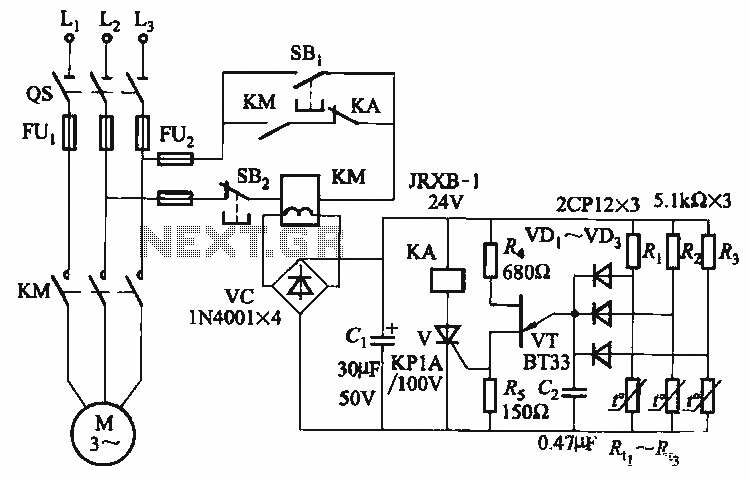
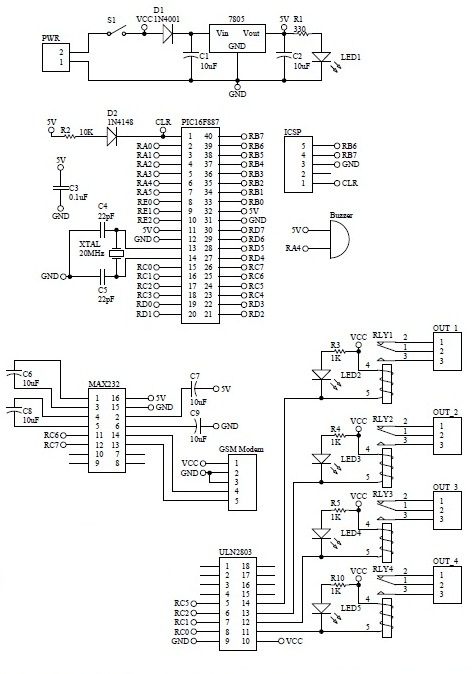
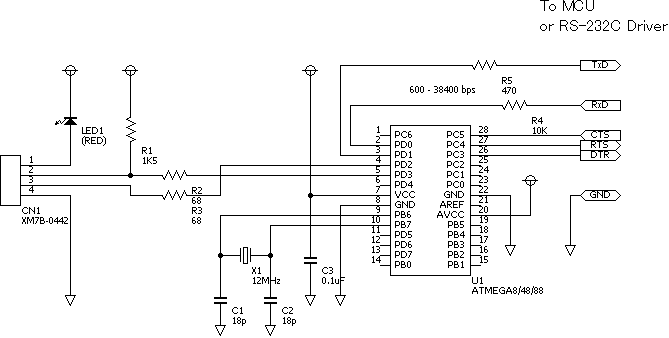
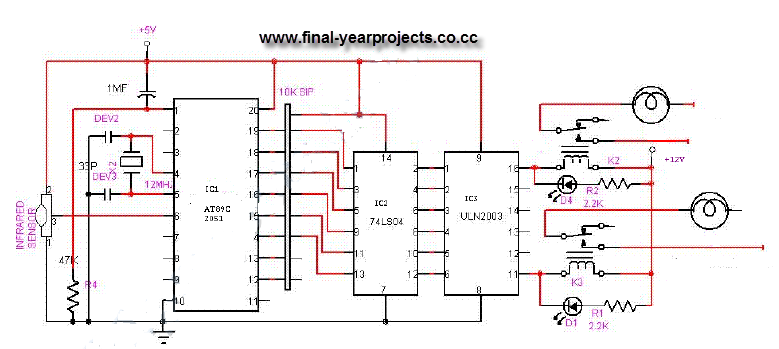
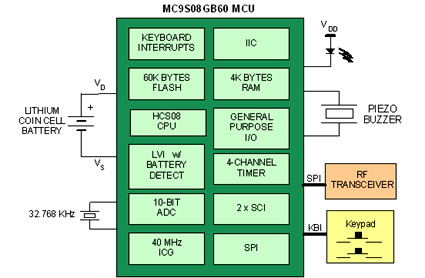
dc motor control avr atmega8
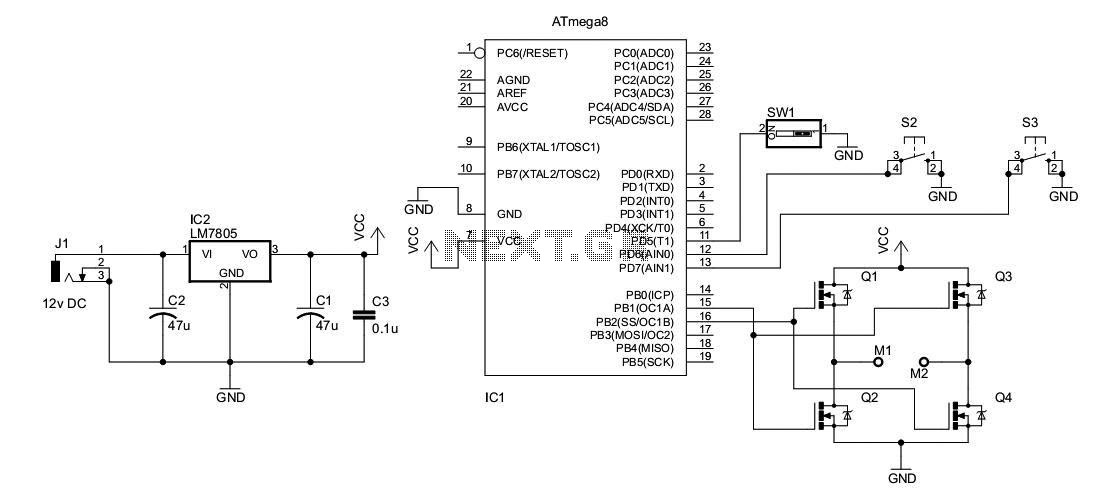
A DC motor from an old personal stereo cassette player has been utilized in this circuit, which provides control over both the speed and direction of the motor. The circuit employs PWM waveforms to drive a MOSFET H-bridge, as illustrated in the schematic. At any given time, only one of the two PWM channels is active, which drives a pair of MOSFETs (either Q1-Q4 or Q3-Q2), while the other two MOSFETs remain in the OFF state. Additionally, toggling the Direction Control switch alters the active PWM channel, thereby activating the alternative pair of MOSFETs. This change in configuration reverses the current flow through the motor, resulting in a change in the rotation direction of the motor shaft.
The circuit design utilizes a DC motor, which is a common component in various applications due to its simplicity and effectiveness. The H-bridge configuration is fundamental in enabling bidirectional control of the motor. The H-bridge consists of four MOSFETs arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for the reversal of current through the motor by switching the active pairs of MOSFETs based on the PWM signals received.
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) technique is employed to control the speed of the motor by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signals. A higher duty cycle corresponds to a higher average voltage across the motor, leading to increased speed, while a lower duty cycle decreases the speed. The active PWM channel determines which pair of MOSFETs is conducting, thereby controlling the flow of current and the direction of the motor.
The Direction Control switch plays a critical role in this circuit. When toggled, it changes the active PWM channel, which in turn activates the opposite pair of MOSFETs. This switching mechanism allows for seamless direction changes in the motor's operation, providing flexibility in applications where the motor needs to reverse its rotation.
In summary, this circuit effectively harnesses the properties of PWM and H-bridge configurations to achieve precise control over the speed and direction of a DC motor, making it suitable for various robotics and automation projects. Proper component selection, including the MOSFET ratings and PWM frequency, is essential to ensure efficient operation and longevity of the circuit.I had used a DC motor from an old personal stereo cassette player. The circuit provides speed and direction control of the motor. The PWM waveforms are