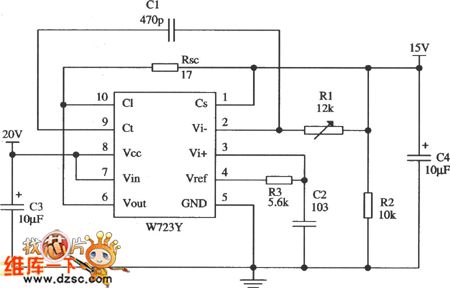
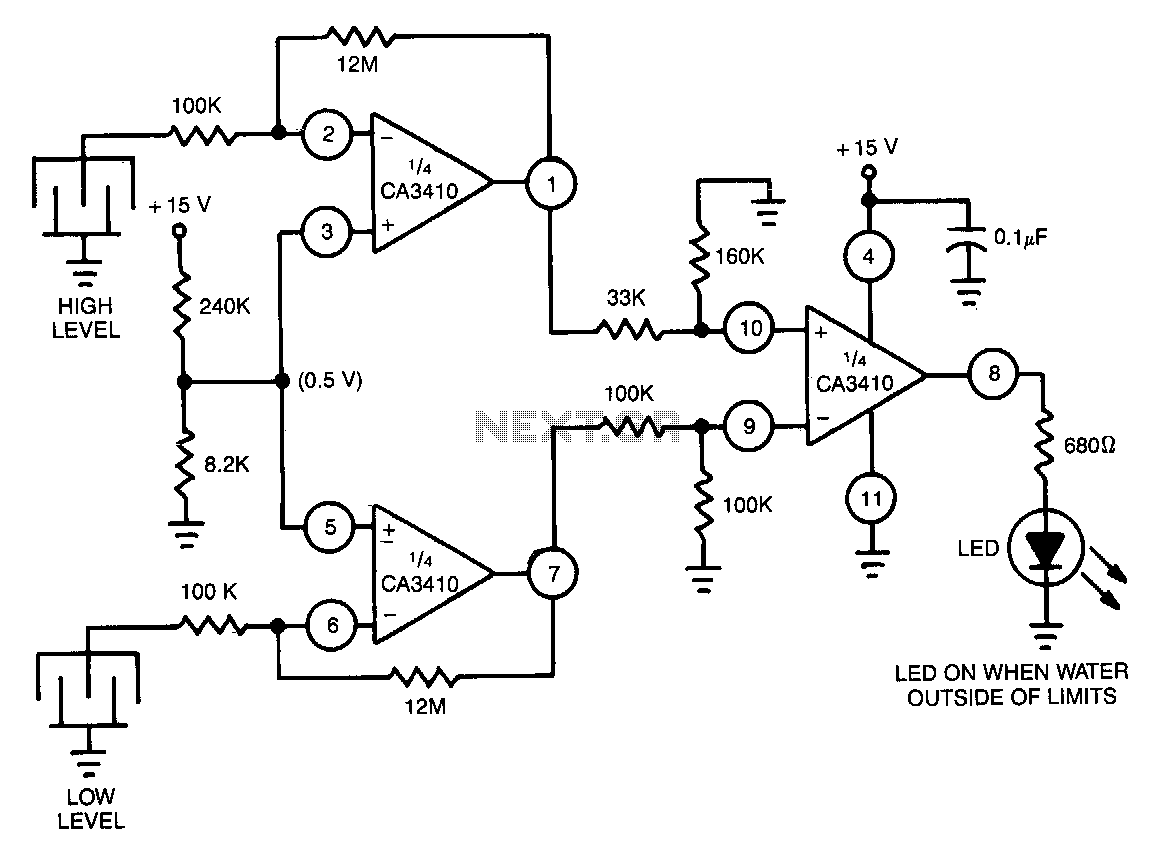
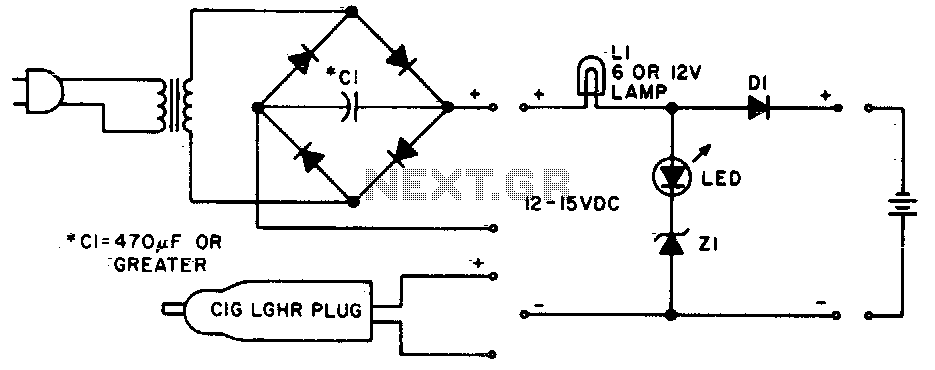
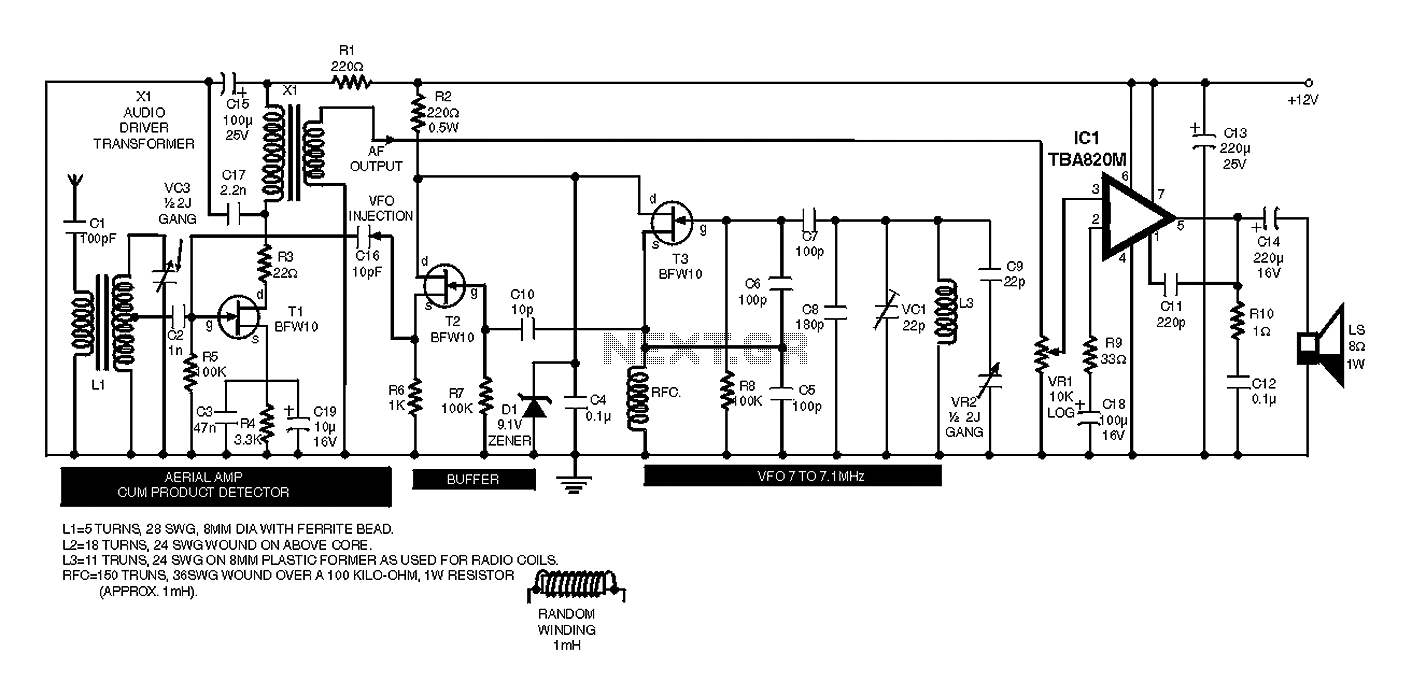
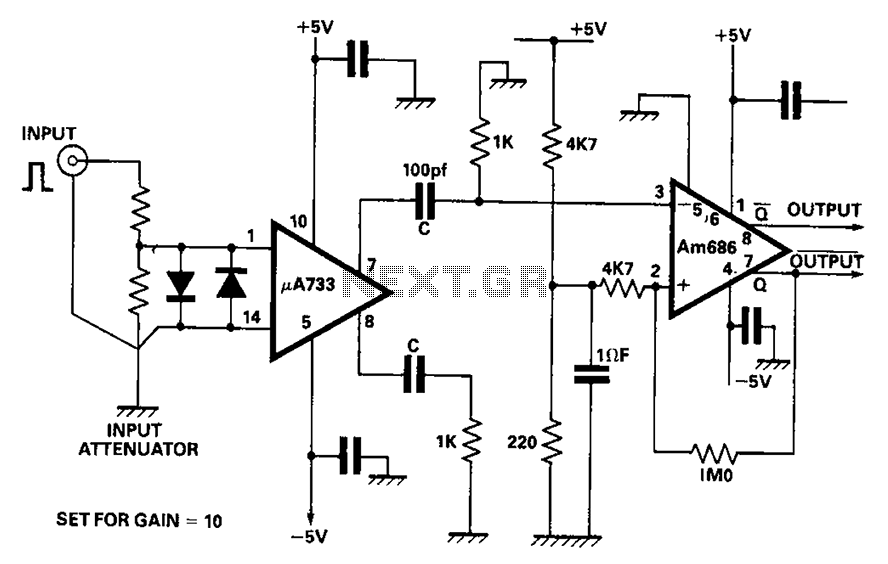
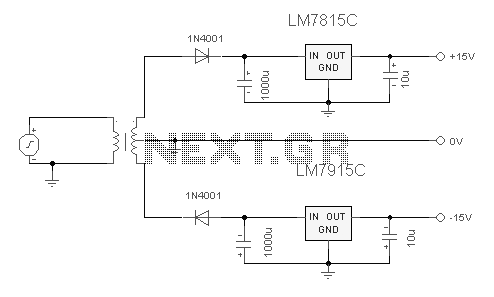
Dual limit comparator
