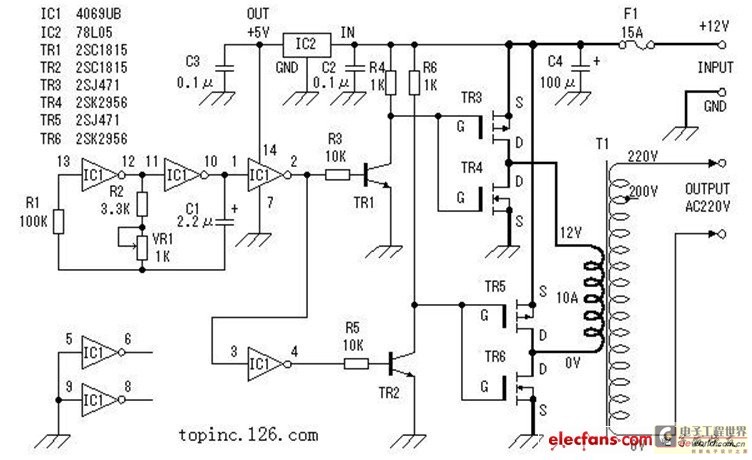
dc to ac inverter with ic cd4047
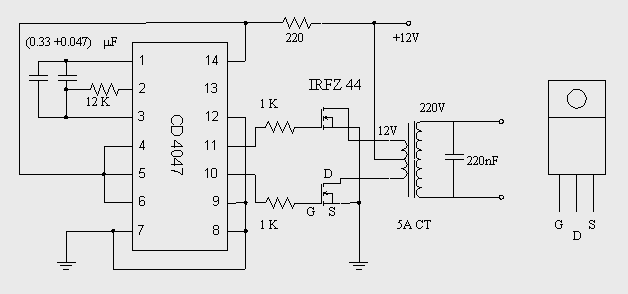
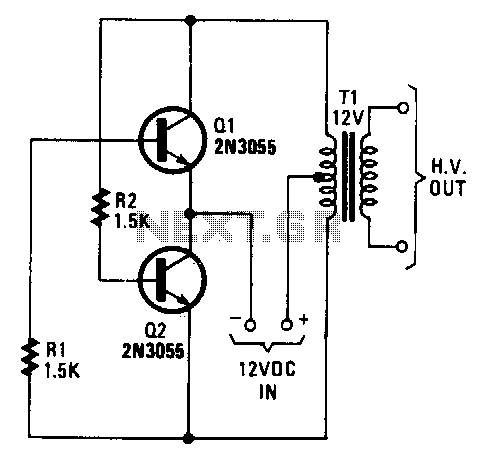
This DC to AC inverter circuit operates based on an unstable multivibrator. In this circuit, the IC CD4047 is selected as the core of the unstable multivibrator because this type of IC provides complementary outputs that are out of phase with each other (pins 10 and 11, as illustrated in Figure 1) and features a 50% duty cycle, which is suitable for generating pulses for the inverter.
The described DC to AC inverter circuit utilizes the CD4047 IC, which is known for its versatility in generating square wave outputs through its astable multivibrator configuration. The IC operates by producing two complementary square wave outputs that are 180 degrees out of phase with each other, which is essential for driving a transformer or a load in an inverter application.
The circuit typically consists of the CD4047 connected to a few passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, to set the frequency of oscillation. The values of these components determine the output frequency, which is crucial for matching the inverter's output to the specifications of the intended AC load. The output from pins 10 and 11 can be fed into a transformer, which steps up the voltage to the required level for AC applications.
In addition to the CD4047, the circuit may include additional components such as diodes for protection, capacitors for filtering, and possibly a heat sink for any power transistors used to amplify the output current. The transformer used in the circuit should be rated for the power requirements of the load to ensure efficient operation.
