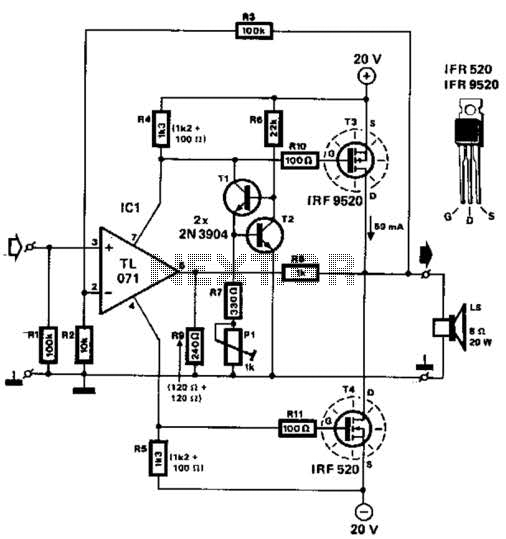
Days to TN-1 Intelligent negative pulse charging circuit
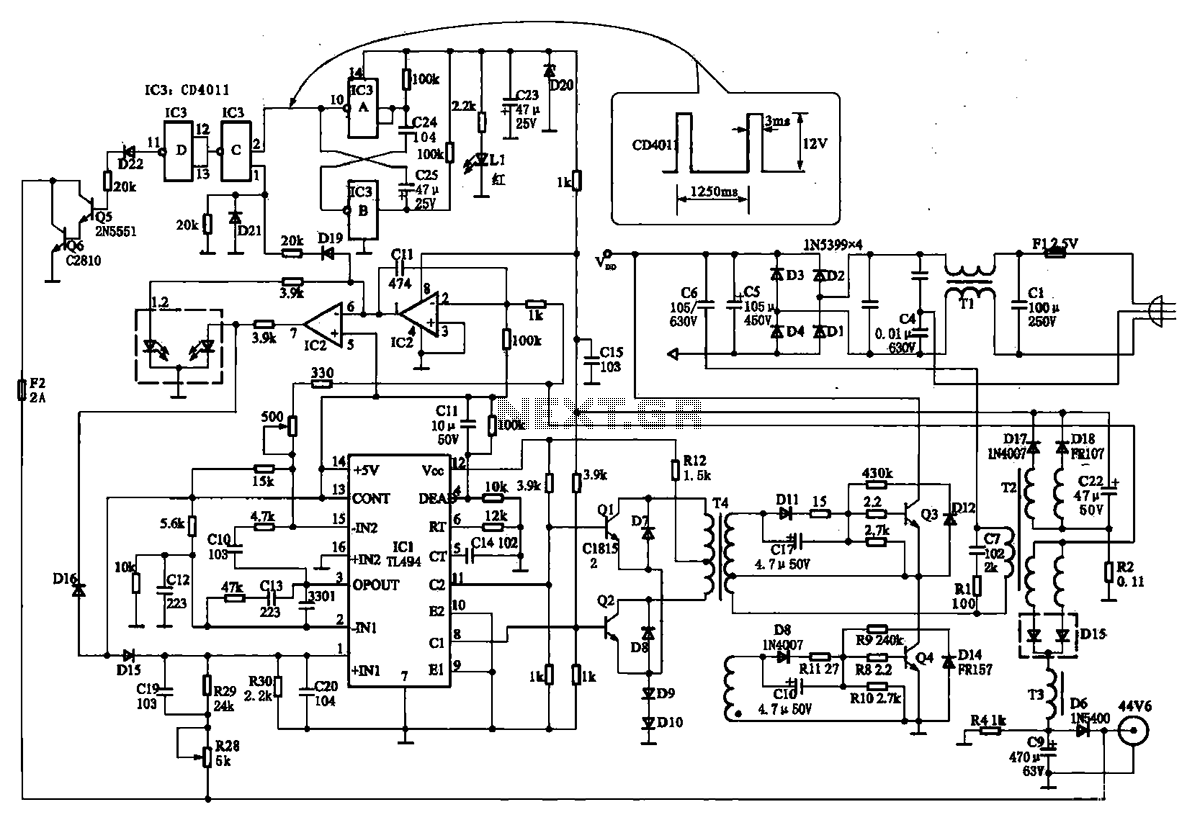
The TN-1 Intelligent Negative Pulse Charging Circuit is a sophisticated device designed for efficient battery charging. It operates as a half-bridge charger, which is a common configuration in such circuits. The negative pulse charging mechanism is facilitated by a discharge switch, which controls the negative load pulse. The pulse oscillator consists of three main components. The discharge switch employs transistor Q6, which prevents short-circuiting between the collector and emitter, thus avoiding battery discharge. When Q6 is turned off, the battery is allowed to recharge. Transistors Q5 and Q6 are directly coupled, forming a Darlington configuration. Q6 is controlled by the negative pulse oscillator and interacts with a load controlled by IC3, made up of components C and D. The D component connects to an inverter that operates in conjunction with a two-input NAND gate. The circuit only activates when both inputs C are at a high level, resulting in a low output, which inverts D to turn on Q6 and discharge the battery. The C component generates a positive pulse from a multivibrator at a frequency of one pulse per second (with a pulse width of 3 ms), while the output from the current detection circuit of IC2 maintains a high level for constant current charging. During this phase, the negative pulse is active. The pulse oscillator, comprising components A and B, is formed by IC3 alongside resistors C24 and C25 (both 100 kΩ) and capacitor C1, creating a multi-harmonic oscillator with distinct charge and discharge time constants of 3 ms and 1250 ms, respectively. The negative pulse charging method enhances charge acceptance and minimizes temperature increases during charging. It is important to note that the charger remains operational during the discharge phase without shutting down the charging circuit.
