Delayed Off Light Switch
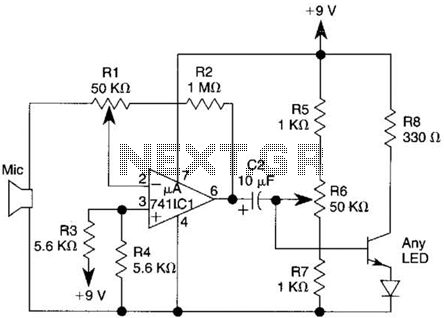
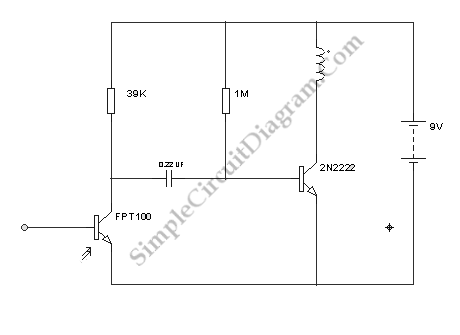
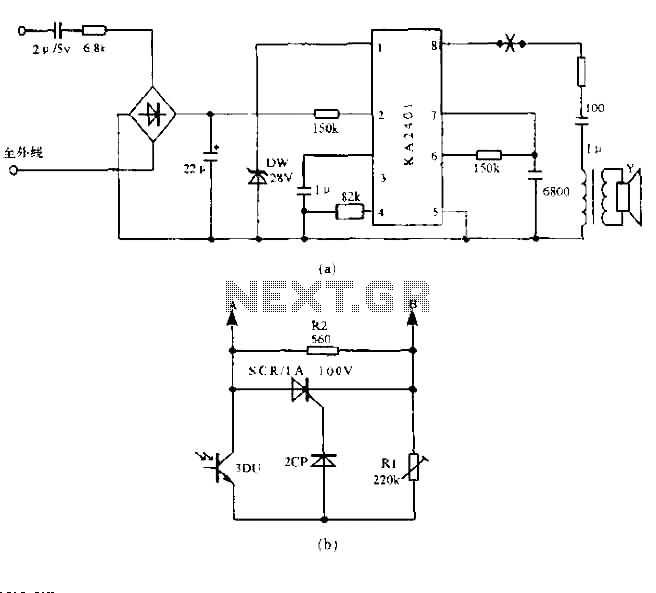
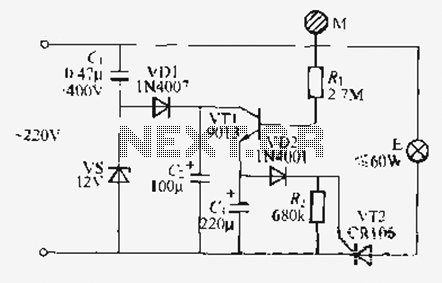
This design utilizes standard metal gate CMOS logic rather than the typical PIC or custom chip. A 22µF capacitor charges during one half of the AC cycle and provides trigger current to the triac during both halves.
The circuit employs a straightforward yet effective approach by integrating metal gate CMOS technology, which is known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity. The use of a 22µF capacitor is critical in this design, as it acts as an energy storage element. During the positive half-cycle of the AC input, the capacitor charges up, reaching a voltage level sufficient to trigger the gate of the triac.
The triac serves as a bidirectional switch, allowing current to flow in both directions once it is triggered. This characteristic is essential for AC applications, where current alternates direction. The design ensures that the triac receives a triggering pulse during both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC waveform. This is accomplished by utilizing the charged capacitor to deliver the necessary current to the triac gate each half-cycle.
In summary, this circuit exemplifies a unique integration of metal gate CMOS logic and passive components, providing a reliable method for controlling AC loads through a triac. The simplicity of the design, combined with the effective use of a capacitor for energy storage, offers a robust solution for applications requiring AC switching without the complexity of microcontroller-based designs.This is an unusual design in that it uses plain metal gate CMOS logic instead of the usual PIC or a custom chip. The 22uF capacitor charges up during one half of the ac cycle, and supplies trigger current to the triac on both halves.
🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a straightforward yet effective approach by integrating metal gate CMOS technology, which is known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity. The use of a 22µF capacitor is critical in this design, as it acts as an energy storage element. During the positive half-cycle of the AC input, the capacitor charges up, reaching a voltage level sufficient to trigger the gate of the triac.
The triac serves as a bidirectional switch, allowing current to flow in both directions once it is triggered. This characteristic is essential for AC applications, where current alternates direction. The design ensures that the triac receives a triggering pulse during both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC waveform. This is accomplished by utilizing the charged capacitor to deliver the necessary current to the triac gate each half-cycle.
In summary, this circuit exemplifies a unique integration of metal gate CMOS logic and passive components, providing a reliable method for controlling AC loads through a triac. The simplicity of the design, combined with the effective use of a capacitor for energy storage, offers a robust solution for applications requiring AC switching without the complexity of microcontroller-based designs.This is an unusual design in that it uses plain metal gate CMOS logic instead of the usual PIC or a custom chip. The 22uF capacitor charges up during one half of the ac cycle, and supplies trigger current to the triac on both halves.
🔗 External reference