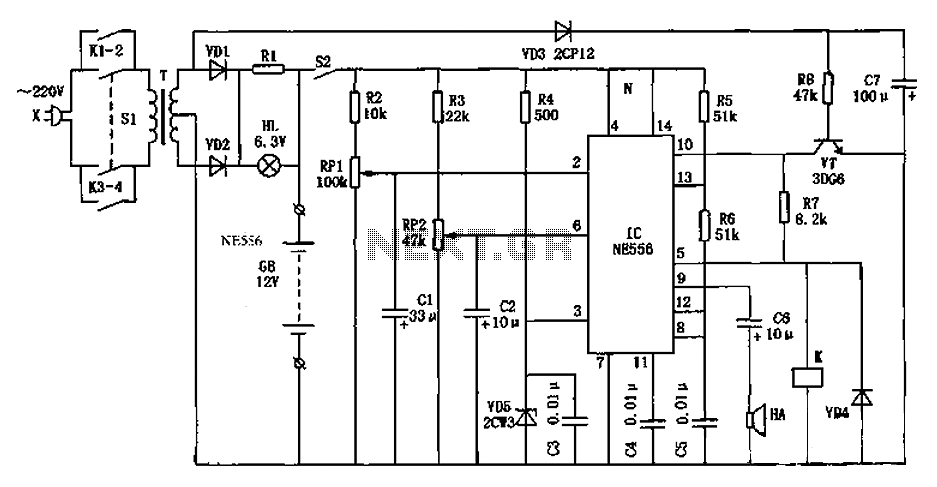
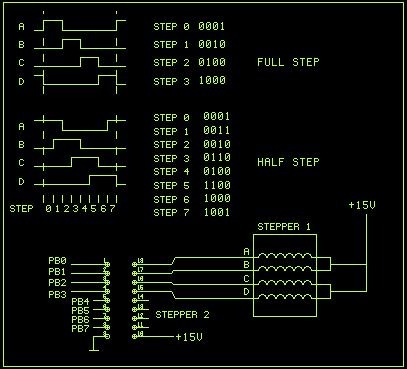
Dual motor drive circuit
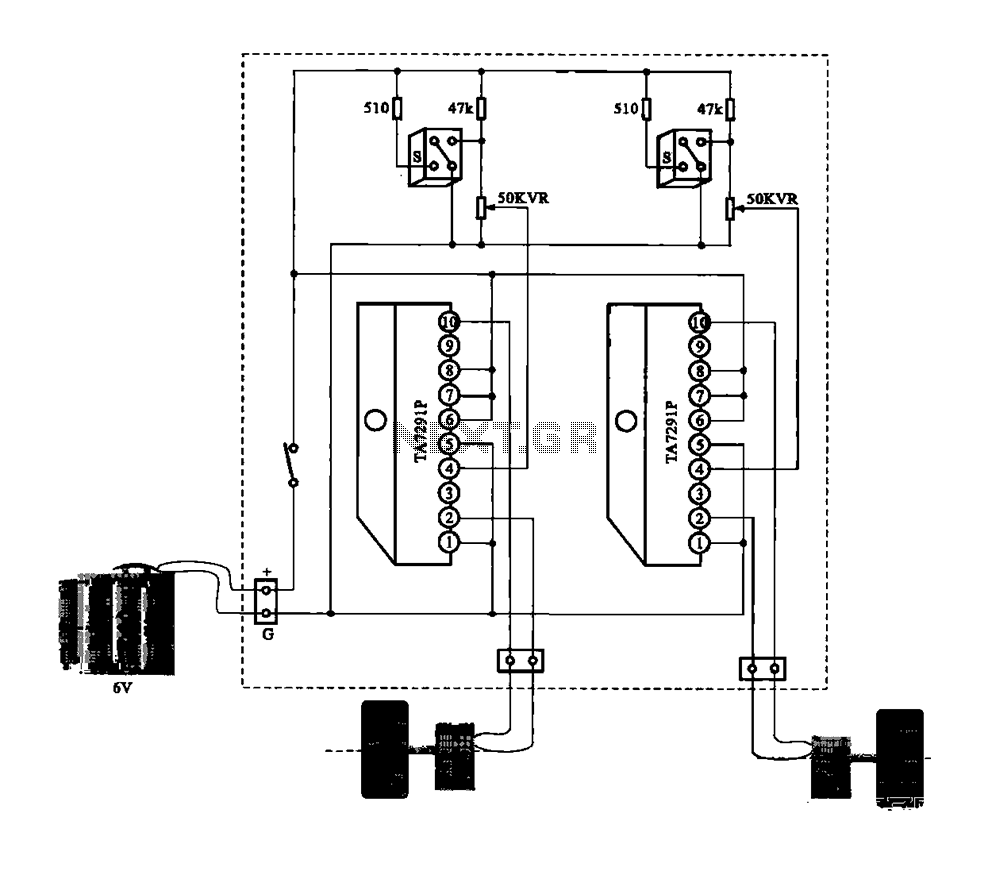
A dual motor drive circuit for automatic tracking consists of two motors that are part of a car structure, which operates based on the principles of a double motor drive system.
The dual motor drive circuit is designed to facilitate automatic tracking functionality in robotic or automated vehicles, such as cars that follow a designated path. The circuit typically includes two DC motors, each responsible for driving one side of the vehicle. By varying the speed and direction of these motors, the vehicle can navigate along a predefined route, which is often marked by a white line or similar guiding feature.
In this configuration, the motors are controlled using a microcontroller that processes input signals from sensors, such as infrared or optical sensors, positioned at the front of the vehicle. These sensors detect the presence of the white line and provide feedback to the microcontroller, which adjusts the motor speeds accordingly to maintain alignment with the line.
The circuit may also incorporate additional components such as motor drivers, which serve to amplify the control signals from the microcontroller to a level sufficient to drive the motors. Power supply considerations are crucial, as the motors require adequate voltage and current to operate effectively. Therefore, a suitable power source, such as batteries or a power adapter, must be integrated into the design.
Furthermore, safety features, such as overcurrent protection and thermal shutdown mechanisms, can be included to prevent damage to the motors and circuit components during operation. The overall design emphasizes efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness, allowing for smooth and precise movement of the vehicle along its tracking path. This dual motor drive circuit serves as a foundational element in various applications, including robotics, automation, and educational projects.Dual motor drive circuit Automatic tracking shows are constituted by two motors (white line) Cars structure, principle and double motor drive circuit.
