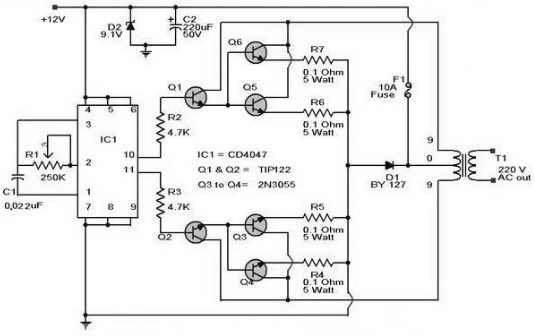
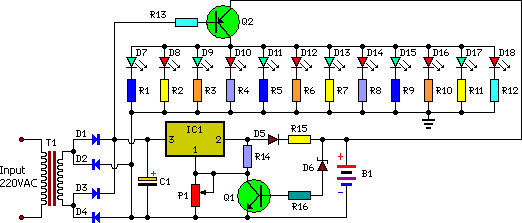
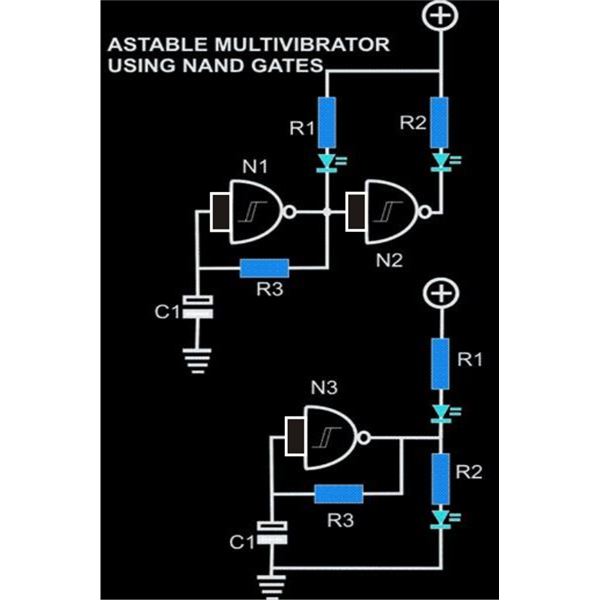
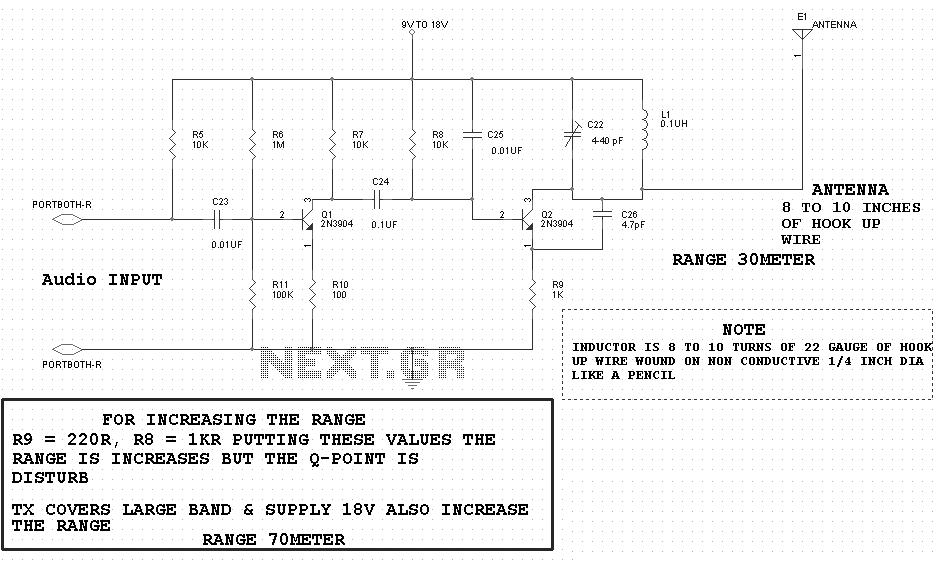
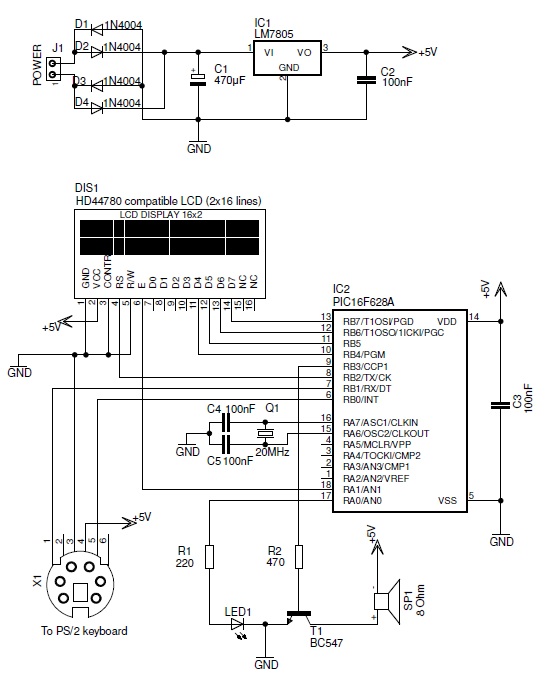
Detected line current Phase protective circuit 2
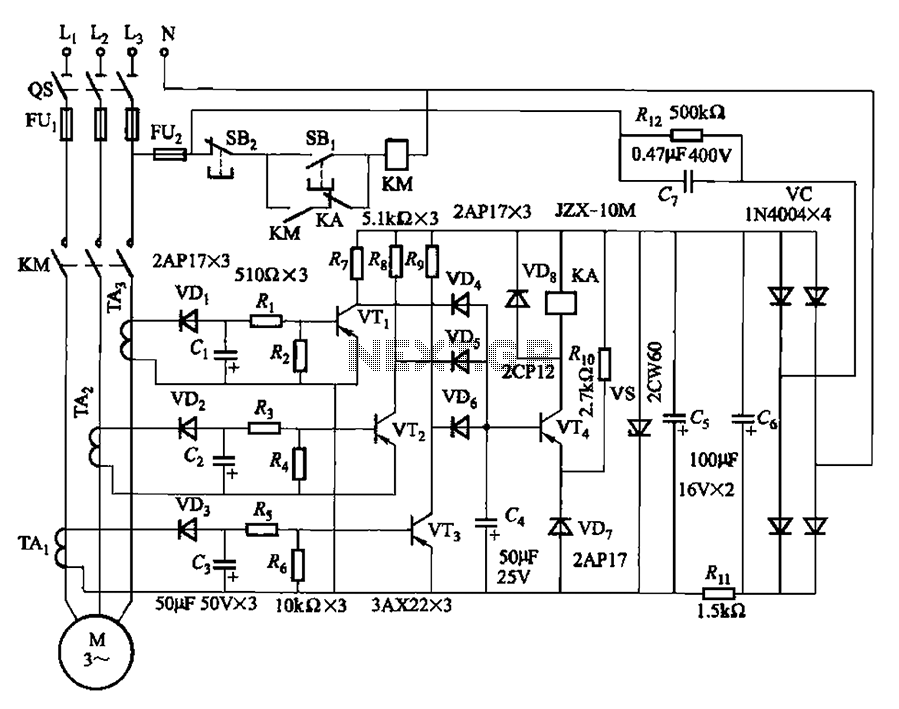
The current detection signal is obtained from three current transformers after rectification and filtering, resulting in three DC voltage outputs. These voltages are applied to transistors VT1, VT2, and VTa between the base and emitter. The signal is amplified by three diodes and then received by diodes VD4, VDs, or gates VD6. An OR gate circuit controls transistor VT4, which turns on or off to manage the engagement or disengagement of relay KA. In the event of a power shortage phase, relay KA engages, causing contactor KM to release and stop the motor. A disadvantage of the protection circuit is that when the stator windings are connected in a star configuration, the phase current does not drop to zero, preventing the relay from actuating.
The described circuit utilizes three current transformers (CTs) to monitor current levels in an electrical system. Each CT outputs a proportional AC current that is subsequently rectified and filtered to provide stable DC voltages. These DC outputs are fed into three separate transistors (VT1, VT2, and VTa), which serve as amplifiers and switches for the signals derived from the CTs.
The amplified signals are then processed by a series of diodes, including VD4, VDs, and VD6, which ensure that only positive voltage signals are passed through for further processing. The OR gate circuit plays a crucial role in the logic of the system, allowing for multiple input signals to control the state of transistor VT4. When the conditions are met (i.e., one or more of the input signals are high), VT4 is activated, which in turn controls the relay KA.
Relay KA is responsible for managing the operation of contactor KM, which is used to control the motor's power supply. When a power shortage is detected, relay KA engages, signaling contactor KM to open and subsequently stopping the motor. This protective feature is critical for preventing damage to the motor during low power conditions.
However, a limitation of this protection circuit arises when the motor's stator windings are configured in a star connection. In this scenario, even during a power shortage, the phase current may not drop to zero due to the characteristics of the star configuration. As a result, the relay may not actuate as intended, potentially leaving the motor unprotected during critical conditions. This issue highlights the need for careful consideration of the motor's winding configuration when designing protective circuits to ensure reliable operation. By the three current transformers Current detection signal obtained after rectification, filtering the output of the three DC voltage, are applied to the transistor VTi, VT2 an d VTa between the base and emitter. Signal by three three- diode after amplification, received by the diode VD4, VDs, or gates VD6 thereof. By the OR gate circuit controls the transistor VT4 turned on or off to control the inter-pull or release of relay KA.
When the power shortage phase, KA pull, the contactor KM release, the motor stops. The disadvantage of the protection circuit, when the stator windings when -shaped connection inside the motor winding down phase current does not drop to zero, and the relay will not action.
The described circuit utilizes three current transformers (CTs) to monitor current levels in an electrical system. Each CT outputs a proportional AC current that is subsequently rectified and filtered to provide stable DC voltages. These DC outputs are fed into three separate transistors (VT1, VT2, and VTa), which serve as amplifiers and switches for the signals derived from the CTs.
The amplified signals are then processed by a series of diodes, including VD4, VDs, and VD6, which ensure that only positive voltage signals are passed through for further processing. The OR gate circuit plays a crucial role in the logic of the system, allowing for multiple input signals to control the state of transistor VT4. When the conditions are met (i.e., one or more of the input signals are high), VT4 is activated, which in turn controls the relay KA.
Relay KA is responsible for managing the operation of contactor KM, which is used to control the motor's power supply. When a power shortage is detected, relay KA engages, signaling contactor KM to open and subsequently stopping the motor. This protective feature is critical for preventing damage to the motor during low power conditions.
However, a limitation of this protection circuit arises when the motor's stator windings are configured in a star connection. In this scenario, even during a power shortage, the phase current may not drop to zero due to the characteristics of the star configuration. As a result, the relay may not actuate as intended, potentially leaving the motor unprotected during critical conditions. This issue highlights the need for careful consideration of the motor's winding configuration when designing protective circuits to ensure reliable operation. By the three current transformers Current detection signal obtained after rectification, filtering the output of the three DC voltage, are applied to the transistor VTi, VT2 an d VTa between the base and emitter. Signal by three three- diode after amplification, received by the diode VD4, VDs, or gates VD6 thereof. By the OR gate circuit controls the transistor VT4 turned on or off to control the inter-pull or release of relay KA.
When the power shortage phase, KA pull, the contactor KM release, the motor stops. The disadvantage of the protection circuit, when the stator windings when -shaped connection inside the motor winding down phase current does not drop to zero, and the relay will not action.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713