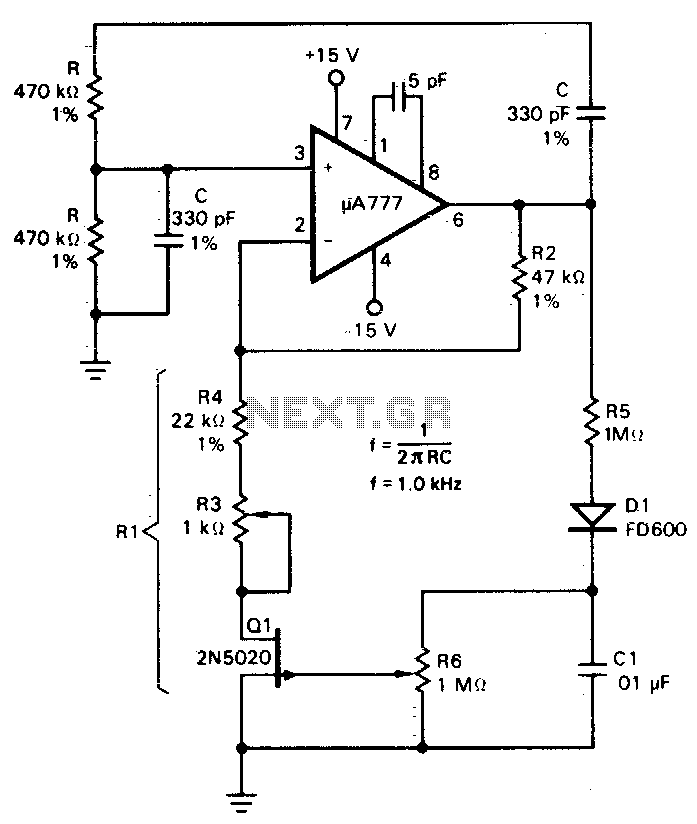
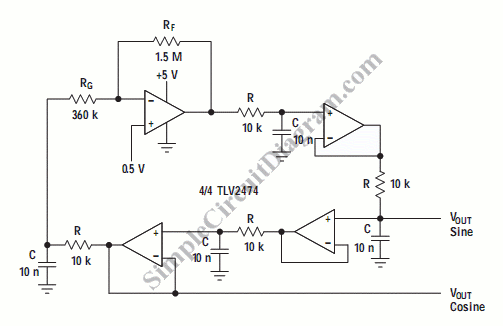
Digitally-controlled oscillator
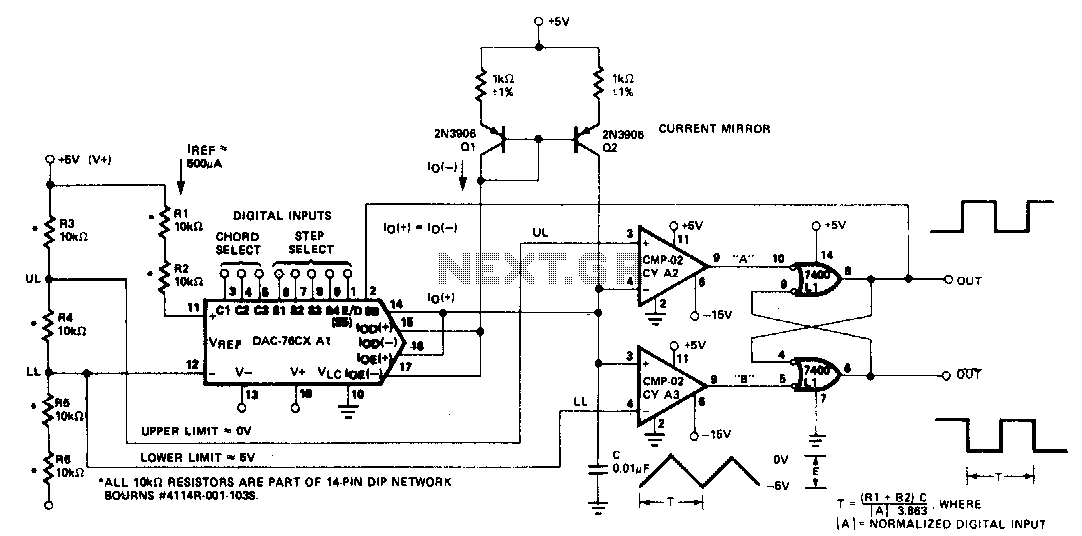
The microprocessor-controlled oscillator has a frequency range of 8159 to 1, covering from 2 Hz to 20 kHz. An exponential, current output integrated circuit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) functions as a programmable current source, alternately charging and discharging a capacitor between precisely controlled upper and lower limits. The circuit features instantaneous frequency change, operates with +5 ±1 V and -15 V ±3 V supplies, and has a dynamic range of a 13-bit DAC.
