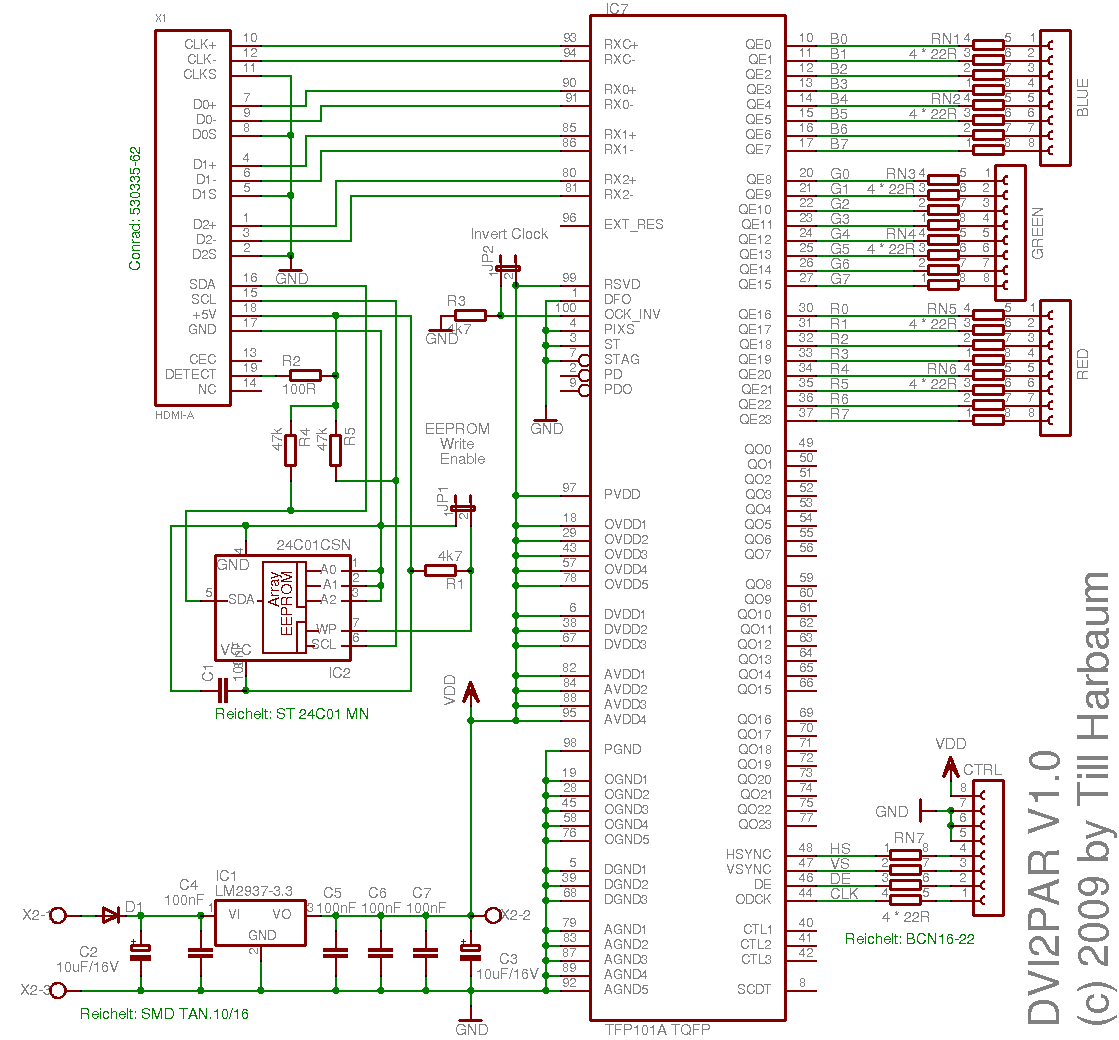
Digital transmission isolator
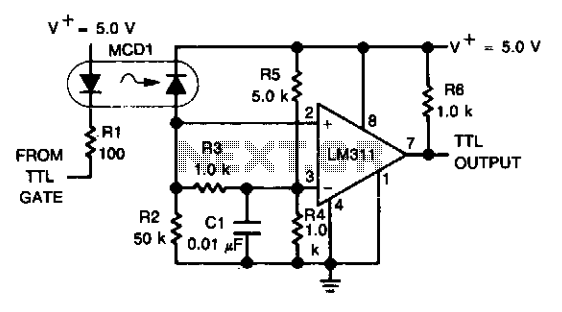
An optoelectronics device is utilized to couple a digital (TTL) signal to another system. The photodiode within the optocoupler drives an LM311 configured to generate a TTL-compatible output. This configuration is particularly beneficial in scenarios where grounds cannot be connected for various reasons.
An optoelectronic coupling system leverages the properties of light to transmit signals between different electrical circuits while maintaining electrical isolation. In this setup, the optocoupler contains a photodiode that converts the incoming digital signal into light, which is then detected by a phototransistor or photodiode on the output side, effectively reproducing the signal in a separate circuit.
The LM311 comparator is employed to process the output from the photodiode. It is configured to operate with a specific threshold voltage, allowing it to output a TTL-compatible signal. This is crucial for interfacing with digital logic circuits, as TTL levels are standard for digital communication. The LM311 can handle a wide range of input voltages and provides a fast response time, making it suitable for high-speed digital applications.
The isolation provided by the optocoupler is essential in applications where different ground potentials exist or where noise from one circuit could interfere with another. This feature ensures that the integrity of the signal is maintained, even in challenging environments. The use of an optoelectronic device in this manner is common in various applications, including data communication, control systems, and interfacing between microcontrollers and peripheral devices.An optoelectronics device is used to couple a digital (TTL) signal to another system. The photodiode in the optocoupler drives an LM311 set up to produce a TTL compatible output. It is useful where grounds are not able to be connected for any reason. 🔗 External reference
An optoelectronic coupling system leverages the properties of light to transmit signals between different electrical circuits while maintaining electrical isolation. In this setup, the optocoupler contains a photodiode that converts the incoming digital signal into light, which is then detected by a phototransistor or photodiode on the output side, effectively reproducing the signal in a separate circuit.
The LM311 comparator is employed to process the output from the photodiode. It is configured to operate with a specific threshold voltage, allowing it to output a TTL-compatible signal. This is crucial for interfacing with digital logic circuits, as TTL levels are standard for digital communication. The LM311 can handle a wide range of input voltages and provides a fast response time, making it suitable for high-speed digital applications.
The isolation provided by the optocoupler is essential in applications where different ground potentials exist or where noise from one circuit could interfere with another. This feature ensures that the integrity of the signal is maintained, even in challenging environments. The use of an optoelectronic device in this manner is common in various applications, including data communication, control systems, and interfacing between microcontrollers and peripheral devices.An optoelectronics device is used to couple a digital (TTL) signal to another system. The photodiode in the optocoupler drives an LM311 set up to produce a TTL compatible output. It is useful where grounds are not able to be connected for any reason. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713