DC Motor Speed Controller
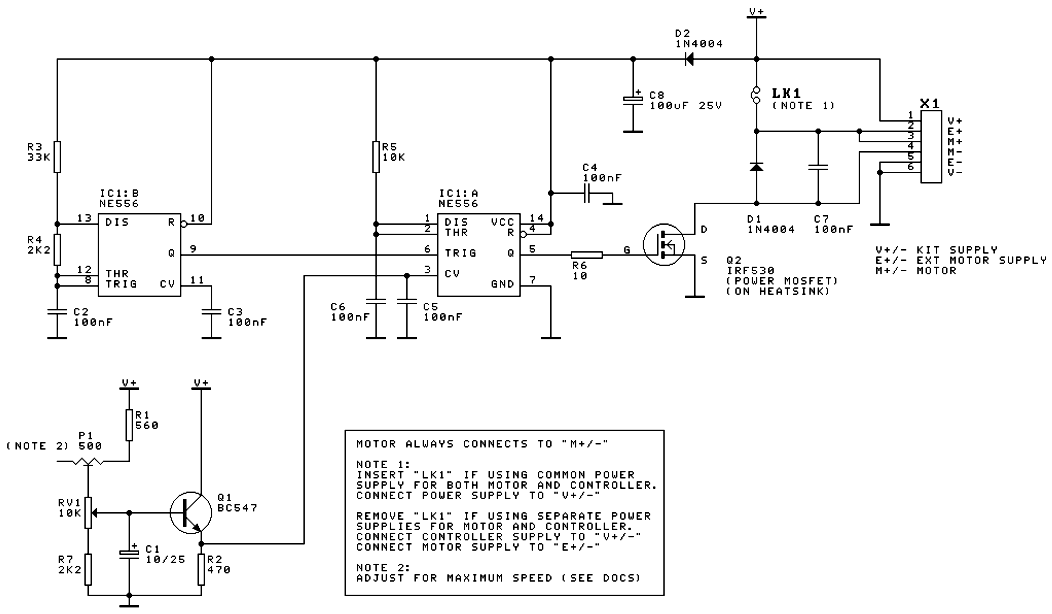
A DC motor speed controller circuit utilizes two timers configured as a Pulse Width Modulator (PWM). The integrated circuit employed for this purpose is the NE556, which is a dual timer/oscillator using NMOS technology.
The DC motor speed controller circuit operates by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal generated by the NE556 timer. This modulation of the PWM signal directly influences the average voltage applied to the DC motor, thereby controlling its speed. The NE556 timer is capable of functioning in both astable and monostable modes, allowing for flexible control strategies.
In this circuit, the two timers can be configured to operate in an astable mode, generating a continuous square wave output. The frequency of this output can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer's pins. The duty cycle of the PWM signal can be fine-tuned by altering the ratio of these resistors, which determines the time the output remains high versus low.
The output from the NE556 is connected to a power transistor, typically an NMOS or a MOSFET, which acts as a switch to control the power delivered to the DC motor. When the PWM signal is high, the transistor conducts, allowing current to flow to the motor, and when the signal is low, the transistor turns off, stopping the current flow. This rapid switching creates an average voltage that the motor experiences, effectively controlling its speed.
Additionally, incorporating feedback mechanisms such as an encoder or tachometer can enhance the performance of the speed controller by providing real-time speed data to adjust the PWM signal dynamically. This feedback loop ensures that the motor maintains a desired speed under varying load conditions, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
Overall, the use of the NE556 in this DC motor speed controller circuit provides a robust and versatile solution for applications requiring precise speed control, making it suitable for various industrial and hobbyist projects.DC motor speed controller circuit, applies two timers connected as a Pulse Width Modulator. The chip put into use will be an nmos dual timer/oscillator NE556 🔗 External reference
The DC motor speed controller circuit operates by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal generated by the NE556 timer. This modulation of the PWM signal directly influences the average voltage applied to the DC motor, thereby controlling its speed. The NE556 timer is capable of functioning in both astable and monostable modes, allowing for flexible control strategies.
In this circuit, the two timers can be configured to operate in an astable mode, generating a continuous square wave output. The frequency of this output can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer's pins. The duty cycle of the PWM signal can be fine-tuned by altering the ratio of these resistors, which determines the time the output remains high versus low.
The output from the NE556 is connected to a power transistor, typically an NMOS or a MOSFET, which acts as a switch to control the power delivered to the DC motor. When the PWM signal is high, the transistor conducts, allowing current to flow to the motor, and when the signal is low, the transistor turns off, stopping the current flow. This rapid switching creates an average voltage that the motor experiences, effectively controlling its speed.
Additionally, incorporating feedback mechanisms such as an encoder or tachometer can enhance the performance of the speed controller by providing real-time speed data to adjust the PWM signal dynamically. This feedback loop ensures that the motor maintains a desired speed under varying load conditions, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
Overall, the use of the NE556 in this DC motor speed controller circuit provides a robust and versatile solution for applications requiring precise speed control, making it suitable for various industrial and hobbyist projects.DC motor speed controller circuit, applies two timers connected as a Pulse Width Modulator. The chip put into use will be an nmos dual timer/oscillator NE556 🔗 External reference