The microprocessor-controlled oscillator circuit is designed to produce a wide range of frequencies, from a minimum of 2 Hz to a maximum of 20 kHz, with a frequency ratio of 8159:1. This feature allows for precise control over the output frequency, making it suitable for various applications that require accurate timing and signal generation. The core of the circuit is an exponential current output DAC, which serves as a programmable current source. This DAC is responsible for generating the necessary charging and discharging currents that control the capacitor's voltage levels.
The capacitor in the circuit is charged and discharged between specific upper and lower voltage limits, which are defined by the application requirements. The ability to rapidly change the frequency is a significant advantage, allowing for instantaneous adjustments without the need for mechanical components. The circuit operates on dual power supplies, providing +5 V ±1 V for the digital components and -15 V ±3 V for the analog components, ensuring stability and reliability in various operating conditions.
The dynamic range of the circuit is determined by the 13-bit resolution of the DAC, allowing for a high level of precision in the output signal. This resolution enables fine adjustments to the current output, which is critical for applications that require detailed signal modulation or waveform generation. The overall design of the oscillator circuit emphasizes flexibility, precision, and rapid response, making it an ideal choice for modern electronic applications that demand high-performance signal generation capabilities.The microprocessor-controlled oscillator has a 8159 to 1 frequency range covering 2 Hz to 20 kHz. An exponential, current output IC DAC functioning as a programmable current source alternately charges and discharges a capacitor between precisely-controlled upper and lower limits The circuit features instantaneous frequency change, operates with +5 ±1 V and -15 V ±3 V supplies, and has the dynamic range of a 13-bit DAC. 🔗 External reference
The microprocessor-controlled oscillator circuit is designed to produce a wide range of frequencies, from a minimum of 2 Hz to a maximum of 20 kHz, with a frequency ratio of 8159:1. This feature allows for precise control over the output frequency, making it suitable for various applications that require accurate timing and signal generation. The core of the circuit is an exponential current output DAC, which serves as a programmable current source. This DAC is responsible for generating the necessary charging and discharging currents that control the capacitor's voltage levels.
The capacitor in the circuit is charged and discharged between specific upper and lower voltage limits, which are defined by the application requirements. The ability to rapidly change the frequency is a significant advantage, allowing for instantaneous adjustments without the need for mechanical components. The circuit operates on dual power supplies, providing +5 V ±1 V for the digital components and -15 V ±3 V for the analog components, ensuring stability and reliability in various operating conditions.
The dynamic range of the circuit is determined by the 13-bit resolution of the DAC, allowing for a high level of precision in the output signal. This resolution enables fine adjustments to the current output, which is critical for applications that require detailed signal modulation or waveform generation. The overall design of the oscillator circuit emphasizes flexibility, precision, and rapid response, making it an ideal choice for modern electronic applications that demand high-performance signal generation capabilities.The microprocessor-controlled oscillator has a 8159 to 1 frequency range covering 2 Hz to 20 kHz. An exponential, current output IC DAC functioning as a programmable current source alternately charges and discharges a capacitor between precisely-controlled upper and lower limits The circuit features instantaneous frequency change, operates with +5 ±1 V and -15 V ±3 V supplies, and has the dynamic range of a 13-bit DAC. 🔗 External reference