Dedicated headphone amplifier integrated amplifier LM4880-03
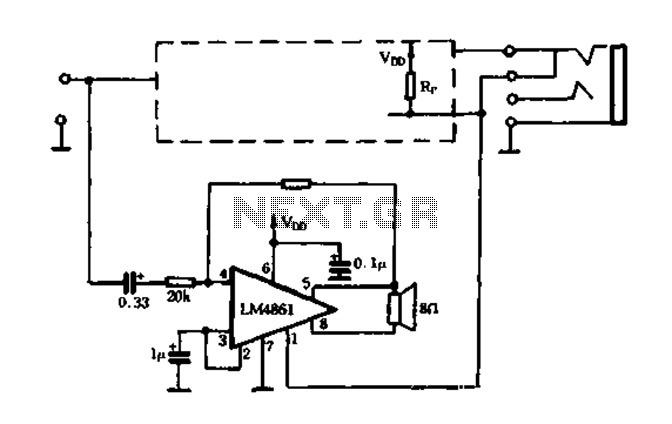
The circuit utilizes a MOSFET to automatically shut down the FIG system. When the headset is inserted, the contact opens, causing the MOSFET gate to connect to a high voltage, allowing current to pass. The LM4880 is configured to enter an amplifying state through the headphone contact and grounding. When the MOSFET is off, it reaches a high power level, resulting in the automatic shutdown of the LM4880. Additionally, the LM4880 can be employed in an automatic application switching power amplifier circuit. The LM4861 can output 0.5W at a voltage of Sv, and when a speaker is connected to the machine's outlet, the O pin is connected to the positive supply through Rv, which automatically turns off the current to the speaker. When the headset is removed, the O pin of the LM4861 connects through contact to ground, activating the working condition, while the LM4880 remains off, allowing both components to operate alternately.
The described circuit leverages a MOSFET for automatic power management in audio applications, ensuring efficient operation when a headset is connected. The MOSFET gate is controlled by the presence of the headset, which alters the voltage at the gate to switch the MOSFET on or off, thereby controlling the flow of current. When the headset is inserted, the circuit allows the LM4880 to amplify audio signals, while simultaneously disconnecting the speaker output, preventing any sound from being emitted through the speakers.
The LM4880 operates as a power amplifier, capable of delivering a power output of up to 0.5W, making it suitable for driving headphones efficiently. The implementation of the LM4861 in this configuration allows for seamless switching between the headphone output and speaker output, enhancing user experience by automatically managing audio pathways based on the device's state. The resistor Rv plays a critical role in controlling the current flow to the speaker, ensuring it is turned off when the headset is in use.
This automatic switching mechanism not only conserves power but also protects the audio components from potential damage due to simultaneous output paths. The design reflects a well-thought-out integration of components that prioritize user convenience and device longevity, making it suitable for portable audio devices where battery life and audio quality are paramount.FIG automatically shut down by the circuit is a MOS FET to achieve. When the headset is inserted, the contact off, MOS tube grid connected high, the tube guide pass., feet grou nded, LM4880 into the amplifying state port allocated through headphones tMOS gate of contacts and R, grounding, MOS tube off, feet to high power level, I. M4880 automatically shut down. l Y a LM4880 can also be made automatic application switching power amplifier circuit, as shown in Figure 5-42.
LM4861 voltage at Sv can output 0.5w power, playback speaker inscribed machine outlet into the headset, O feet connected to the positive supply by Rv, current speaker automatically turns off. As you pull, LM4861 of O feet through contact and care, grounded into working condition, while I.M4880 but just off t work alternately with each other.
The described circuit leverages a MOSFET for automatic power management in audio applications, ensuring efficient operation when a headset is connected. The MOSFET gate is controlled by the presence of the headset, which alters the voltage at the gate to switch the MOSFET on or off, thereby controlling the flow of current. When the headset is inserted, the circuit allows the LM4880 to amplify audio signals, while simultaneously disconnecting the speaker output, preventing any sound from being emitted through the speakers.
The LM4880 operates as a power amplifier, capable of delivering a power output of up to 0.5W, making it suitable for driving headphones efficiently. The implementation of the LM4861 in this configuration allows for seamless switching between the headphone output and speaker output, enhancing user experience by automatically managing audio pathways based on the device's state. The resistor Rv plays a critical role in controlling the current flow to the speaker, ensuring it is turned off when the headset is in use.
This automatic switching mechanism not only conserves power but also protects the audio components from potential damage due to simultaneous output paths. The design reflects a well-thought-out integration of components that prioritize user convenience and device longevity, making it suitable for portable audio devices where battery life and audio quality are paramount.FIG automatically shut down by the circuit is a MOS FET to achieve. When the headset is inserted, the contact off, MOS tube grid connected high, the tube guide pass., feet grou nded, LM4880 into the amplifying state port allocated through headphones tMOS gate of contacts and R, grounding, MOS tube off, feet to high power level, I. M4880 automatically shut down. l Y a LM4880 can also be made automatic application switching power amplifier circuit, as shown in Figure 5-42.
LM4861 voltage at Sv can output 0.5w power, playback speaker inscribed machine outlet into the headset, O feet connected to the positive supply by Rv, current speaker automatically turns off. As you pull, LM4861 of O feet through contact and care, grounded into working condition, while I.M4880 but just off t work alternately with each other.