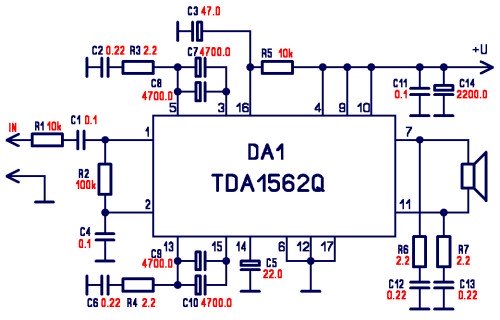
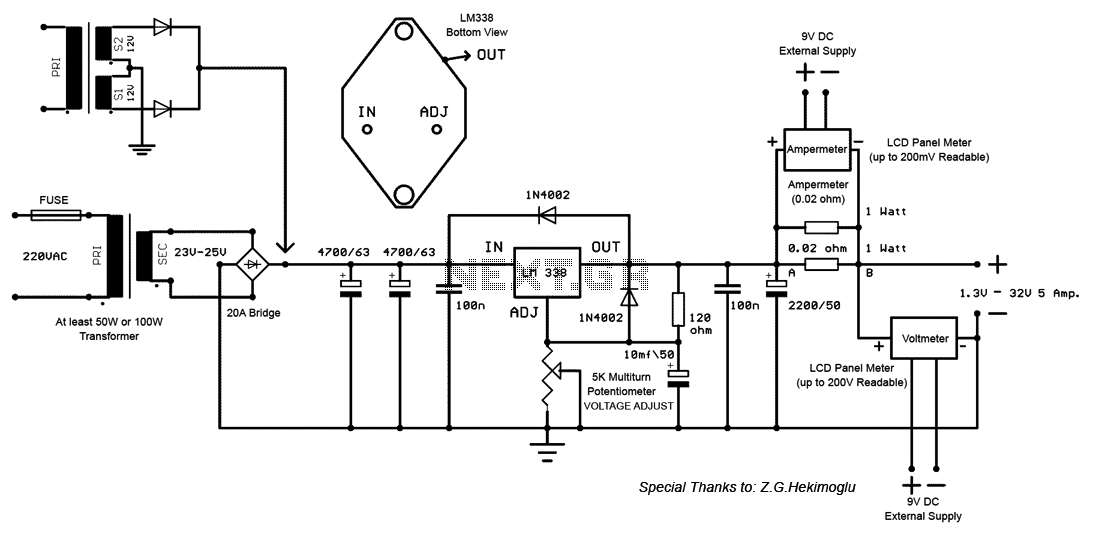
DC Motor Clockwise Anticlockwise Control H-bridge Circuit
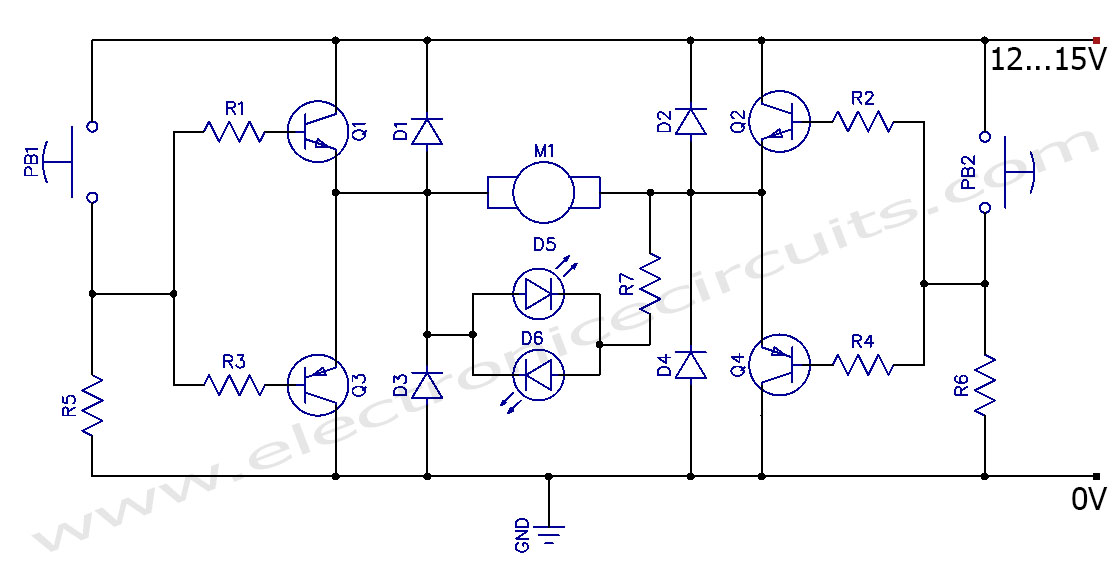
This circuit can control the direction of a DC motor, allowing it to operate in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions (forward and backward).
