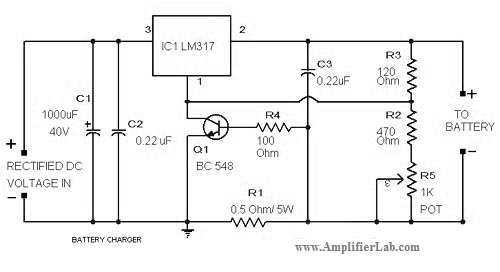
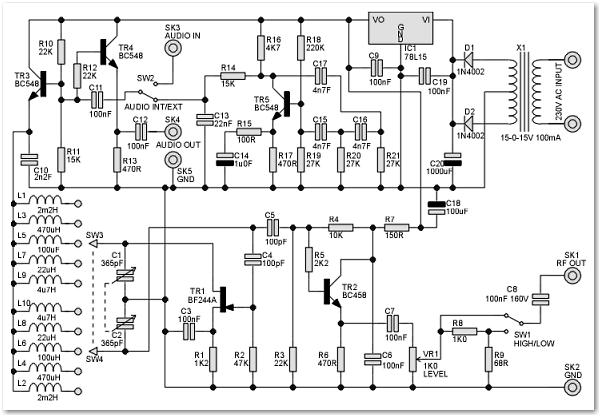
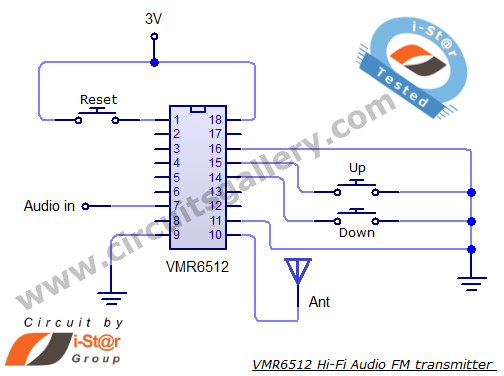
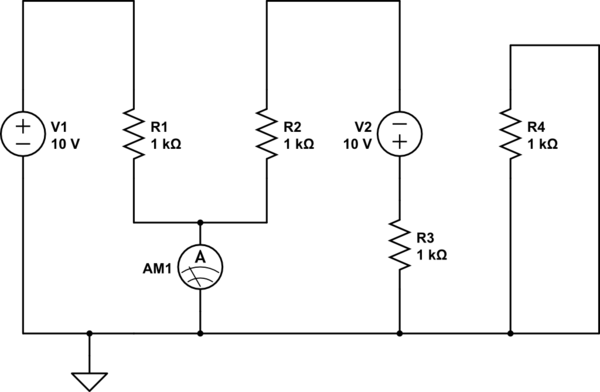
The basic circuit diagram of a constant current source mirror
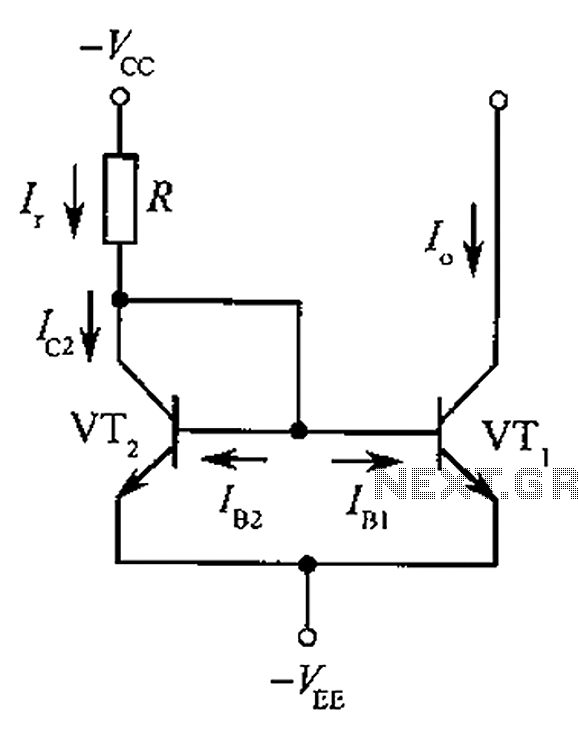
The circuit depicted is a mirror substantially constant current source circuit, in which transistors VT1 and VT2 are matched to each other. The figure illustrates that the current through Ir is equal to Ic2 plus the sum of base currents IB1 and IB2. Due to the symmetry of VT1 and VT2, their collector currents are equal to their respective base currents.
The circuit operates as a current mirror, a fundamental configuration used in analog electronics to replicate a current in one branch of the circuit to another branch. In this design, transistors VT1 and VT2 are typically matched NPN or PNP devices, ensuring that they have similar characteristics, which is crucial for maintaining accuracy in current mirroring.
The circuit's operation begins with the reference current, which flows through VT1. This reference current is set by the resistor connected to the base of VT1. The output current, which is mirrored in VT2, is derived from the relationship established between the collector and base currents. The symmetry in the transistors ensures that variations in temperature or power supply do not significantly affect the performance of the current source.
In practical applications, this configuration is often used in differential amplifiers, current steering circuits, and biasing networks, where precise control of current is essential. The current mirror's ability to maintain a constant output current, regardless of load variations, makes it an invaluable component in integrated circuit design.
To enhance performance, additional components such as resistors or capacitors may be included to improve stability and bandwidth. Additionally, careful layout considerations are necessary to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the circuit's performance. As shown for the mirror substantially constant current source circuit, wherein VT1, VT2 is matched to the tube. The figure shows Ir Ic2 + IB1 + IB2 Because VT1, VT2 are symmetr ical, their collector currents are equal to the base current, so there
The circuit operates as a current mirror, a fundamental configuration used in analog electronics to replicate a current in one branch of the circuit to another branch. In this design, transistors VT1 and VT2 are typically matched NPN or PNP devices, ensuring that they have similar characteristics, which is crucial for maintaining accuracy in current mirroring.
The circuit's operation begins with the reference current, which flows through VT1. This reference current is set by the resistor connected to the base of VT1. The output current, which is mirrored in VT2, is derived from the relationship established between the collector and base currents. The symmetry in the transistors ensures that variations in temperature or power supply do not significantly affect the performance of the current source.
In practical applications, this configuration is often used in differential amplifiers, current steering circuits, and biasing networks, where precise control of current is essential. The current mirror's ability to maintain a constant output current, regardless of load variations, makes it an invaluable component in integrated circuit design.
To enhance performance, additional components such as resistors or capacitors may be included to improve stability and bandwidth. Additionally, careful layout considerations are necessary to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the circuit's performance. As shown for the mirror substantially constant current source circuit, wherein VT1, VT2 is matched to the tube. The figure shows Ir Ic2 + IB1 + IB2 Because VT1, VT2 are symmetr ical, their collector currents are equal to the base current, so there