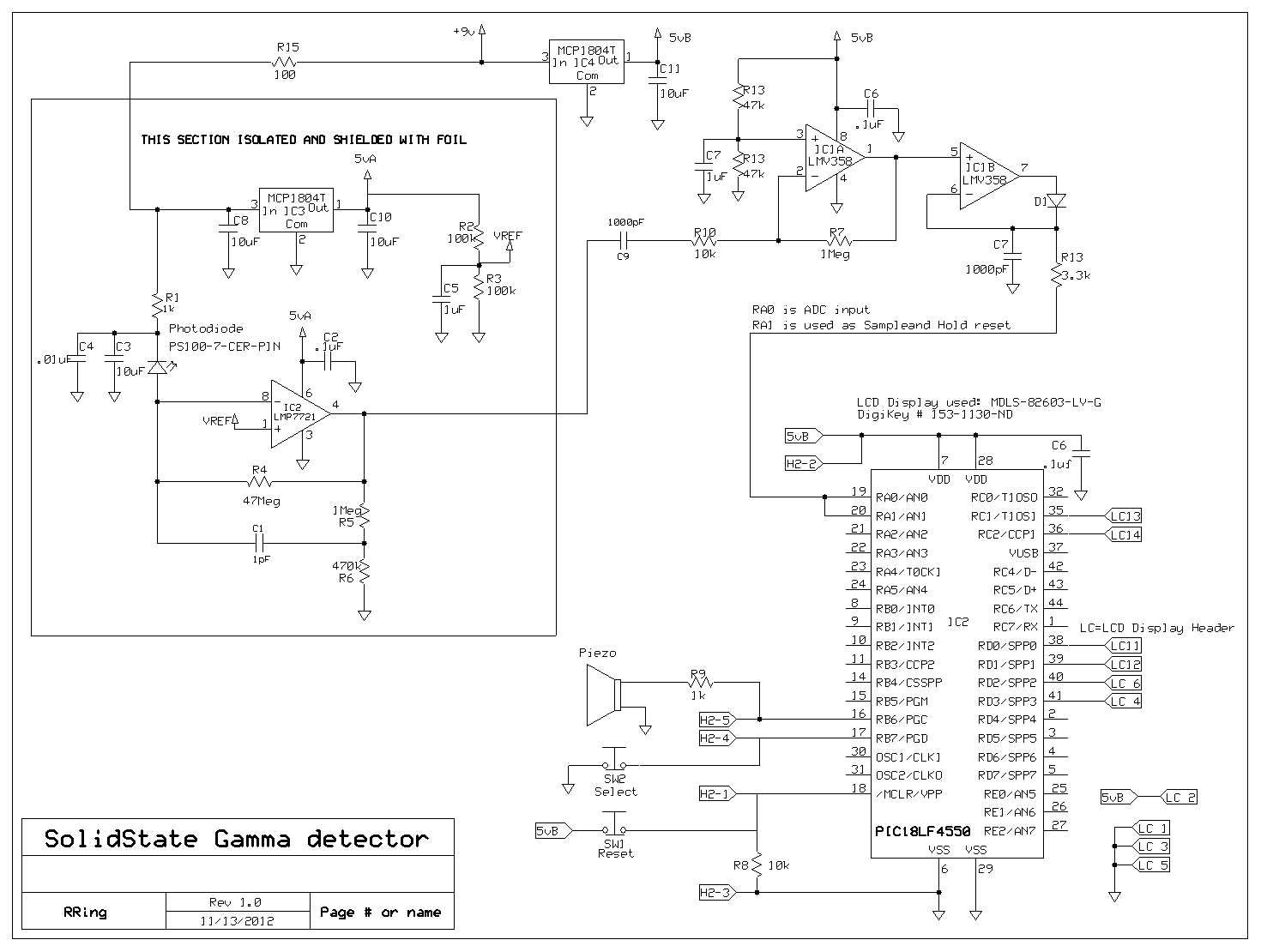
Double-ended limit detector
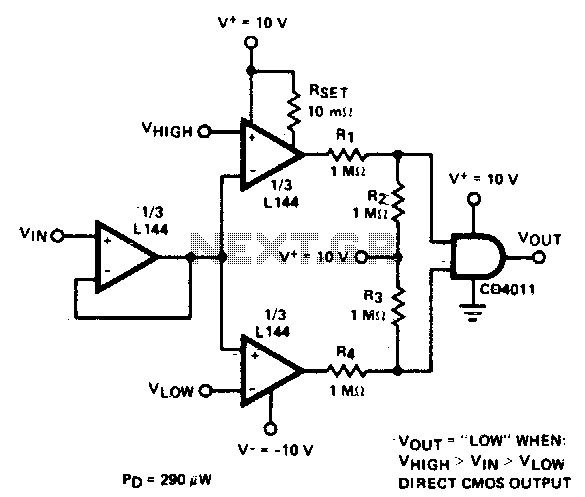
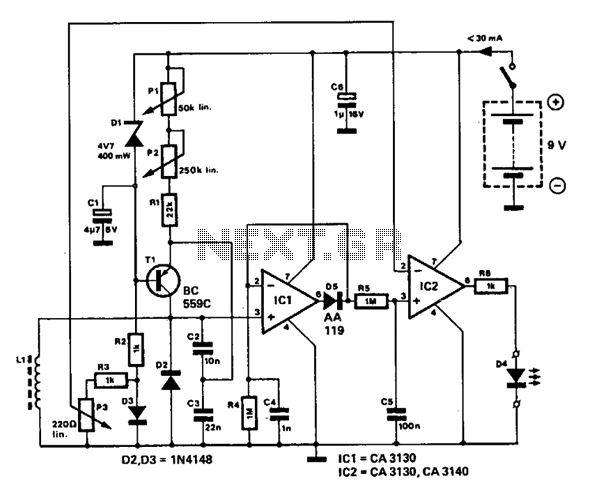
The detector employs three sections of an L144 and a CMOS NAND gate to create a low-power voltage monitor. The 1 MΩ resistors R1, R2, R3, and R4 convert the bipolar ±10 V swing of the operational amplifiers to a 0 to 10 V swing that is suitable for the ground-referenced CMOS logic. The total power dissipation is 290 µW while within limits and 330 µW when out of limits.
The circuit utilizes the L144 operational amplifier in conjunction with a CMOS NAND gate to effectively monitor voltage levels with minimal power consumption. The three sections of the L144 serve to amplify and process the input voltage, which fluctuates between ±10 V. This bipolar signal is transformed into a unipolar output ranging from 0 to 10 V through the use of four 1 MΩ resistors (R1, R2, R3, and R4).
These resistors are configured to create a voltage divider network that ensures the output remains within the acceptable range for the CMOS logic, which is referenced to ground. This design choice is crucial for maintaining compatibility with the digital logic levels required for subsequent processing stages.
The power dissipation characteristics of the circuit are noteworthy, with a total of 290 µW when the monitored voltage is within specified limits, indicating efficient operation under normal conditions. However, when the voltage exceeds the defined limits, the power dissipation increases to 330 µW, which may indicate a need for further analysis or additional protective measures in high-voltage scenarios.
Overall, this low-power voltage monitor circuit is suitable for applications where energy efficiency is paramount, and its design ensures reliable performance in monitoring voltage levels across a range of operational conditions.Detector uses three sections of an L144 and a CMOS NAND gate to make a very low power voltage monitor. The 1 MO resistors Rl, R2, R3, and R4 translate the bipolar ±10 V swing of the op amps to a 0 to 10 V swing acceptable to the ground-referenced CMOS logic
