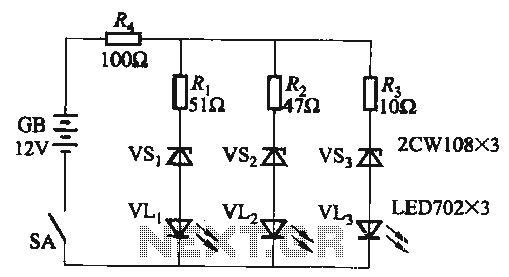
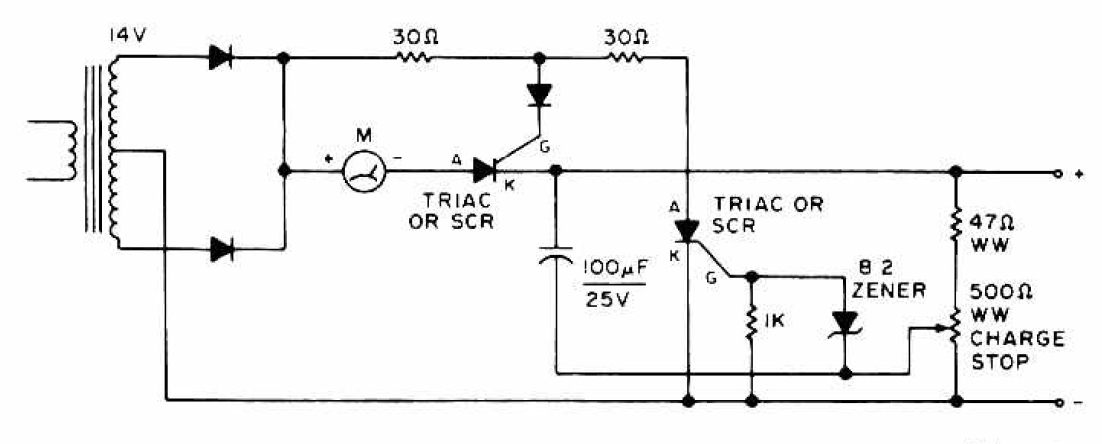
Ni-cad charger with current and voltage limiting
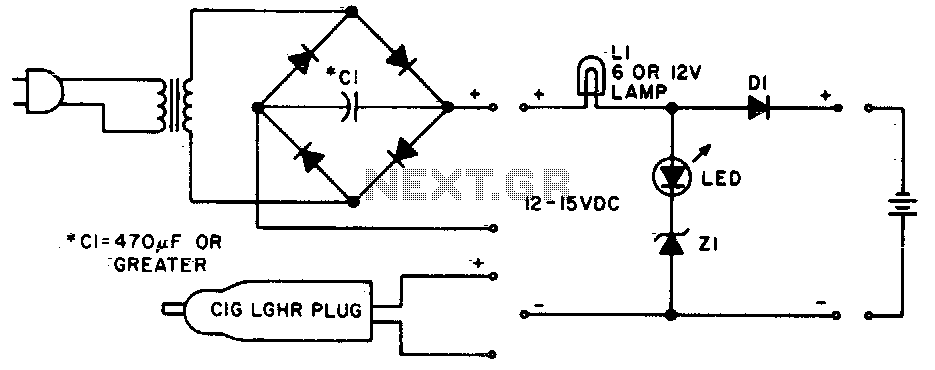
Lamp LI will glow brightly while the LED remains off when the battery is low and charging. Conversely, the LED will illuminate brightly, and the light bulb will be dim when the battery is nearly charged. Lamp LI should be rated for the desired current, typically the battery capacity divided by 10. Diode D1 must be rated for at least 1 A, and Zener diode Z1 should be a 1W component with a voltage rating determined by the full-charge battery voltage minus 1 V. Once the battery is fully charged, the circuit will maintain a float charge at approximately battery capacity divided by 100 mA.
The described circuit operates as a battery charging indicator and protection mechanism. The main components include a light bulb (LI), an LED, a diode (D1), and a Zener diode (Z1). The light bulb serves as a visual indication of the charging state of the battery. When the battery voltage is low, the circuit allows for a higher current draw, illuminating the light bulb brightly to signal that charging is in progress. The LED remains off during this state to prevent confusion about the charging status.
As the battery approaches full charge, the circuit transitions to a lower current state. In this condition, the LED lights up brightly, indicating that the battery is nearly charged, while the light bulb dims due to reduced current flow. This dual indication helps users easily monitor the charging process and the battery's health.
The diode (D1) is critical for ensuring that the current does not exceed 1 A, protecting the circuit from potential damage due to excessive current. The Zener diode (Z1) plays a vital role in voltage regulation; it is selected based on the full-charge voltage of the battery, minus a 1 V margin to allow for safe operation without overcharging.
Once fully charged, the circuit enters a float charge mode, where it maintains a small current, approximately equal to the battery capacity divided by 100 mA. This float charging is essential for maintaining the battery's charge without overcharging, thereby extending its life and ensuring reliable performance. The design of this circuit provides a straightforward and effective solution for battery management, combining visual indicators with protective components to enhance usability and safety.Lamp LI will glow brightly and the LED will be out when the battery is low and being charged, but the LED will be bright and the light bulb dim when the battery is almost ready. Ll should be a light bulb rated for the current you want (usually the battery capacity divided by 10).
Diode D1 should be at least 1 A, and Z1 is a 1W zener diode with a voltage determined by the full-charge battery voltage minus 1 V After the battery is fully charged, the circuit will float it at about battery capacity divided by 100 mA. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a battery charging indicator and protection mechanism. The main components include a light bulb (LI), an LED, a diode (D1), and a Zener diode (Z1). The light bulb serves as a visual indication of the charging state of the battery. When the battery voltage is low, the circuit allows for a higher current draw, illuminating the light bulb brightly to signal that charging is in progress. The LED remains off during this state to prevent confusion about the charging status.
As the battery approaches full charge, the circuit transitions to a lower current state. In this condition, the LED lights up brightly, indicating that the battery is nearly charged, while the light bulb dims due to reduced current flow. This dual indication helps users easily monitor the charging process and the battery's health.
The diode (D1) is critical for ensuring that the current does not exceed 1 A, protecting the circuit from potential damage due to excessive current. The Zener diode (Z1) plays a vital role in voltage regulation; it is selected based on the full-charge voltage of the battery, minus a 1 V margin to allow for safe operation without overcharging.
Once fully charged, the circuit enters a float charge mode, where it maintains a small current, approximately equal to the battery capacity divided by 100 mA. This float charging is essential for maintaining the battery's charge without overcharging, thereby extending its life and ensuring reliable performance. The design of this circuit provides a straightforward and effective solution for battery management, combining visual indicators with protective components to enhance usability and safety.Lamp LI will glow brightly and the LED will be out when the battery is low and being charged, but the LED will be bright and the light bulb dim when the battery is almost ready. Ll should be a light bulb rated for the current you want (usually the battery capacity divided by 10).
Diode D1 should be at least 1 A, and Z1 is a 1W zener diode with a voltage determined by the full-charge battery voltage minus 1 V After the battery is fully charged, the circuit will float it at about battery capacity divided by 100 mA. 🔗 External reference