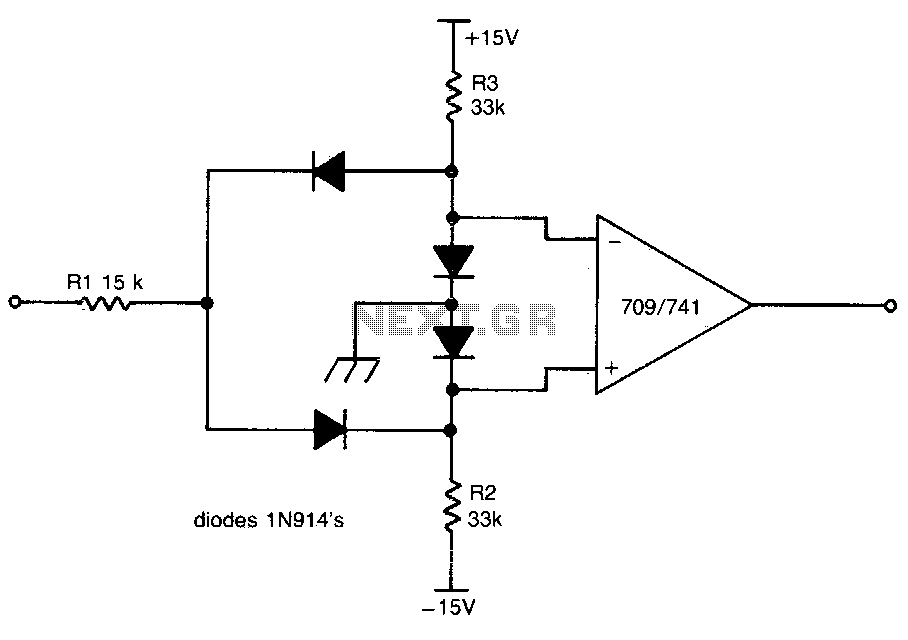
This circuit provides a positive output when the input voltage exceeds 8 volts. Within these limits, the output remains negative. The threshold for the positive output is set by the ratio of resistors R1 and R2, while the threshold for the negative output is determined by the ratio of R1 and R3. The forward voltage drop across the diodes must be taken into account. The output can be inverted by swapping the inputs to the operational amplifier. The 709 operational amplifier is utilized without frequency compensation.
