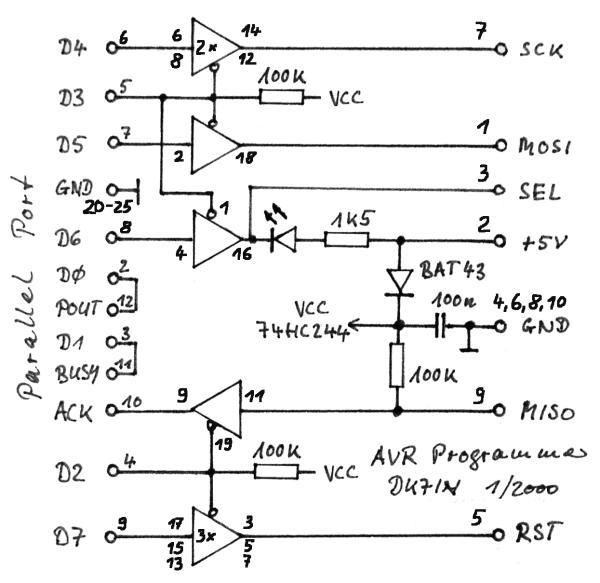
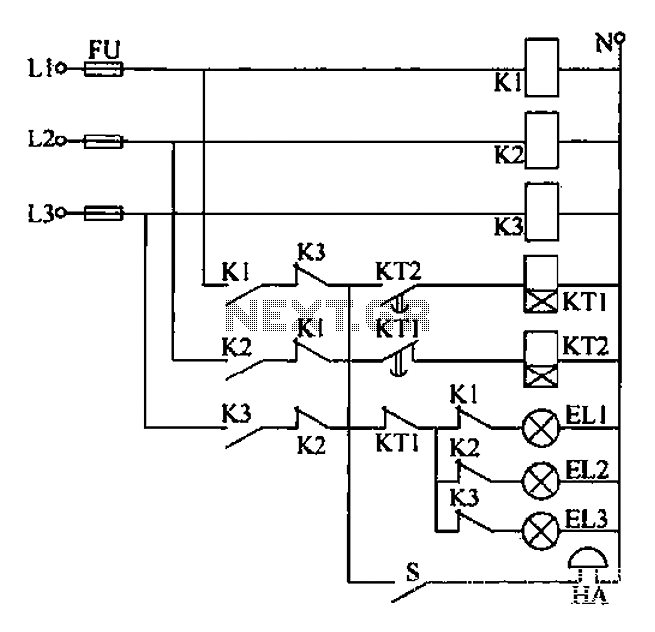
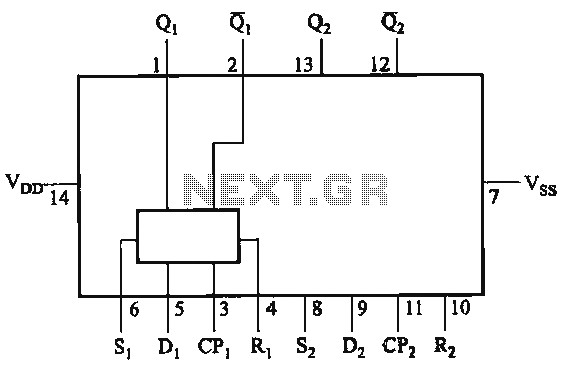
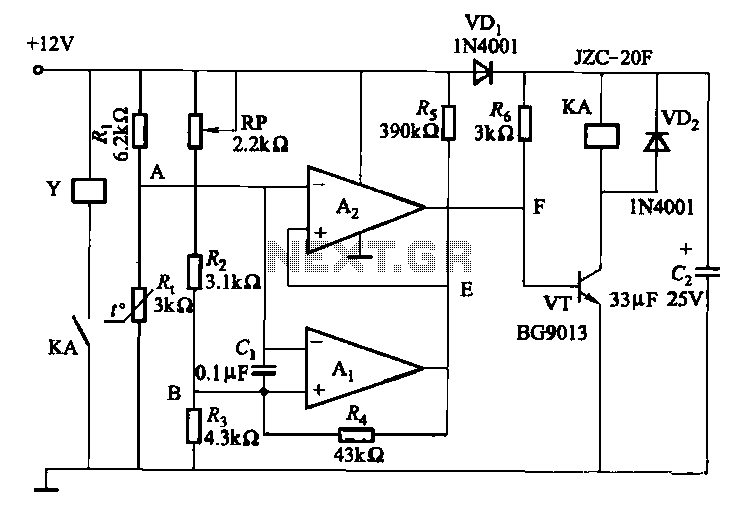
PWM Controller Circuit
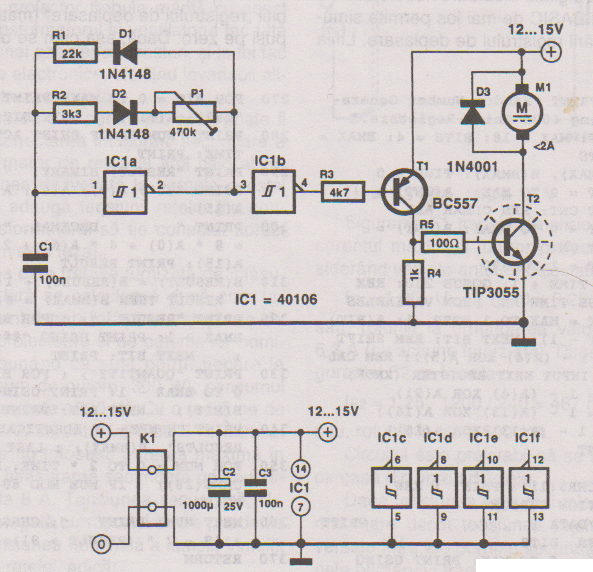
This PWM controller circuit is suitable for managing small motors with a maximum current consumption of 2A. For higher currents, additional cooling is required.
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller circuit is designed to efficiently control the speed of small DC motors by varying the power supplied to the motor. The circuit operates by switching the power on and off at a high frequency, effectively controlling the average voltage and current delivered to the motor. This is achieved through the use of a MOSFET or transistor that acts as a switch, allowing for precise modulation of the motor's performance.
In this configuration, the PWM signal is generated by a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM IC, which determines the duty cycle of the signal. The duty cycle is the ratio of the on-time to the total period of the PWM signal, and it directly influences the speed of the motor; a higher duty cycle results in a faster motor speed, while a lower duty cycle slows the motor down.
For applications requiring current levels above 2A, it is essential to incorporate additional cooling measures, such as heat sinks or active cooling systems, to prevent overheating of the components, particularly the switching device. The circuit may also include protective features such as diodes to prevent back EMF from damaging the control circuitry when the motor is turned off.