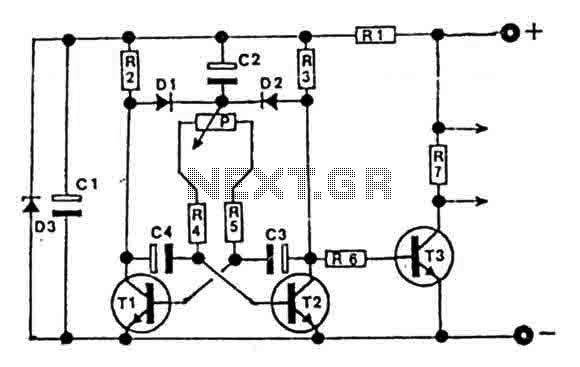
The described circuit employs an H-bridge configuration, which is essential for reversing the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor, thereby enabling bidirectional control. The H-bridge consists of four switches (transistors or MOSFETs) arranged in a bridge configuration. When two opposite switches are activated, current flows through the motor in one direction, causing it to rotate clockwise. Conversely, activating the other two switches reverses the current flow, resulting in counterclockwise rotation.
Control signals for the H-bridge can be generated using a microcontroller or a simple control circuit. For example, a microcontroller can provide PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals to modulate the speed of the motor in addition to controlling its direction. A push-button switch or a joystick can be used to manually change the direction of the motor, providing an intuitive interface for operation.
Protection features such as flyback diodes are often included in the design to prevent voltage spikes generated by the inductive load of the motor from damaging the control circuitry. Additionally, current sensing can be integrated to monitor the motor's load and prevent overheating or stalling conditions.
This bidirectional motor control circuit is widely used in various applications, including robotics, conveyor systems, and automated machinery, where precise control over motor direction and speed is required.This circuit can control direction of a DC motor. This can operate the motor in both directions (Bi-direction) Clockwise and Anticlockwise (forward and back) 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs an H-bridge configuration, which is essential for reversing the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor, thereby enabling bidirectional control. The H-bridge consists of four switches (transistors or MOSFETs) arranged in a bridge configuration. When two opposite switches are activated, current flows through the motor in one direction, causing it to rotate clockwise. Conversely, activating the other two switches reverses the current flow, resulting in counterclockwise rotation.
Control signals for the H-bridge can be generated using a microcontroller or a simple control circuit. For example, a microcontroller can provide PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals to modulate the speed of the motor in addition to controlling its direction. A push-button switch or a joystick can be used to manually change the direction of the motor, providing an intuitive interface for operation.
Protection features such as flyback diodes are often included in the design to prevent voltage spikes generated by the inductive load of the motor from damaging the control circuitry. Additionally, current sensing can be integrated to monitor the motor's load and prevent overheating or stalling conditions.
This bidirectional motor control circuit is widely used in various applications, including robotics, conveyor systems, and automated machinery, where precise control over motor direction and speed is required.This circuit can control direction of a DC motor. This can operate the motor in both directions (Bi-direction) Clockwise and Anticlockwise (forward and back) 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
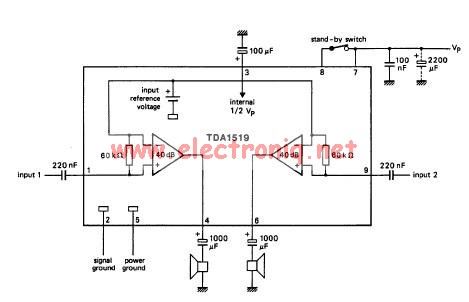
%2Busing%2Bop%2Bamp%2B741%2Bic%2B.png)