The TN-1 Intelligent Negative Pulse Charging Circuit is engineered to optimize battery performance through a carefully structured pulse charging methodology. The use of a half-bridge configuration allows for efficient energy transfer and management within the circuit. The discharge switch, Q6, serves a critical function in maintaining the integrity of the battery by preventing unintended discharges, thus ensuring that energy is conserved effectively during the charging process.
The Darlington pair formed by Q5 and Q6 amplifies the control signals, allowing for more precise management of the discharge and charge cycles. This arrangement is particularly beneficial in applications where rapid switching and high current handling are required. The integration of IC3, along with components C and D, provides a robust framework for controlling the pulse generation, thereby allowing for the modulation of the charging process based on real-time feedback from the battery's state.
The oscillator design, utilizing resistors and capacitors to establish time constants, ensures that the charging pulses are delivered in a manner that enhances battery chemistry, promoting better charge acceptance and reducing thermal stress. This is crucial for prolonging battery life and maintaining performance standards, especially in applications where batteries are subjected to frequent charge and discharge cycles.
In conclusion, the TN-1 Intelligent Negative Pulse Charging Circuit represents a significant advancement in battery charging technology, combining sophisticated control mechanisms with efficient energy management to deliver superior charging performance while safeguarding battery health.Days to TN-1 Intelligent negative pulse charging circuit Is a day to TN-I intelligent negative pulse charging circuit. This charger is the main part of the typical half-bridge two chargers, and FIG constituting 2-75 charger circuit is basically the same. This introduces negative pulse charging circuit works. This part of the circuit by the discharge switch, the negative load control pulse, the pulse oscillator consists of three parts. Discharge switch is transistor Q6. Q6 is avoided, the collector and emitter of the battery short circuit, battery discharge. Q6 is turned off, the battery charge to restore power. Q5 and Q6 are directly coupled, commonly known as Darlington. Q6 by loading negative pulse oscillator and joint control. Negative pulse load is controlled by IC3 composed of C and D, D connected to the inverter (circuit in parallel with the two input NAND gate as a NAND gate), only two inputs C are high level, feet is low, the D-inverting make Q6 is turned on, the battery to discharge.
C feet from the multivibrator 1 per second (pulse width 3 ms) positive pulse, C of O feet from the current detection circuit of IC2 O feet, constant current charging O feet high almost electric. In this case, negative pulse to work. Pulse oscillator A and B by the IC3 and C24, C25, two 100 k: C1 resistor constitute a typical multi-harmonic oscillator, charge and discharge time constants different high 3 ms, low 1250 ms.
Negative pulse charging can be improved charge acceptance, reduce the charge temperature. Said charger during discharge, do not turn off the charging circuit.
The TN-1 Intelligent Negative Pulse Charging Circuit is engineered to optimize battery performance through a carefully structured pulse charging methodology. The use of a half-bridge configuration allows for efficient energy transfer and management within the circuit. The discharge switch, Q6, serves a critical function in maintaining the integrity of the battery by preventing unintended discharges, thus ensuring that energy is conserved effectively during the charging process.
The Darlington pair formed by Q5 and Q6 amplifies the control signals, allowing for more precise management of the discharge and charge cycles. This arrangement is particularly beneficial in applications where rapid switching and high current handling are required. The integration of IC3, along with components C and D, provides a robust framework for controlling the pulse generation, thereby allowing for the modulation of the charging process based on real-time feedback from the battery's state.
The oscillator design, utilizing resistors and capacitors to establish time constants, ensures that the charging pulses are delivered in a manner that enhances battery chemistry, promoting better charge acceptance and reducing thermal stress. This is crucial for prolonging battery life and maintaining performance standards, especially in applications where batteries are subjected to frequent charge and discharge cycles.
In conclusion, the TN-1 Intelligent Negative Pulse Charging Circuit represents a significant advancement in battery charging technology, combining sophisticated control mechanisms with efficient energy management to deliver superior charging performance while safeguarding battery health.Days to TN-1 Intelligent negative pulse charging circuit Is a day to TN-I intelligent negative pulse charging circuit. This charger is the main part of the typical half-bridge two chargers, and FIG constituting 2-75 charger circuit is basically the same. This introduces negative pulse charging circuit works. This part of the circuit by the discharge switch, the negative load control pulse, the pulse oscillator consists of three parts. Discharge switch is transistor Q6. Q6 is avoided, the collector and emitter of the battery short circuit, battery discharge. Q6 is turned off, the battery charge to restore power. Q5 and Q6 are directly coupled, commonly known as Darlington. Q6 by loading negative pulse oscillator and joint control. Negative pulse load is controlled by IC3 composed of C and D, D connected to the inverter (circuit in parallel with the two input NAND gate as a NAND gate), only two inputs C are high level, feet is low, the D-inverting make Q6 is turned on, the battery to discharge.
C feet from the multivibrator 1 per second (pulse width 3 ms) positive pulse, C of O feet from the current detection circuit of IC2 O feet, constant current charging O feet high almost electric. In this case, negative pulse to work. Pulse oscillator A and B by the IC3 and C24, C25, two 100 k: C1 resistor constitute a typical multi-harmonic oscillator, charge and discharge time constants different high 3 ms, low 1250 ms.
Negative pulse charging can be improved charge acceptance, reduce the charge temperature. Said charger during discharge, do not turn off the charging circuit.