teleplone circuit
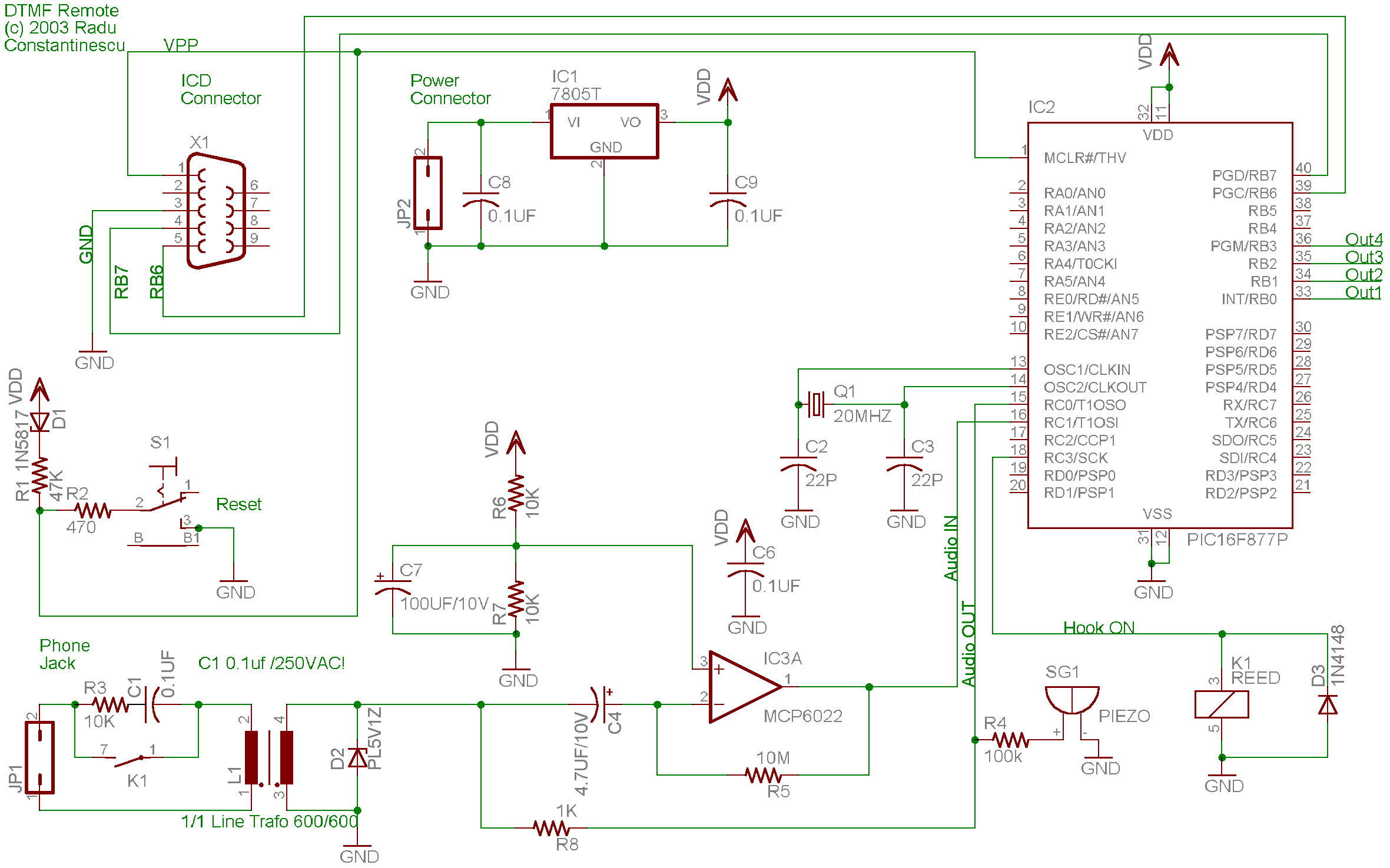
A telephone remote control system allows users to perform various functions remotely using their phone. This system automates complex tasks, simplifying the development and operation of telephone systems.
The telephone remote control system is designed to enhance user interaction with telecommunication devices by enabling remote management of specific functions. The circuit typically consists of a microcontroller, which serves as the central processing unit, and various input/output interfaces that facilitate communication between the user’s phone and the controlled device.
The microcontroller is programmed to interpret signals received from the phone, which may be transmitted via SMS, DTMF tones, or through a dedicated app. The input module can include a GSM module for SMS communication or a tone decoder for DTMF signal processing. Upon receiving a command, the microcontroller executes the corresponding function, which may involve activating relays, controlling motors, or interfacing with other electronic components.
The circuit design may include a power supply module to ensure stable operation, along with protection circuits to safeguard against voltage spikes. Additionally, the layout should consider signal integrity, minimizing noise and interference to maintain reliable communication between the phone and the remote control system.
To facilitate user interaction, the system may be equipped with status indicators such as LEDs to provide visual feedback on the operation of various functions. The overall design aims to create a user-friendly interface that allows for seamless control over the desired functionalities, thereby improving the efficiency and convenience of telephone operations.Telephone remote control for some of the ideas is the time, now can let you own a phone to do remote control, this is the procedure and circuit. Automatically executed complex functions. Facilitate the development of a telephone. 🔗 External reference
The telephone remote control system is designed to enhance user interaction with telecommunication devices by enabling remote management of specific functions. The circuit typically consists of a microcontroller, which serves as the central processing unit, and various input/output interfaces that facilitate communication between the user’s phone and the controlled device.
The microcontroller is programmed to interpret signals received from the phone, which may be transmitted via SMS, DTMF tones, or through a dedicated app. The input module can include a GSM module for SMS communication or a tone decoder for DTMF signal processing. Upon receiving a command, the microcontroller executes the corresponding function, which may involve activating relays, controlling motors, or interfacing with other electronic components.
The circuit design may include a power supply module to ensure stable operation, along with protection circuits to safeguard against voltage spikes. Additionally, the layout should consider signal integrity, minimizing noise and interference to maintain reliable communication between the phone and the remote control system.
To facilitate user interaction, the system may be equipped with status indicators such as LEDs to provide visual feedback on the operation of various functions. The overall design aims to create a user-friendly interface that allows for seamless control over the desired functionalities, thereby improving the efficiency and convenience of telephone operations.Telephone remote control for some of the ideas is the time, now can let you own a phone to do remote control, this is the procedure and circuit. Automatically executed complex functions. Facilitate the development of a telephone. 🔗 External reference