used for driving the MOSFET H-bridge as shown in the schematic: At a time only one of the two PWM channel is active, driving only two MOSFETS (either Q1-Q4 or Q3-Q2). Other two MOSFETs remain OFF. Whenever the Direction Control switch is toggled, the PWM channel is also changed, driving the alternative pair of MOSFET, which changes the direction of current flow through motor, resulting in the direction change in rotation of motor shaft. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design utilizes a DC motor, which is a common component in various applications due to its simplicity and effectiveness. The H-bridge configuration is fundamental in enabling bidirectional control of the motor. The H-bridge consists of four MOSFETs arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for the reversal of current through the motor by switching the active pairs of MOSFETs based on the PWM signals received.
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) technique is employed to control the speed of the motor by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signals. A higher duty cycle corresponds to a higher average voltage across the motor, leading to increased speed, while a lower duty cycle decreases the speed. The active PWM channel determines which pair of MOSFETs is conducting, thereby controlling the flow of current and the direction of the motor.
The Direction Control switch plays a critical role in this circuit. When toggled, it changes the active PWM channel, which in turn activates the opposite pair of MOSFETs. This switching mechanism allows for seamless direction changes in the motor's operation, providing flexibility in applications where the motor needs to reverse its rotation.
In summary, this circuit effectively harnesses the properties of PWM and H-bridge configurations to achieve precise control over the speed and direction of a DC motor, making it suitable for various robotics and automation projects. Proper component selection, including the MOSFET ratings and PWM frequency, is essential to ensure efficient operation and longevity of the circuit.I had used a DC motor from an old personal stereo cassette player. The circuit provides speed and direction control of the motor. The PWM waveforms are used for driving the MOSFET H-bridge as shown in the schematic: At a time only one of the two PWM channel is active, driving only two MOSFETS (either Q1-Q4 or Q3-Q2). Other two MOSFETs remain OFF. Whenever the Direction Control switch is toggled, the PWM channel is also changed, driving the alternative pair of MOSFET, which changes the direction of current flow through motor, resulting in the direction change in rotation of motor shaft. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713