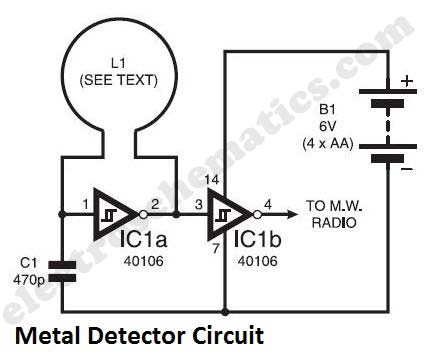
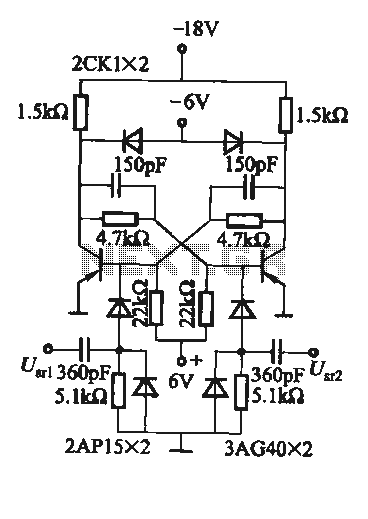
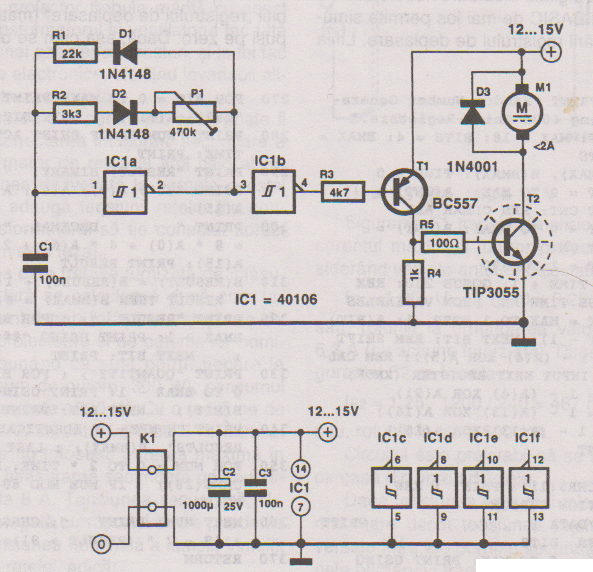
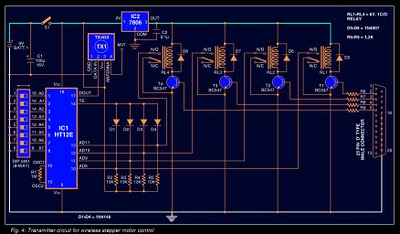
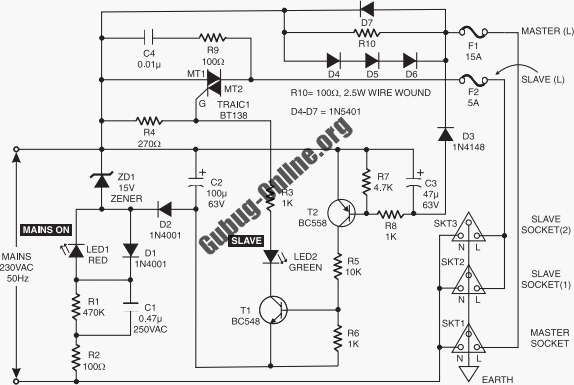
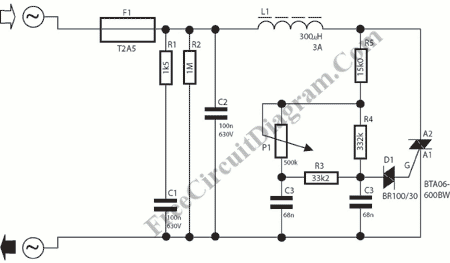
Discharge before memory circuit
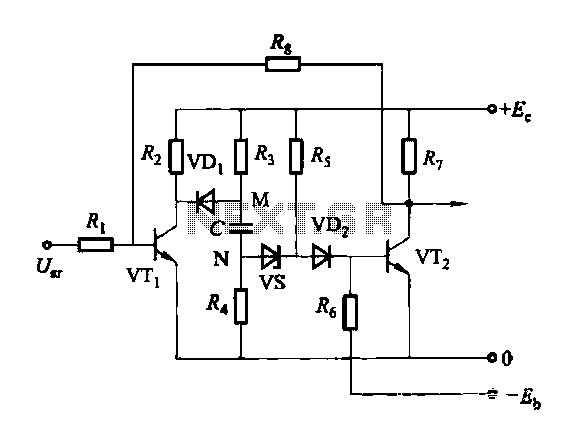
Discharge before memory circuit. Before the memory circuit is activated, a delay reset circuit is required. When the input signal triggers an action, timing begins, and after a specified delay, the circuit reverts to its original state. During this interval, regardless of whether the input signal remains active, the circuit continues to operate, maintaining the output signal.
The discharge before memory circuit serves a crucial role in digital electronics, particularly in applications where precise timing and state management are essential. This circuit typically incorporates a delay reset mechanism that ensures the memory element does not respond to input signals instantaneously.
The circuit design often includes a timing component, such as a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, which defines the delay period. Upon receiving an input signal, the timing mechanism initiates, allowing the circuit to maintain its output state for the duration of the delay. This ensures that transient input signals do not inadvertently alter the memory state, thus providing stability and reliability in signal processing.
In practical implementations, the delay reset circuit can be configured using various components, such as operational amplifiers, flip-flops, or dedicated timer ICs, depending on the complexity and requirements of the application. The output signal, which remains stable during the delay period, is typically connected to subsequent stages in a digital system, ensuring that downstream components receive a consistent and accurate representation of the desired state.
In summary, the discharge before memory circuit, with its delay reset functionality, is integral to achieving controlled operation in digital systems, effectively managing input signals and ensuring that memory circuits function as intended without unintended disruptions.Discharge before memory circuit Before the memory circuit is considered instantaneous action, the delay reset circuit. When the input signal to one that is action, and start ti ming, after after a delay, the circuit returns to the original state. During this period, regardless of whether the input signal is persistent, the circuit remains operation state, and the output signal.
The discharge before memory circuit serves a crucial role in digital electronics, particularly in applications where precise timing and state management are essential. This circuit typically incorporates a delay reset mechanism that ensures the memory element does not respond to input signals instantaneously.
The circuit design often includes a timing component, such as a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, which defines the delay period. Upon receiving an input signal, the timing mechanism initiates, allowing the circuit to maintain its output state for the duration of the delay. This ensures that transient input signals do not inadvertently alter the memory state, thus providing stability and reliability in signal processing.
In practical implementations, the delay reset circuit can be configured using various components, such as operational amplifiers, flip-flops, or dedicated timer ICs, depending on the complexity and requirements of the application. The output signal, which remains stable during the delay period, is typically connected to subsequent stages in a digital system, ensuring that downstream components receive a consistent and accurate representation of the desired state.
In summary, the discharge before memory circuit, with its delay reset functionality, is integral to achieving controlled operation in digital systems, effectively managing input signals and ensuring that memory circuits function as intended without unintended disruptions.Discharge before memory circuit Before the memory circuit is considered instantaneous action, the delay reset circuit. When the input signal to one that is action, and start ti ming, after after a delay, the circuit returns to the original state. During this period, regardless of whether the input signal is persistent, the circuit remains operation state, and the output signal.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713