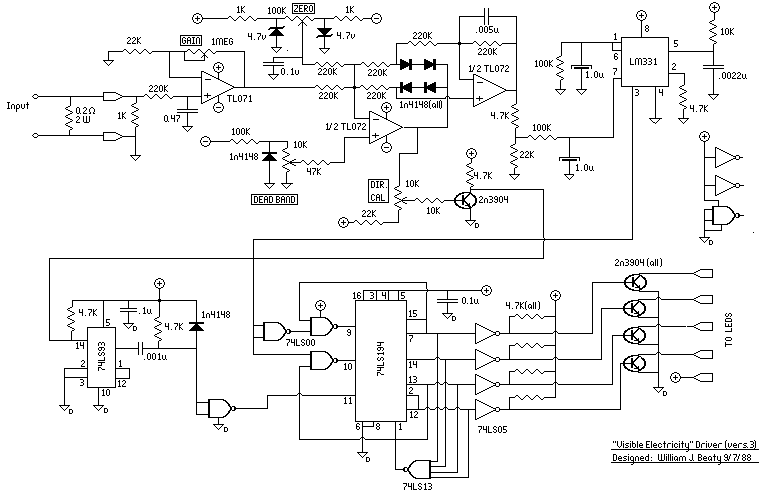
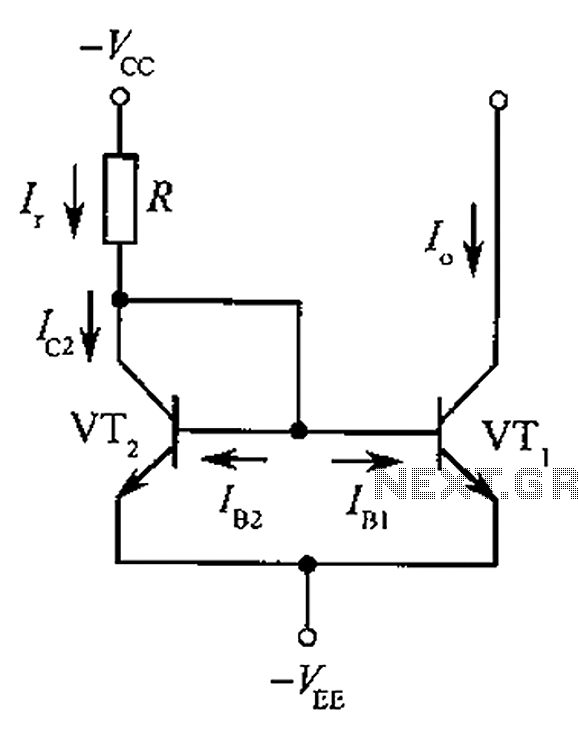
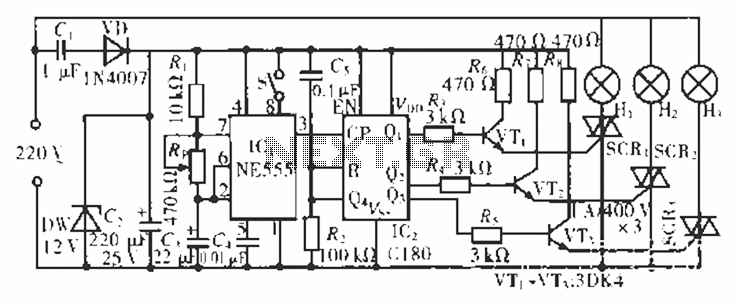
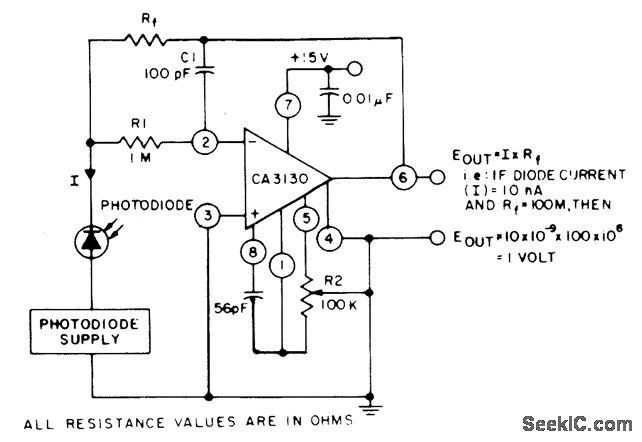
Computer-Controlled 4-20mA Current Loop
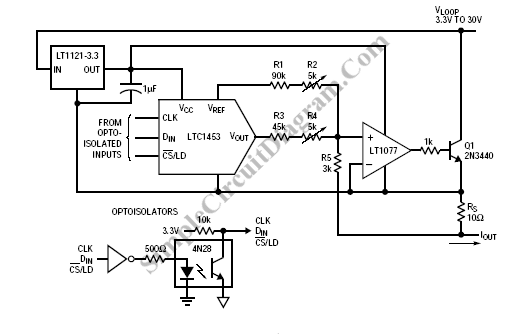
In certain industries, a computer-controlled 4-20 mA current loop is utilized to manage various equipment. This current loop is employed to transmit a signal over a distance.