Overall, this PWM controller circuit provides an efficient and effective means of controlling small motors, making it suitable for a variety of applications in robotics, automation, and other electronic projects.This PWM Controller circuit is ideal for controlling small motors with 2A maximum current consumption. For higher currents you need additional cooling for.. 🔗 External reference
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller circuit is designed to efficiently control the speed of small DC motors by varying the power supplied to the motor. The circuit operates by switching the power on and off at a high frequency, effectively controlling the average voltage and current delivered to the motor. This is achieved through the use of a MOSFET or transistor that acts as a switch, allowing for precise modulation of the motor's performance.
In this configuration, the PWM signal is generated by a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM IC, which determines the duty cycle of the signal. The duty cycle is the ratio of the on-time to the total period of the PWM signal, and it directly influences the speed of the motor; a higher duty cycle results in a faster motor speed, while a lower duty cycle slows the motor down.
For applications requiring current levels above 2A, it is essential to incorporate additional cooling measures, such as heat sinks or active cooling systems, to prevent overheating of the components, particularly the switching device. The circuit may also include protective features such as diodes to prevent back EMF from damaging the control circuitry when the motor is turned off.
Overall, this PWM controller circuit provides an efficient and effective means of controlling small motors, making it suitable for a variety of applications in robotics, automation, and other electronic projects.This PWM Controller circuit is ideal for controlling small motors with 2A maximum current consumption. For higher currents you need additional cooling for.. 🔗 External reference