The described circuit functions as a voltage comparator with hysteresis, featuring an operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration. When the input voltage surpasses the defined threshold of 8 volts, the op-amp outputs a positive voltage. This behavior is crucial for applications requiring a clear distinction between high and low voltage levels.
The resistors R1, R2, and R3 play a vital role in setting the reference voltages for the op-amp. Specifically, R1 is connected to the inverting input, while R2 and R3 are configured to establish the non-inverting input reference. The ratio of R1 to R2 determines the upper threshold for the positive output, while the ratio of R1 to R3 sets the lower threshold for the negative output. It is essential to ensure that these resistors are selected appropriately to achieve the desired voltage levels.
The forward voltage drop across the diodes in the circuit must be accounted for, as it can affect the accuracy of the output voltage. Diodes typically exhibit a forward voltage drop of approximately 0.7 volts for silicon diodes, which should be included in the calculations when determining the exact threshold voltages.
Inverting the output can be easily accomplished by reversing the inputs to the op-amp. This feature adds versatility to the circuit, allowing it to be used in various applications where an inverted output signal is required.
The use of the 709 operational amplifier without frequency compensation indicates that the circuit is designed for low-frequency applications, where phase margin and stability are less of a concern. However, it is important to consider the bandwidth and slew rate limitations of the 709 to ensure that the circuit performs adequately for the intended application. Overall, this circuit design is efficient for voltage detection and can be adapted for various electronic systems requiring precise voltage thresholds.This circuit gives a positive output when the input voltage exceeds 8 volts. Between these limits the output is negative. The positive limit point is determined by the ratio of Rl, R2, and the negative point by Rl, R3. The forward voltage drop across the diodes must be allowed for. The output may be inverted by reversing the inputs to the op amp The 709 is used without frequency compensation.
The described circuit functions as a voltage comparator with hysteresis, featuring an operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration. When the input voltage surpasses the defined threshold of 8 volts, the op-amp outputs a positive voltage. This behavior is crucial for applications requiring a clear distinction between high and low voltage levels.
The resistors R1, R2, and R3 play a vital role in setting the reference voltages for the op-amp. Specifically, R1 is connected to the inverting input, while R2 and R3 are configured to establish the non-inverting input reference. The ratio of R1 to R2 determines the upper threshold for the positive output, while the ratio of R1 to R3 sets the lower threshold for the negative output. It is essential to ensure that these resistors are selected appropriately to achieve the desired voltage levels.
The forward voltage drop across the diodes in the circuit must be accounted for, as it can affect the accuracy of the output voltage. Diodes typically exhibit a forward voltage drop of approximately 0.7 volts for silicon diodes, which should be included in the calculations when determining the exact threshold voltages.
Inverting the output can be easily accomplished by reversing the inputs to the op-amp. This feature adds versatility to the circuit, allowing it to be used in various applications where an inverted output signal is required.
The use of the 709 operational amplifier without frequency compensation indicates that the circuit is designed for low-frequency applications, where phase margin and stability are less of a concern. However, it is important to consider the bandwidth and slew rate limitations of the 709 to ensure that the circuit performs adequately for the intended application. Overall, this circuit design is efficient for voltage detection and can be adapted for various electronic systems requiring precise voltage thresholds.This circuit gives a positive output when the input voltage exceeds 8 volts. Between these limits the output is negative. The positive limit point is determined by the ratio of Rl, R2, and the negative point by Rl, R3. The forward voltage drop across the diodes must be allowed for. The output may be inverted by reversing the inputs to the op amp The 709 is used without frequency compensation.