The total power dissipation is 290 µW while in limit and 330 /xW while out of limit.
The circuit utilizes the L144 operational amplifier in conjunction with a CMOS NAND gate to effectively monitor voltage levels with minimal power consumption. The three sections of the L144 serve to amplify and process the input voltage, which fluctuates between ±10 V. This bipolar signal is transformed into a unipolar output ranging from 0 to 10 V through the use of four 1 MΩ resistors (R1, R2, R3, and R4).
These resistors are configured to create a voltage divider network that ensures the output remains within the acceptable range for the CMOS logic, which is referenced to ground. This design choice is crucial for maintaining compatibility with the digital logic levels required for subsequent processing stages.
The power dissipation characteristics of the circuit are noteworthy, with a total of 290 µW when the monitored voltage is within specified limits, indicating efficient operation under normal conditions. However, when the voltage exceeds the defined limits, the power dissipation increases to 330 µW, which may indicate a need for further analysis or additional protective measures in high-voltage scenarios.
Overall, this low-power voltage monitor circuit is suitable for applications where energy efficiency is paramount, and its design ensures reliable performance in monitoring voltage levels across a range of operational conditions.Detector uses three sections of an L144 and a CMOS NAND gate to make a very low power voltage monitor. The 1 MO resistors Rl, R2, R3, and R4 translate the bipolar ±10 V swing of the op amps to a 0 to 10 V swing acceptable to the ground-referenced CMOS logic
The total power dissipation is 290 µW while in limit and 330 /xW while out of limit.