
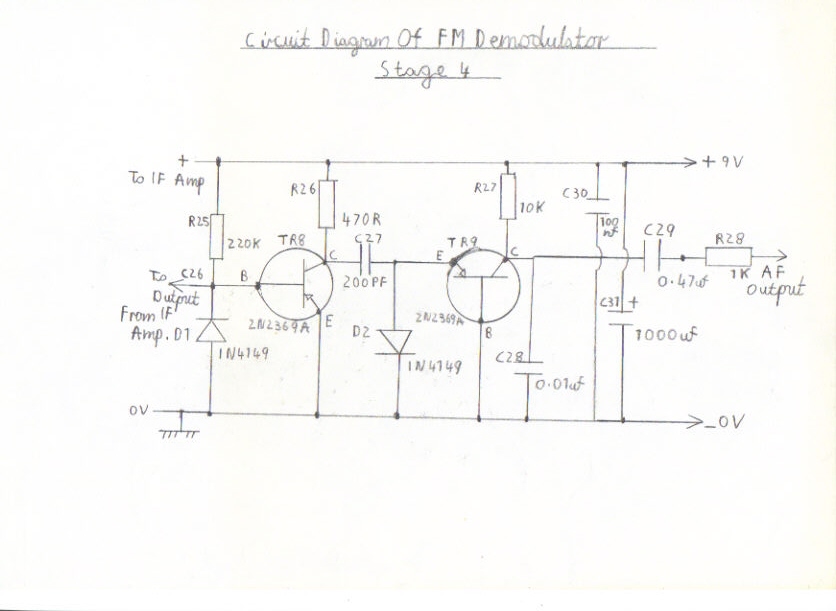
double conversion pulse counting fm tuner
No description available.
Related Circuits
The boards are powered by two 9-volt alkaline batteries. The circuits are a compilation of those found in the Radio Shack Engineering Handbook for constructing pulse-modulated LED transmitters and receivers. The laser diode "D1" is replaced with an affordable...
This circuit functions as a missing pulse detector, utilized in the General Purpose Controller Board with Basic Stamp 1. It monitors an input pulse train, and when a pulse is missed, the output of the 555 timer switches to...
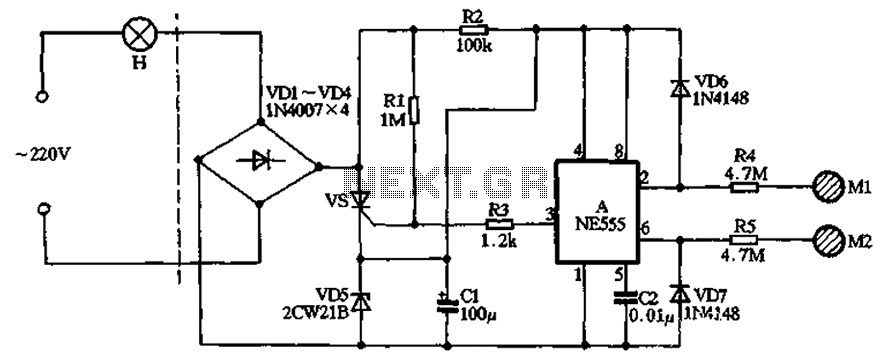
The circuit illustrated in the figure features a dashed line on the left, representing a standard lighting circuit, while the right side is responsible for the dual functionality of touch activation using the NE555 timer. Components VD1 through VD4...
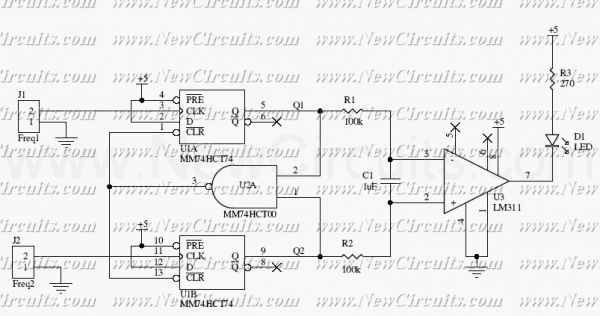
This circuit uses a 74HCT74, 74HCT00, and a LM311 to form a frequency comparator. The two pulse trains are fed to two D-type flip-flops (triggered by the leading edges). The flip-flops' outputs are compared in a NAND gate. If...
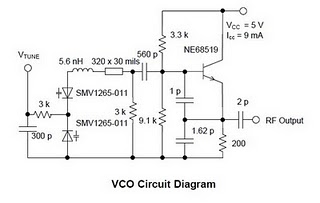
The high performance of modern set-top DBS TV tuners necessitates the development of broadband voltage control oscillator (VCO) designs that are cost-effective. Design engineers face the challenge of creating high-performance, low-cost VCOs. The traditional Colpitts oscillator design is commonly...
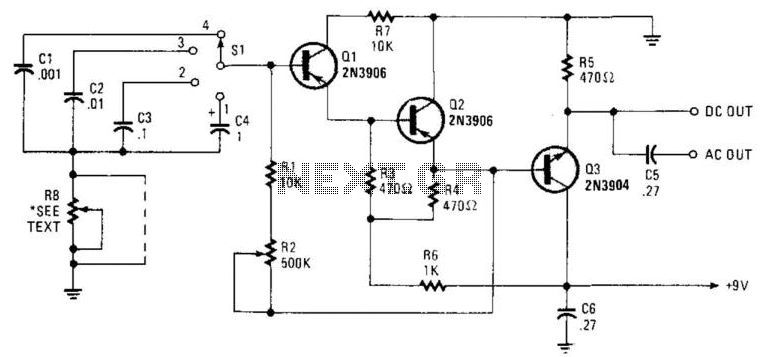
Seven narrow pulses ranging from 2 Hz to 50 kHz are generated by this circuit. Capacitors C1 through C4 provide frequency ranges in decode steps. Resistors R1 and R2 regulate the charging time of capacitors C1 through C4. R2...
We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze traffic, and serve personalized ads. By clicking "Accept", you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more