Digital thermometer circuit
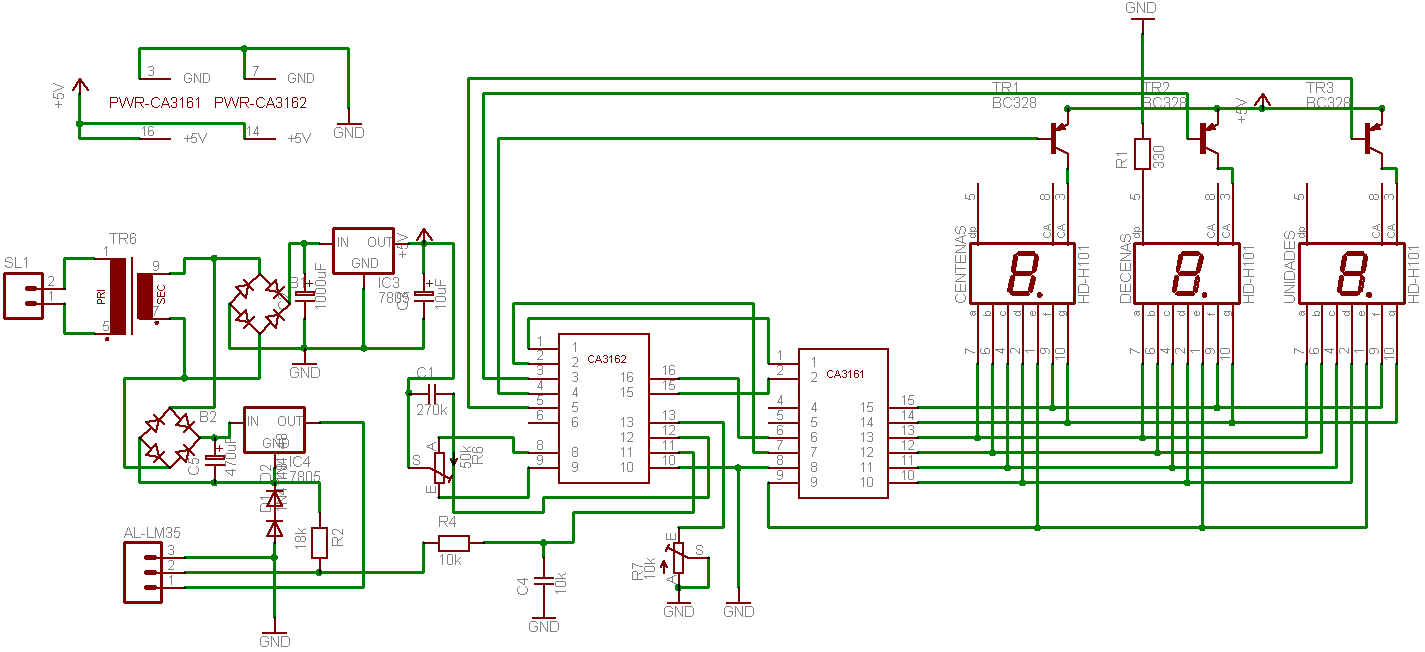
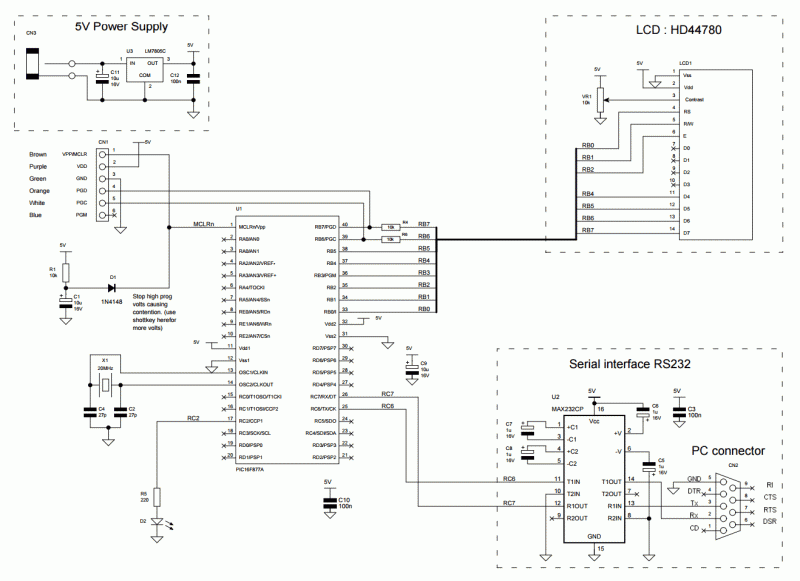
A highly accurate digital thermometer utilizing an LM35 probe with a resolution of 0.1 degrees Celsius. The circuit includes two adjustable components. The first, R5, is used to calibrate the display to zero. To perform this calibration, the end of R4 connected to the temperature probe must be grounded while adjusting R5 until the display reads 0:0:0. After calibration, the LM35 probe is connected to terminals 2 and 3, as indicated on the circuit schematic. The temperature measurement is taken by measuring the voltage between the unconnected terminal (output of the probe) and ground with a multimeter set to the 1 Volt range. The voltage reading corresponds to the ambient temperature; for instance, a reading of 0.236 volts indicates a temperature of 23.6 degrees Celsius. Once the measurement is obtained, terminal 1 of the probe is connected to the circuit, and R7 is adjusted to match the previously measured value.