The 4-20 mA current loop is a standard method for transmitting analog signals in industrial environments, particularly for process control and instrumentation applications. The current loop operates on the principle of varying current levels to represent different values of a physical measurement, such as temperature, pressure, or flow rate.
In this system, 4 mA typically represents the lowest end of the measurement range, while 20 mA signifies the highest end. This range provides a clear distinction between the minimum and maximum values, allowing for accurate monitoring and control of the equipment. The choice of a 4-20 mA loop is advantageous due to its inherent noise immunity, as the current remains constant regardless of the resistance of the transmission line, thus ensuring reliable signal integrity over long distances.
The current loop consists of a transmitter, which converts the physical measurement into a corresponding current signal, and a receiver, which interprets this signal to control the equipment accordingly. The transmitter may be a sensor or a transducer that is calibrated to output a specific current based on the measured variable. The receiver can be a programmable logic controller (PLC), a digital display, or any other control system capable of processing the current signal.
Powering the loop can be accomplished through a variety of methods, including using a dedicated power supply or a loop-powered device that draws its operating power from the current loop itself. This configuration simplifies installation and reduces the need for additional wiring.
In summary, the computer-controlled 4-20 mA current loop is a robust and reliable method for transmitting analog signals in industrial applications, facilitating effective equipment control and monitoring.In some industries, to control the some equipments they are use computer-controlled 4-20mA current loop. This current loop is used transmit a signal over a.. 🔗 External reference
The 4-20 mA current loop is a standard method for transmitting analog signals in industrial environments, particularly for process control and instrumentation applications. The current loop operates on the principle of varying current levels to represent different values of a physical measurement, such as temperature, pressure, or flow rate.
In this system, 4 mA typically represents the lowest end of the measurement range, while 20 mA signifies the highest end. This range provides a clear distinction between the minimum and maximum values, allowing for accurate monitoring and control of the equipment. The choice of a 4-20 mA loop is advantageous due to its inherent noise immunity, as the current remains constant regardless of the resistance of the transmission line, thus ensuring reliable signal integrity over long distances.
The current loop consists of a transmitter, which converts the physical measurement into a corresponding current signal, and a receiver, which interprets this signal to control the equipment accordingly. The transmitter may be a sensor or a transducer that is calibrated to output a specific current based on the measured variable. The receiver can be a programmable logic controller (PLC), a digital display, or any other control system capable of processing the current signal.
Powering the loop can be accomplished through a variety of methods, including using a dedicated power supply or a loop-powered device that draws its operating power from the current loop itself. This configuration simplifies installation and reduces the need for additional wiring.
In summary, the computer-controlled 4-20 mA current loop is a robust and reliable method for transmitting analog signals in industrial applications, facilitating effective equipment control and monitoring.In some industries, to control the some equipments they are use computer-controlled 4-20mA current loop. This current loop is used transmit a signal over a.. 🔗 External reference