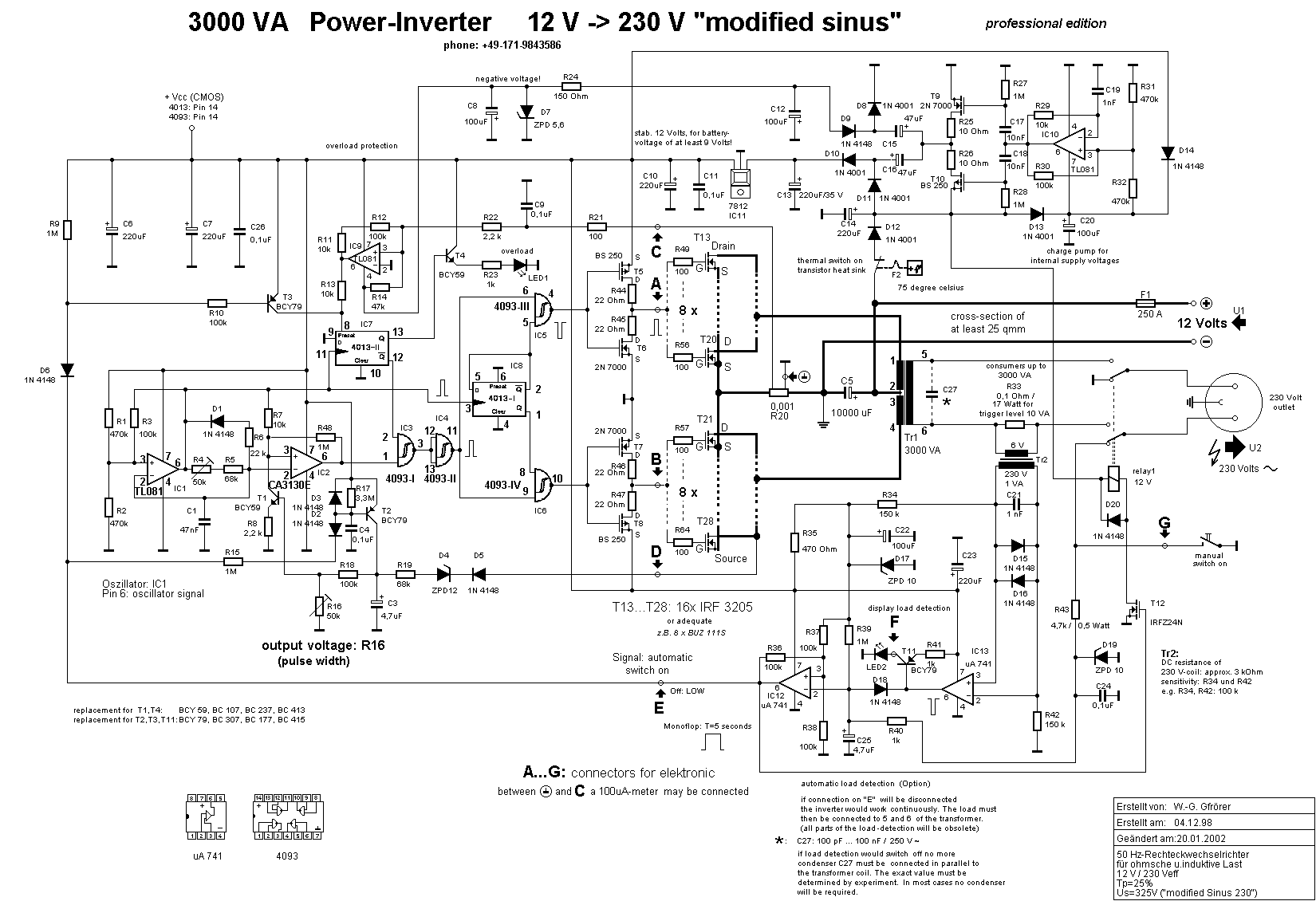
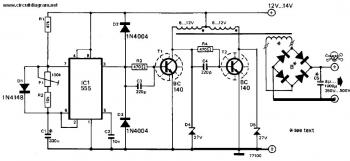
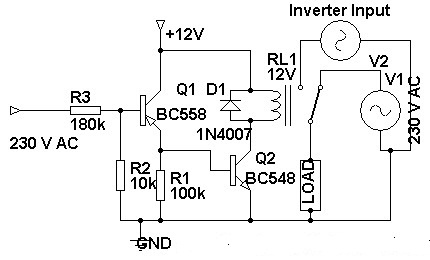
The inverter circuit is particularly useful in applications where DC power, such as from batteries or solar panels, needs to be converted to AC power for household appliances or other AC devices. This design offers a reliable and efficient method to achieve such conversion while maintaining the necessary output characteristics.This DC to AC inverter circuit work based on unstable multi vibrator does. In this circuit, IC CD4047 is chosen as a heart of unstable multivibrator, because this IC type gives a complementary output that has opposite phase to another ( pin 10 and 11 as seen in Figure 1), and has 50 % duty cycle that satisfy to generate a pulse for inverter. 🔗 External reference
The described DC to AC inverter circuit utilizes the CD4047 IC, which is known for its versatility in generating square wave outputs through its astable multivibrator configuration. The IC operates by producing two complementary square wave outputs that are 180 degrees out of phase with each other, which is essential for driving a transformer or a load in an inverter application.
The circuit typically consists of the CD4047 connected to a few passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, to set the frequency of oscillation. The values of these components determine the output frequency, which is crucial for matching the inverter's output to the specifications of the intended AC load. The output from pins 10 and 11 can be fed into a transformer, which steps up the voltage to the required level for AC applications.
In addition to the CD4047, the circuit may include additional components such as diodes for protection, capacitors for filtering, and possibly a heat sink for any power transistors used to amplify the output current. The transformer used in the circuit should be rated for the power requirements of the load to ensure efficient operation.
The inverter circuit is particularly useful in applications where DC power, such as from batteries or solar panels, needs to be converted to AC power for household appliances or other AC devices. This design offers a reliable and efficient method to achieve such conversion while maintaining the necessary output characteristics.This DC to AC inverter circuit work based on unstable multi vibrator does. In this circuit, IC CD4047 is chosen as a heart of unstable multivibrator, because this IC type gives a complementary output that has opposite phase to another ( pin 10 and 11 as seen in Figure 1), and has 50 % duty cycle that satisfy to generate a pulse for inverter. 🔗 External reference