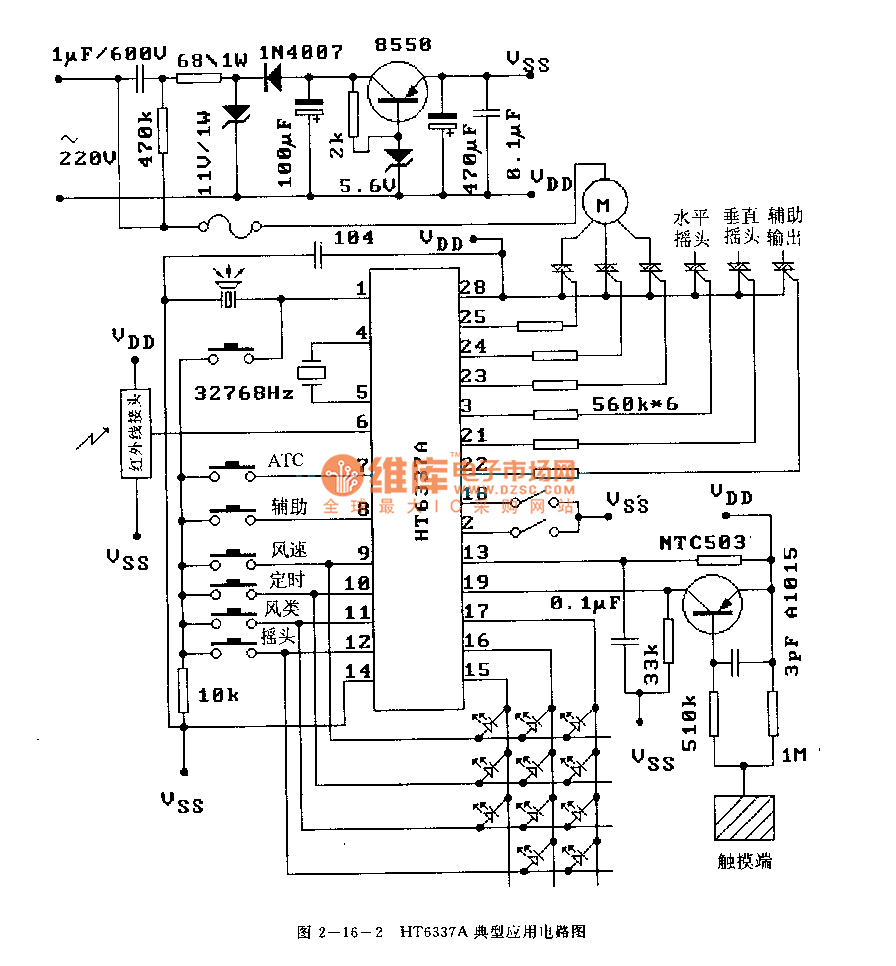
DTL internal structure of the inverter circuit
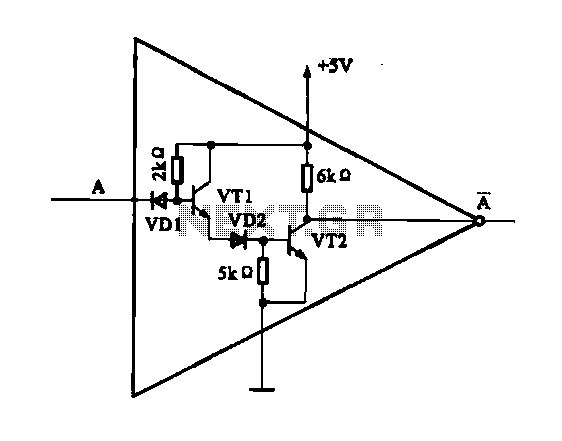
The internal structure of the DTL inverter circuit (M5936P) is composed of inputs with diodes and transistors for signal processing, powered by a +5V supply. When the input terminal A is at a high level (digital 1), diode VDI is off, transistor VT1 is turned on, and transistor VT2 conducts, resulting in a low output (digital 0). Conversely, when the input is low (digital 0), diode VD1 conducts, transistor VT1 is off, and transistor VT2 is also off, leading to a high output (digital 1).
The M5936P DTL (Diode-Transistor Logic) inverter circuit utilizes a combination of diodes and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) to perform its logical operations. The circuit is powered by a +5V supply, which is standard for digital logic circuits, ensuring compatibility with other digital components.
In the high input state, where terminal A receives a logic high (digital 1), diode VDI becomes reverse-biased, preventing current flow through it. Concurrently, this condition allows transistor VT1 to turn on, which then drives the base of transistor VT2. As a result, transistor VT2 enters saturation, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus producing a low output state (digital 0) at the output terminal.
In contrast, when the input state is low (digital 0), diode VD1 becomes forward-biased, allowing current to flow through it. This action turns off transistor VT1, which in turn keeps transistor VT2 in the off state as well. Consequently, the output terminal reflects a high state (digital 1), indicating that no current flows through the output.
This inverter circuit exemplifies the fundamental operation of DTL logic, where the combination of diodes and transistors effectively implements logical inversion. The design is efficient for small signal processing applications and can be integrated into larger DTL logic families for more complex digital systems. The simplicity of the inverter circuit allows for easy expansion and incorporation into various digital applications while maintaining reliability and performance.DTL internal structure shown in the inverter circuit (M5936P) is. Inputs with diodes, transistors signal processing, power supply is + 5V. When the input terminal A high level (digital I ) when the diode VDI off, VTI transistor is turned on, the transistor VT2 conduction output is low (digital O ). When the input is low (the number 0 ), the diode VD1 conduction, transistor VT1 off, transistor VT2 off, output high (the number 1 ).
The M5936P DTL (Diode-Transistor Logic) inverter circuit utilizes a combination of diodes and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) to perform its logical operations. The circuit is powered by a +5V supply, which is standard for digital logic circuits, ensuring compatibility with other digital components.
In the high input state, where terminal A receives a logic high (digital 1), diode VDI becomes reverse-biased, preventing current flow through it. Concurrently, this condition allows transistor VT1 to turn on, which then drives the base of transistor VT2. As a result, transistor VT2 enters saturation, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus producing a low output state (digital 0) at the output terminal.
In contrast, when the input state is low (digital 0), diode VD1 becomes forward-biased, allowing current to flow through it. This action turns off transistor VT1, which in turn keeps transistor VT2 in the off state as well. Consequently, the output terminal reflects a high state (digital 1), indicating that no current flows through the output.
This inverter circuit exemplifies the fundamental operation of DTL logic, where the combination of diodes and transistors effectively implements logical inversion. The design is efficient for small signal processing applications and can be integrated into larger DTL logic families for more complex digital systems. The simplicity of the inverter circuit allows for easy expansion and incorporation into various digital applications while maintaining reliability and performance.DTL internal structure shown in the inverter circuit (M5936P) is. Inputs with diodes, transistors signal processing, power supply is + 5V. When the input terminal A high level (digital I ) when the diode VDI off, VTI transistor is turned on, the transistor VT2 conduction output is low (digital O ). When the input is low (the number 0 ), the diode VD1 conduction, transistor VT1 off, transistor VT2 off, output high (the number 1 ).