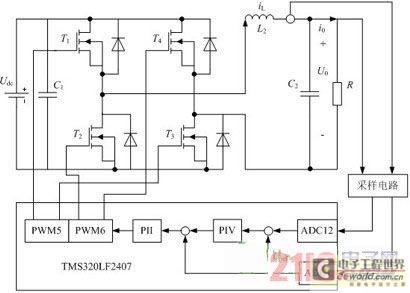
Control motor PWM schematic
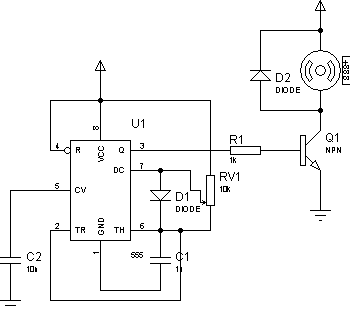
There are two primary methods to control the speed of a DC motor: by varying the supply voltage and through pulse width modulation (PWM). The first method is less convenient, particularly in digital systems, as it necessitates the use of analog circuitry. The second method, PWM, is more suitable for digital systems since it relies solely on digital signals. PWM involves adjusting the switching speed and pulse width, known as the duty cycle, which is the ratio of the signal's ON time to its total period (T). In the provided diagram, two signals are illustrated; the first has a duty cycle of t1/T = 1/3, while the second has a duty cycle of t2/T = 2/3, with both signals having the same period. This technique allows for motor speed control via the PWM output of a microcontroller or through a simple PWM control circuit using an IC555 timer. The duty cycle can be modified using a potentiometer (RV1), while the period remains constant since the overall resistance between Vcc and pin 6 of the 555 timer does not change.
The control of DC motor speed using PWM is a widely adopted practice in modern electronic systems due to its efficiency and precision. In a PWM setup, the average voltage supplied to the motor is effectively controlled by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal. A higher duty cycle corresponds to a longer ON time, resulting in a higher average voltage and increased motor speed. Conversely, a lower duty cycle reduces the average voltage and slows the motor.
The implementation of PWM can be achieved using various microcontrollers, which can generate PWM signals with precise timing. Alternatively, the IC555 timer can be configured in astable mode to create a PWM signal. In this configuration, the duty cycle can be adjusted by changing the resistance value of the potentiometer (RV1). The IC555 timer operates by charging and discharging a capacitor through resistors, which determines the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal.
For practical applications, the IC555 circuit can be connected to a DC motor through a suitable driver circuit to handle the current requirements. This driver circuit may include transistors or MOSFETs, which can switch the motor on and off rapidly according to the PWM signal, allowing for smooth speed control. It is essential to ensure that the components used in the circuit can handle the motor's current and voltage specifications to avoid damage.
Overall, PWM provides a robust solution for controlling DC motor speeds in various applications, from robotics to industrial automation, enabling precise and efficient motor management.In general there are two ways to control DC motor speed: by varying supply voltage and pulse width modulation (PWM). First control method is not convenient especially in digital systems. It requires analog circuitry and so on. Second motor speed control method is very convenient for digital systems, because all control is made using only digital s
ignals. As you already know PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is all about switching speed and pulse width (duty cycle). Duty cycle is ratio of signal time ON/T. T is period of signal. In above diagram you see two signals. First duty cycle is about t1/T=1/3 and another`s duty cycle would be about t2/T=2/3. And notice the period of signals are the same. In this way you can control motor speed using microcontrollers PWM output or if you need you may use simple control motor PWM schematic constructed using IC555 timer circuit: Without going too deep in to 555 timer`s performance analysis I can mention that duty cycle can be changed using potentiometer RV1.
The period of signal won`t change as over all resistance between Vcc and 555 pin 6 does not change. We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The control of DC motor speed using PWM is a widely adopted practice in modern electronic systems due to its efficiency and precision. In a PWM setup, the average voltage supplied to the motor is effectively controlled by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal. A higher duty cycle corresponds to a longer ON time, resulting in a higher average voltage and increased motor speed. Conversely, a lower duty cycle reduces the average voltage and slows the motor.
The implementation of PWM can be achieved using various microcontrollers, which can generate PWM signals with precise timing. Alternatively, the IC555 timer can be configured in astable mode to create a PWM signal. In this configuration, the duty cycle can be adjusted by changing the resistance value of the potentiometer (RV1). The IC555 timer operates by charging and discharging a capacitor through resistors, which determines the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal.
For practical applications, the IC555 circuit can be connected to a DC motor through a suitable driver circuit to handle the current requirements. This driver circuit may include transistors or MOSFETs, which can switch the motor on and off rapidly according to the PWM signal, allowing for smooth speed control. It is essential to ensure that the components used in the circuit can handle the motor's current and voltage specifications to avoid damage.
Overall, PWM provides a robust solution for controlling DC motor speeds in various applications, from robotics to industrial automation, enabling precise and efficient motor management.In general there are two ways to control DC motor speed: by varying supply voltage and pulse width modulation (PWM). First control method is not convenient especially in digital systems. It requires analog circuitry and so on. Second motor speed control method is very convenient for digital systems, because all control is made using only digital s
ignals. As you already know PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is all about switching speed and pulse width (duty cycle). Duty cycle is ratio of signal time ON/T. T is period of signal. In above diagram you see two signals. First duty cycle is about t1/T=1/3 and another`s duty cycle would be about t2/T=2/3. And notice the period of signals are the same. In this way you can control motor speed using microcontrollers PWM output or if you need you may use simple control motor PWM schematic constructed using IC555 timer circuit: Without going too deep in to 555 timer`s performance analysis I can mention that duty cycle can be changed using potentiometer RV1.
The period of signal won`t change as over all resistance between Vcc and 555 pin 6 does not change. We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
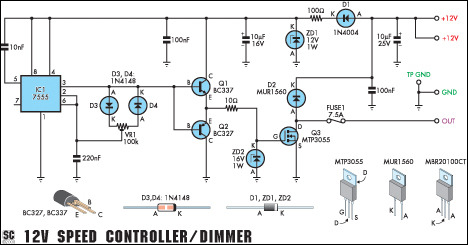
C0QBmk~%24(KGrHqIOKkIEq4M%2Bu,)1BK2zHH580Q~~_35.gif)