Current-Limited 6-V Charger
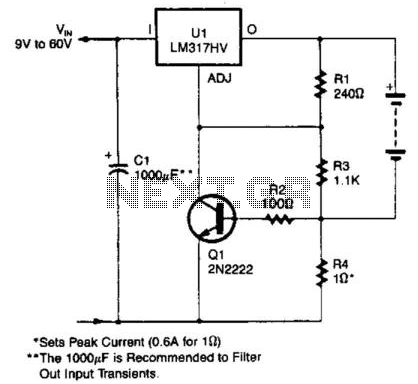
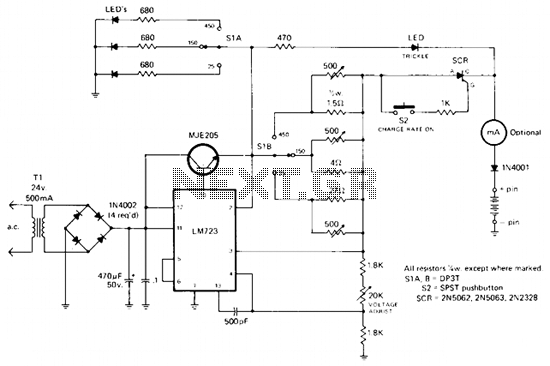
An LM317HV regulator is utilized as a current-limited charger. If the current through R4 exceeds 0.6 A, Q1 is activated, which pulls the ADJ terminal of the LM317HV to ground and reduces the battery charging current.
The LM317HV is a versatile adjustable linear voltage regulator capable of providing a stable output voltage while allowing for current limiting features. In this configuration, the regulator is employed to maintain a safe charging current for a connected battery. The resistor R4 is strategically placed to monitor the charging current; when this current surpasses a predefined threshold of 0.6 A, it triggers the transistor Q1.
When Q1 is activated, it effectively connects the ADJ terminal of the LM317HV to ground. This action alters the feedback loop of the regulator, causing the output voltage to decrease. As a result, the charging current supplied to the battery is reduced, preventing potential damage from overcurrent conditions. This current limiting mechanism is essential in battery charging applications where maintaining a safe charge level is critical to the longevity and safety of the battery.
In practical applications, careful selection of R4 is necessary to ensure accurate current sensing. The value of R4 can be calculated based on the desired current limit and the voltage drop across it at the threshold current. Additionally, Q1 must be chosen based on its current handling capabilities and voltage ratings to ensure reliable operation under the defined conditions.
Overall, this configuration provides an effective solution for current-limited battery charging, enhancing the reliability and safety of the charging process. An LM317HV regulator is used as a current-limited charger. If current through R4 exceeds 0.6 A, Ql is biased on , which pulls the ADJ terminal of the LM317 HV to ground and reduces the battery-charging current. 🔗 External reference
The LM317HV is a versatile adjustable linear voltage regulator capable of providing a stable output voltage while allowing for current limiting features. In this configuration, the regulator is employed to maintain a safe charging current for a connected battery. The resistor R4 is strategically placed to monitor the charging current; when this current surpasses a predefined threshold of 0.6 A, it triggers the transistor Q1.
When Q1 is activated, it effectively connects the ADJ terminal of the LM317HV to ground. This action alters the feedback loop of the regulator, causing the output voltage to decrease. As a result, the charging current supplied to the battery is reduced, preventing potential damage from overcurrent conditions. This current limiting mechanism is essential in battery charging applications where maintaining a safe charge level is critical to the longevity and safety of the battery.
In practical applications, careful selection of R4 is necessary to ensure accurate current sensing. The value of R4 can be calculated based on the desired current limit and the voltage drop across it at the threshold current. Additionally, Q1 must be chosen based on its current handling capabilities and voltage ratings to ensure reliable operation under the defined conditions.
Overall, this configuration provides an effective solution for current-limited battery charging, enhancing the reliability and safety of the charging process. An LM317HV regulator is used as a current-limited charger. If current through R4 exceeds 0.6 A, Ql is biased on , which pulls the ADJ terminal of the LM317 HV to ground and reduces the battery-charging current. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713