digital volume control
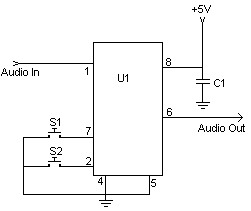
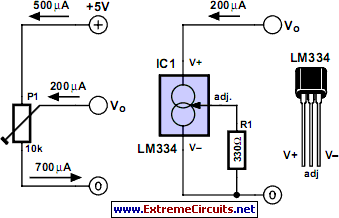
Utilizing a dual polarity power supply (+-5V is suitable) can resolve most clipping issues. It is necessary to consult the data sheet for the appropriate pins to connect the voltages.
A dual polarity power supply is essential in many electronic circuits, particularly in operational amplifier configurations and analog signal processing applications. The use of a +-5V power supply provides a balanced voltage range that allows for both positive and negative signal swings, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
In a typical schematic, the power supply connections will be made to specific pins on the integrated circuit (IC) as indicated in the manufacturer's data sheet. These connections are vital for the proper operation of the circuit. The positive voltage will connect to the V+ pin, while the negative voltage will connect to the V- pin. It is important to ensure that these connections are made correctly to avoid damaging the IC.
Additionally, the circuit may include bypass capacitors connected close to the power supply pins to filter out any high-frequency noise that could affect performance. These capacitors help stabilize the voltage levels and improve the overall reliability of the circuit.
When designing the layout, it is advisable to keep the power supply traces short and wide to minimize resistance and inductance, which can lead to voltage drops and unwanted noise. Ground planes should also be considered to provide a common reference point for all components, further enhancing the circuit's performance.
Overall, implementing a dual polarity power supply not only addresses clipping issues but also contributes to the overall robustness and fidelity of the electronic circuit. Proper attention to the details outlined in the data sheet and careful layout considerations will ensure optimal performance.Using a dual polariity power supply (+-5V works fine) will cure most clipping problems. You will have to check the data sheet for the correct pins to connect your voltages. 🔗 External reference
A dual polarity power supply is essential in many electronic circuits, particularly in operational amplifier configurations and analog signal processing applications. The use of a +-5V power supply provides a balanced voltage range that allows for both positive and negative signal swings, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
In a typical schematic, the power supply connections will be made to specific pins on the integrated circuit (IC) as indicated in the manufacturer's data sheet. These connections are vital for the proper operation of the circuit. The positive voltage will connect to the V+ pin, while the negative voltage will connect to the V- pin. It is important to ensure that these connections are made correctly to avoid damaging the IC.
Additionally, the circuit may include bypass capacitors connected close to the power supply pins to filter out any high-frequency noise that could affect performance. These capacitors help stabilize the voltage levels and improve the overall reliability of the circuit.
When designing the layout, it is advisable to keep the power supply traces short and wide to minimize resistance and inductance, which can lead to voltage drops and unwanted noise. Ground planes should also be considered to provide a common reference point for all components, further enhancing the circuit's performance.
Overall, implementing a dual polarity power supply not only addresses clipping issues but also contributes to the overall robustness and fidelity of the electronic circuit. Proper attention to the details outlined in the data sheet and careful layout considerations will ensure optimal performance.Using a dual polariity power supply (+-5V works fine) will cure most clipping problems. You will have to check the data sheet for the correct pins to connect your voltages. 🔗 External reference