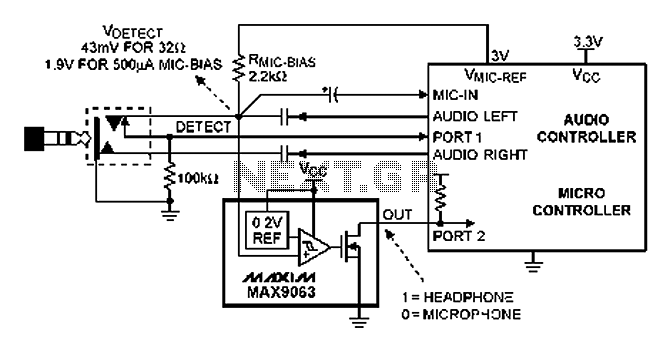
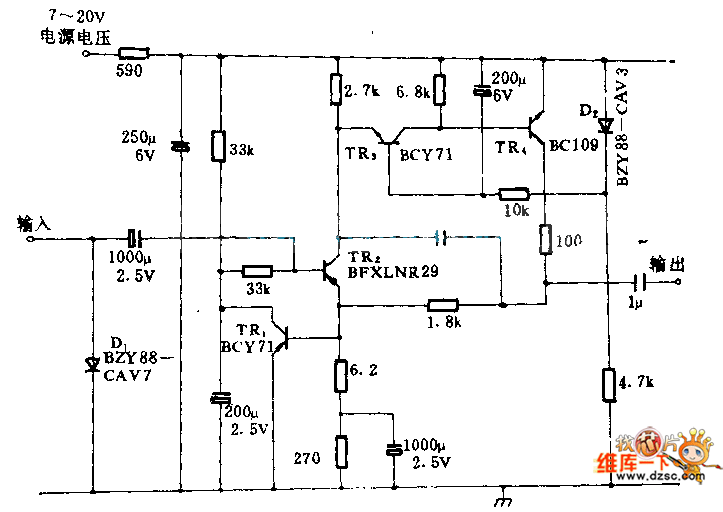
Demo comparator
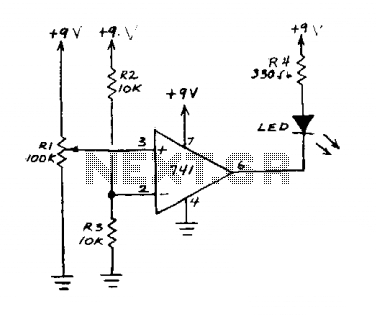
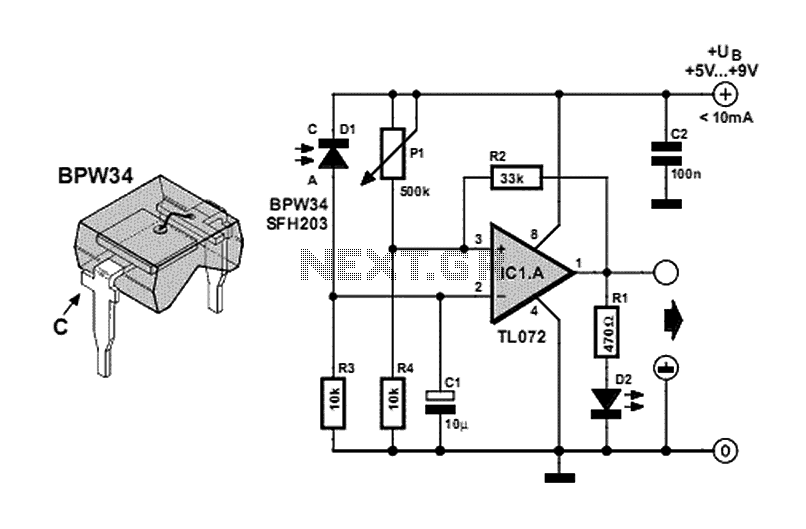
This circuit is an operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration that operates without a feedback resistor. The junction point of resistors R2 and R3 establishes the reference voltage. When the input voltage, determined by resistor R1, falls below this reference voltage, the LED illuminates. Conversely, if the input voltage exceeds the reference voltage, the LED turns off.
The described circuit utilizes an op-amp in a comparator configuration. In this setup, the op-amp compares the voltage at its non-inverting input (connected to R1) with the reference voltage established at the junction of resistors R2 and R3. The output of the op-amp will switch states based on this comparison.
Resistor R1 is responsible for setting the input voltage level. When this voltage is lower than the reference voltage, the output of the op-amp will go high, activating the LED. The LED serves as an indicator, providing visual feedback regarding the input voltage relative to the reference voltage.
The reference voltage is determined by the resistor divider formed by R2 and R3. By selecting appropriate values for these resistors, the desired threshold for the input voltage can be established. If the input voltage exceeds the reference voltage, the output of the op-amp will drop to a low state, turning the LED off.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications where voltage level monitoring is required, such as in battery management systems, voltage level indicators, or as part of a more complex control system. Proper selection of the op-amp and passive components is crucial for ensuring the desired performance and stability of the circuit.This circuit is an op amp without a feedback resistor. R2 and R3 junction point sets the reference voltage. When the input voltage set by Rl is below the reference voltage the LED glows. If voltage is above reference, the LED goes off. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes an op-amp in a comparator configuration. In this setup, the op-amp compares the voltage at its non-inverting input (connected to R1) with the reference voltage established at the junction of resistors R2 and R3. The output of the op-amp will switch states based on this comparison.
Resistor R1 is responsible for setting the input voltage level. When this voltage is lower than the reference voltage, the output of the op-amp will go high, activating the LED. The LED serves as an indicator, providing visual feedback regarding the input voltage relative to the reference voltage.
The reference voltage is determined by the resistor divider formed by R2 and R3. By selecting appropriate values for these resistors, the desired threshold for the input voltage can be established. If the input voltage exceeds the reference voltage, the output of the op-amp will drop to a low state, turning the LED off.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications where voltage level monitoring is required, such as in battery management systems, voltage level indicators, or as part of a more complex control system. Proper selection of the op-amp and passive components is crucial for ensuring the desired performance and stability of the circuit.This circuit is an op amp without a feedback resistor. R2 and R3 junction point sets the reference voltage. When the input voltage set by Rl is below the reference voltage the LED glows. If voltage is above reference, the LED goes off. 🔗 External reference