The dual motor drive circuit is designed to facilitate automatic tracking functionality in robotic or automated vehicles, such as cars that follow a designated path. The circuit typically includes two DC motors, each responsible for driving one side of the vehicle. By varying the speed and direction of these motors, the vehicle can navigate along a predefined route, which is often marked by a white line or similar guiding feature.
In this configuration, the motors are controlled using a microcontroller that processes input signals from sensors, such as infrared or optical sensors, positioned at the front of the vehicle. These sensors detect the presence of the white line and provide feedback to the microcontroller, which adjusts the motor speeds accordingly to maintain alignment with the line.
The circuit may also incorporate additional components such as motor drivers, which serve to amplify the control signals from the microcontroller to a level sufficient to drive the motors. Power supply considerations are crucial, as the motors require adequate voltage and current to operate effectively. Therefore, a suitable power source, such as batteries or a power adapter, must be integrated into the design.
Furthermore, safety features, such as overcurrent protection and thermal shutdown mechanisms, can be included to prevent damage to the motors and circuit components during operation. The overall design emphasizes efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness, allowing for smooth and precise movement of the vehicle along its tracking path. This dual motor drive circuit serves as a foundational element in various applications, including robotics, automation, and educational projects.Dual motor drive circuit Automatic tracking shows are constituted by two motors (white line) Cars structure, principle and double motor drive circuit.