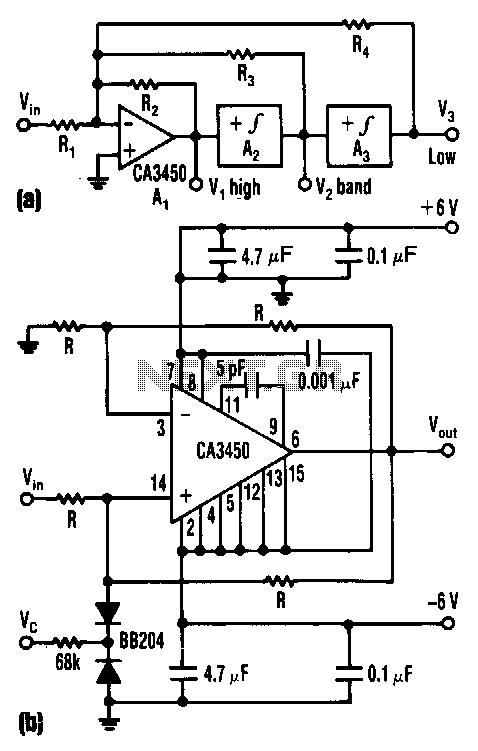
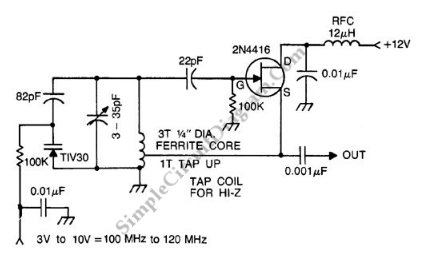
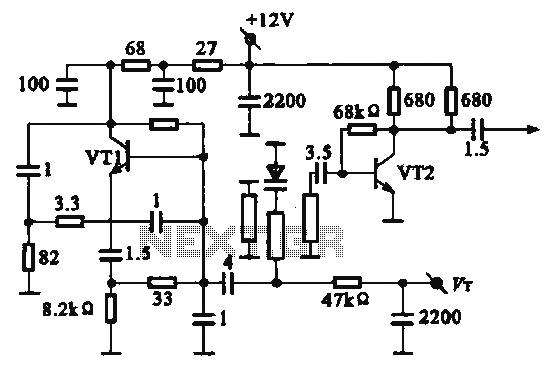
Crystal controlled butler oscillator
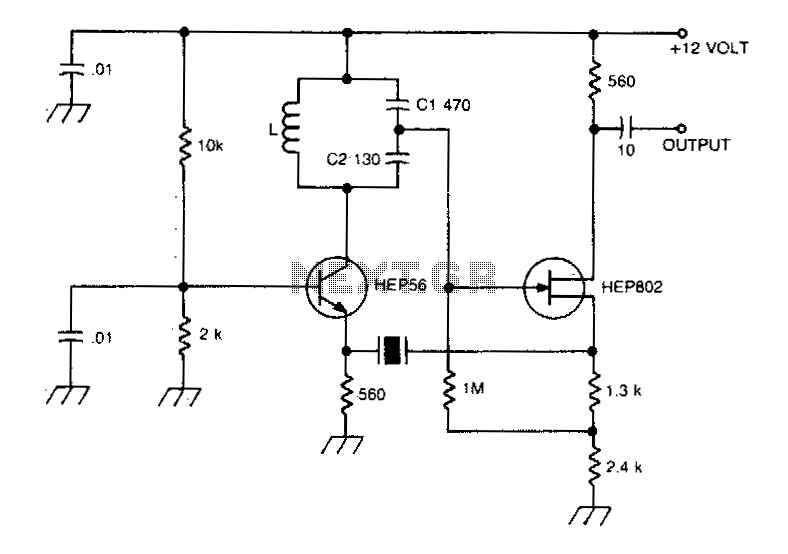
A typical Butler oscillator operating within the frequency range of 20 to 100 MHz incorporates a Field Effect Transistor (FET) in the second stage of its configuration. The circuit exhibits reliability issues when utilizing two bipolar transistors. In some instances, the design may incorporate two FETs instead. The frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the values of the inductance (L) and capacitance (C) within the circuit.
The Butler oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output signal. It is characterized by its ability to produce stable frequencies across a designated range, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems and signal processing. The oscillator employs a feedback mechanism that is essential for maintaining oscillation.
In the typical configuration, the first stage of the Butler oscillator consists of an active device, such as a FET or a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), which amplifies the input signal. The second stage is crucial for determining the oscillator's performance; therefore, the use of a FET is preferred due to its high input impedance and lower noise characteristics compared to BJTs. The inclusion of a second FET can enhance reliability and performance, especially when the circuit requires consistent oscillation without distortion.
The frequency of oscillation is a function of the LC tank circuit formed by the inductor and capacitor. The resonant frequency (f) can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π√(LC))
where L is the inductance in henries and C is the capacitance in farads. By selecting appropriate values for L and C, the desired frequency within the 20-100 MHz range can be achieved. The design must also consider factors such as component tolerances, parasitic capacitances, and inductances, which can affect the overall frequency stability and performance of the oscillator.
In summary, the Butler oscillator is a versatile circuit design that utilizes FETs for improved reliability and performance. The frequency of oscillation is critically dependent on the chosen LC values, making careful selection of these components essential for achieving the desired operational characteristics.A typical Butler oscillator (20-100 MHz) uses an FET in the second stage; the circuit is not reliable with two bipolars. Sometimes two FETs are used Frequency is determined by LC values. 🔗 External reference
The Butler oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output signal. It is characterized by its ability to produce stable frequencies across a designated range, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems and signal processing. The oscillator employs a feedback mechanism that is essential for maintaining oscillation.
In the typical configuration, the first stage of the Butler oscillator consists of an active device, such as a FET or a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), which amplifies the input signal. The second stage is crucial for determining the oscillator's performance; therefore, the use of a FET is preferred due to its high input impedance and lower noise characteristics compared to BJTs. The inclusion of a second FET can enhance reliability and performance, especially when the circuit requires consistent oscillation without distortion.
The frequency of oscillation is a function of the LC tank circuit formed by the inductor and capacitor. The resonant frequency (f) can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π√(LC))
where L is the inductance in henries and C is the capacitance in farads. By selecting appropriate values for L and C, the desired frequency within the 20-100 MHz range can be achieved. The design must also consider factors such as component tolerances, parasitic capacitances, and inductances, which can affect the overall frequency stability and performance of the oscillator.
In summary, the Butler oscillator is a versatile circuit design that utilizes FETs for improved reliability and performance. The frequency of oscillation is critically dependent on the chosen LC values, making careful selection of these components essential for achieving the desired operational characteristics.A typical Butler oscillator (20-100 MHz) uses an FET in the second stage; the circuit is not reliable with two bipolars. Sometimes two FETs are used Frequency is determined by LC values. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713