The circuit design for the digital thermometer incorporates an LM35 temperature sensor, which outputs a linear voltage signal proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. The LM35 operates with a scale factor of 10 mV per degree Celsius, allowing for precise temperature readings. The circuit is configured to include a microcontroller or a display module to interpret the voltage signal from the LM35 and convert it into a readable temperature format.
The calibration process is critical for ensuring accurate readings. The adjustment of R5 to set the display to zero is essential for eliminating any offset errors that may occur in the measurement system. The grounding of R4 during this process ensures that the reference point for the voltage measurement is stable and accurate.
After calibration, the LM35 probe is connected to the designated terminals. The voltage output from the probe is then measured against the ground using a multimeter, which must be set to the appropriate range to capture the expected voltage output accurately. This step is crucial as it establishes the baseline for the temperature reading. The conversion of the voltage reading to temperature is straightforward; for instance, a voltage reading of 0.236 volts directly translates to a temperature of 23.6 degrees Celsius.
Once the initial measurement is taken, connecting terminal 1 of the LM35 to the circuit allows for continuous temperature monitoring. The adjustment of R7 fine-tunes the output to align with the measured value, ensuring that the displayed temperature is accurate.
This digital thermometer circuit is suitable for various applications where precise temperature measurement is required, including laboratory environments, HVAC systems, and general temperature monitoring tasks. The simplicity of the design, combined with the precision of the LM35 sensor, makes it an effective tool for accurate temperature readings.A very precise digital thermometer with LM35 probe (0, 1 degree of freedom). The circuit has two adjustments. One of them, R5, adjusts the displays to 0. To perform this, we have to connect the extreme part of R4 (that goes to the temperature probe) to the ground and we turn R5 until we see 0:0:0. Afterwards, we connect the probe LM35 to terminals 2 and 3 which are marked in the circuit. This is how we Then we measure the values between the non connected terminal, which is the out of the probe, and the ground, with the tester, adjusted to 1 Volt (bottom of the scale). The tension which is shown represents the temperature in the room. For example, if it marks 0. 236, the temperature is 23, 6 C. When we have the measure, we connect the terminal 1 of the probe to the circuit and we adjust R7 until it gives us the value of what we had measured.
🔗 External reference
The circuit design for the digital thermometer incorporates an LM35 temperature sensor, which outputs a linear voltage signal proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. The LM35 operates with a scale factor of 10 mV per degree Celsius, allowing for precise temperature readings. The circuit is configured to include a microcontroller or a display module to interpret the voltage signal from the LM35 and convert it into a readable temperature format.
The calibration process is critical for ensuring accurate readings. The adjustment of R5 to set the display to zero is essential for eliminating any offset errors that may occur in the measurement system. The grounding of R4 during this process ensures that the reference point for the voltage measurement is stable and accurate.
After calibration, the LM35 probe is connected to the designated terminals. The voltage output from the probe is then measured against the ground using a multimeter, which must be set to the appropriate range to capture the expected voltage output accurately. This step is crucial as it establishes the baseline for the temperature reading. The conversion of the voltage reading to temperature is straightforward; for instance, a voltage reading of 0.236 volts directly translates to a temperature of 23.6 degrees Celsius.
Once the initial measurement is taken, connecting terminal 1 of the LM35 to the circuit allows for continuous temperature monitoring. The adjustment of R7 fine-tunes the output to align with the measured value, ensuring that the displayed temperature is accurate.
This digital thermometer circuit is suitable for various applications where precise temperature measurement is required, including laboratory environments, HVAC systems, and general temperature monitoring tasks. The simplicity of the design, combined with the precision of the LM35 sensor, makes it an effective tool for accurate temperature readings.A very precise digital thermometer with LM35 probe (0, 1 degree of freedom). The circuit has two adjustments. One of them, R5, adjusts the displays to 0. To perform this, we have to connect the extreme part of R4 (that goes to the temperature probe) to the ground and we turn R5 until we see 0:0:0. Afterwards, we connect the probe LM35 to terminals 2 and 3 which are marked in the circuit. This is how we Then we measure the values between the non connected terminal, which is the out of the probe, and the ground, with the tester, adjusted to 1 Volt (bottom of the scale). The tension which is shown represents the temperature in the room. For example, if it marks 0. 236, the temperature is 23, 6 C. When we have the measure, we connect the terminal 1 of the probe to the circuit and we adjust R7 until it gives us the value of what we had measured.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713