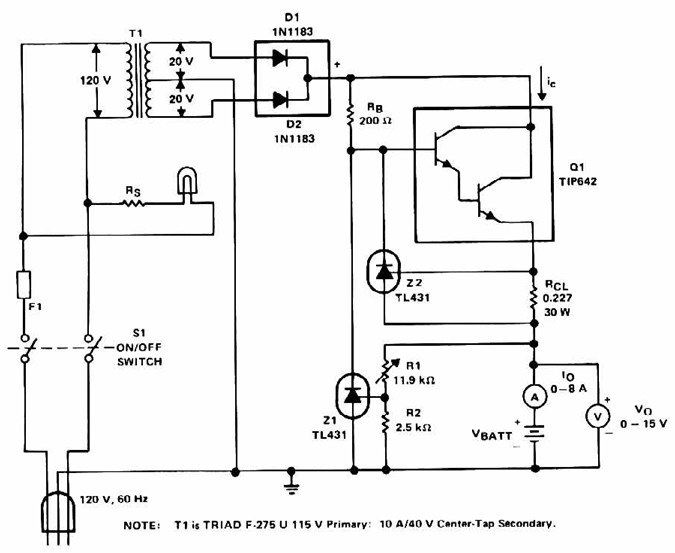
Differential Current Sensing Inside H Bridge
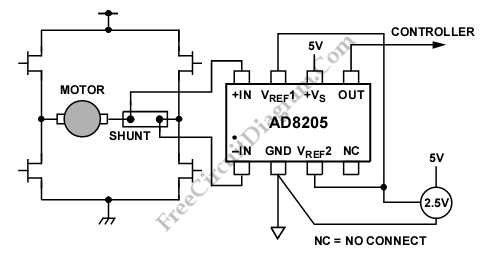
A differential current sensing circuit is integrated within an H-bridge configuration, as illustrated in the schematic diagram below. This circuit exemplifies the application of the AD8205, which is capable of measuring current in both directions as the motor changes direction and the H-bridge switches. The circuit achieves high accuracy in current measurement due to the placement of the AD8205 in the center of the H-bridge. In comparison to a ground-referenced operational amplifier, this configuration is superior because ground serves as an unstable reference voltage, leading to inaccuracies in measurement.
The differential current sensing circuit utilizing the AD8205 is designed to monitor the current flowing through an H-bridge, which is commonly used for controlling motors in various applications. The H-bridge consists of four switches (typically MOSFETs or BJTs) arranged in a configuration that allows for the reversal of motor direction by controlling the current flow through the motor winding.
The AD8205 is an instrumentation amplifier with a high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), making it ideal for applications where the ground potential may fluctuate. By placing the AD8205 in the middle of the H-bridge, the circuit can accurately sense the voltage drop across a shunt resistor inserted in series with the motor. This arrangement enables the measurement of current irrespective of the direction of flow, which is essential for bidirectional motor control.
In operation, as the H-bridge switches are activated to change the motor's direction, the AD8205 continuously monitors the voltage across the shunt resistor, converting this voltage into a proportional output voltage. This output can then be fed into a microcontroller or other processing unit for further analysis, enabling real-time monitoring and control of the motor's performance.
The differential sensing approach mitigates the effects of noise and voltage fluctuations that may occur in the ground reference, enhancing the reliability and precision of current measurements. This makes the circuit suitable for applications requiring precise motor control, such as robotics, automotive systems, and industrial automation.
Overall, the integration of the AD8205 within the H-bridge circuit exemplifies an effective method for achieving accurate current measurement in dynamic environments, ensuring optimal performance and control of motor-driven systems.A differential current sensing that is inserted inside a H bridge circuit. is shown in the schematic diagram below. This circuit is one example of AD8205 application. The AD8205 measures current in both directions as the motor changes direction and H-bridge switches. This circuit has high accuracy in current measurement because AD8205 is placed in the middle of the H-bridge. Compared with a ground referenced op amp, this circuit is better, because ground is unstable reference voltage, so ground referenced op amp is inaccurate. [Circuit`s schematic diagram source: Analog Devices Application Note] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles.
Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The differential current sensing circuit utilizing the AD8205 is designed to monitor the current flowing through an H-bridge, which is commonly used for controlling motors in various applications. The H-bridge consists of four switches (typically MOSFETs or BJTs) arranged in a configuration that allows for the reversal of motor direction by controlling the current flow through the motor winding.
The AD8205 is an instrumentation amplifier with a high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), making it ideal for applications where the ground potential may fluctuate. By placing the AD8205 in the middle of the H-bridge, the circuit can accurately sense the voltage drop across a shunt resistor inserted in series with the motor. This arrangement enables the measurement of current irrespective of the direction of flow, which is essential for bidirectional motor control.
In operation, as the H-bridge switches are activated to change the motor's direction, the AD8205 continuously monitors the voltage across the shunt resistor, converting this voltage into a proportional output voltage. This output can then be fed into a microcontroller or other processing unit for further analysis, enabling real-time monitoring and control of the motor's performance.
The differential sensing approach mitigates the effects of noise and voltage fluctuations that may occur in the ground reference, enhancing the reliability and precision of current measurements. This makes the circuit suitable for applications requiring precise motor control, such as robotics, automotive systems, and industrial automation.
Overall, the integration of the AD8205 within the H-bridge circuit exemplifies an effective method for achieving accurate current measurement in dynamic environments, ensuring optimal performance and control of motor-driven systems.A differential current sensing that is inserted inside a H bridge circuit. is shown in the schematic diagram below. This circuit is one example of AD8205 application. The AD8205 measures current in both directions as the motor changes direction and H-bridge switches. This circuit has high accuracy in current measurement because AD8205 is placed in the middle of the H-bridge. Compared with a ground referenced op amp, this circuit is better, because ground is unstable reference voltage, so ground referenced op amp is inaccurate. [Circuit`s schematic diagram source: Analog Devices Application Note] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles.
Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference