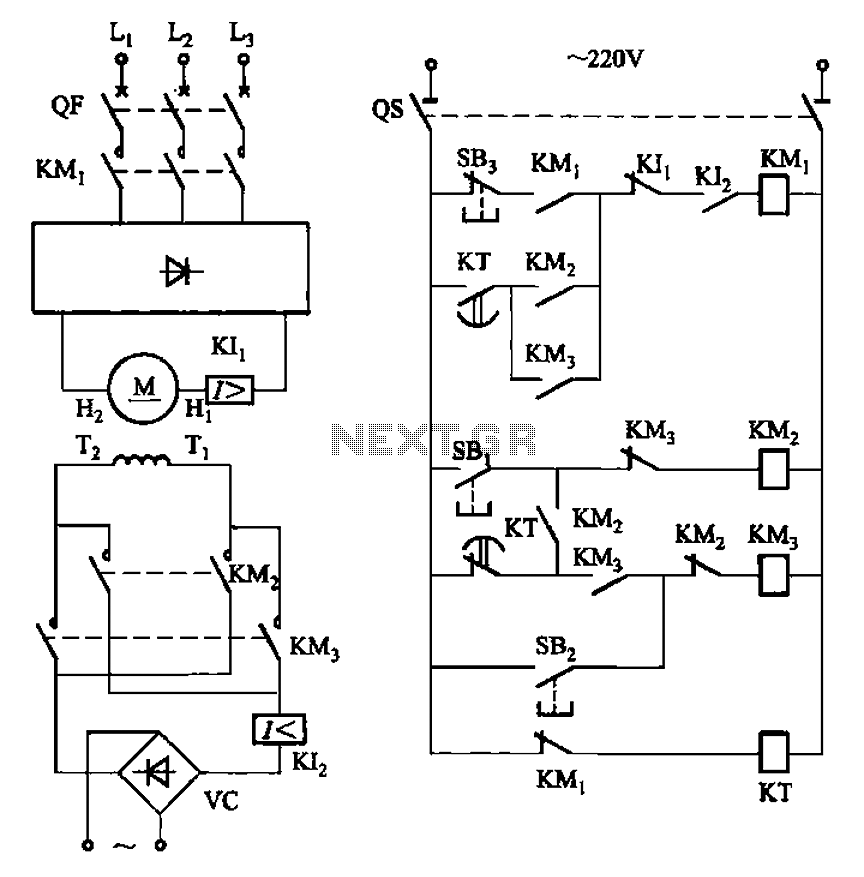
DZW75-48/5050II input circuit

220V (5Hz) alternating voltage passes through the Z1 circuit filter, which filters the signal before sending it to the connection point of the AC over-voltage and under-voltage protection relay K2. During normal operation, the K2 connection point should be closed, connecting the AC 220V voltage to the AC current-limiting resistance R4. After startup, a delay period occurs, during which R1 is short-circuited by the K1 connection point. This setup sends the power frequency to the bridge rectifier for rectification, resulting in a DC output voltage of 300V, smoothed by a parallel-connected condenser bank to complete the AC to DC transformation. R2 serves as a leakage resistance. The Z1 circuit filter is utilized to suppress and absorb strong pulse interference affecting the rectifier in the electrical network, thereby enhancing the reliability of the rectifier. Additionally, the circuit filter's good common mode and differential mode insertion loss effectively inhibit high-frequency interference signals generated by high-frequency switching converters, isolating the rectifier from the electric fence to prevent mutual interference. The AC over-voltage and under-voltage protection circuit receives the AC 220V voltage after filtering through the circuit filter and then sends it to a reducing transformer. The AC current limiting delay circuit ensures that the AC voltage can switch into the machine within the normal working range. The auxiliary power supply builds time after the AC power supply is switched on, and after a delay period, the AC current-limiting resistance can be short-circuited. This delay period is managed by the AC current limiting delay circuit.
The circuit design integrates several critical components to ensure reliable operation and protection of the system. The Z1 filter plays a pivotal role in mitigating electrical noise and transients, which can adversely affect the rectifier's performance. By using capacitors and inductors in the Z1 filter, both common mode and differential mode noise are effectively attenuated, leading to improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference.
The relay K2 operates as a protective mechanism, monitoring the AC voltage levels. In the event of over-voltage or under-voltage conditions, K2 disconnects the load, preventing potential damage to downstream components. The use of a current-limiting resistor R4 is crucial for managing inrush currents during startup, ensuring that the system operates within safe limits.
The bridge rectifier is designed to convert the AC voltage to a stable DC output. The choice of diodes within the rectifier is essential, as they must withstand the peak inverse voltage and provide efficient conduction to minimize power losses. The output capacitor bank, connected in parallel, smooths the rectified voltage, reducing ripple and providing a stable DC supply for further processing.
R2, as a leakage resistance, serves to discharge the capacitor bank during shutdown, ensuring safety and preventing capacitor damage from residual charge. The AC current limiting delay circuit is engineered with precision to allow for a controlled startup sequence. This is critical in applications where sudden surges in current can lead to circuit damage or operational instability.
Overall, this circuit schematic illustrates a robust design tailored for AC to DC conversion with integrated protective features, ensuring both operational reliability and safety in various electrical applications.220V (5Hz) alternating voltagepass Z1 circuit filter filtering, then it will send to the connect point of AC over voltage, under voltage protect relay K2. When normal working, K2 connect point should up-close, connect AC 220V voltage to AC current-limiting resistance R4 (after starting up, delay period of time, R1 is short-circuit by K1 connec
t point), send to power frequency bridge rectifier rectifying, get DC 300V output voltage through parallel connection condenser bank smoothed filtering, finish power frequency AC/DV transform. R2 is leak resistance. (2) Z1 circuit filter is used for suppressing and absorbing obstruction of strong pulse to rectifier on electric network, increasing the reliability of rectifier.
At the same time, the good common mode and difference module insertion loss of circuit filter can effectively inhibit inverted output high frequency interfering signal generated by high frequency switching converter, it canisolate rectifier and electric fence, avoid mutual interference. (3) AC over voltage, under voltage protection circuit, AC 220V voltage sended to reducing transformer after through circuit filter filtering.
(4)AC current limiting delay circuit, AC voltage can switch-in machine in normal work range, build time at auxiliary power supply after AC power supply switch-in, andby a period of time delay after auxiliary power supply build, it can make AC current-limiting resistance short-circuit, this period time is AC current limiting delay, it is finish by AC current limiting delay circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design integrates several critical components to ensure reliable operation and protection of the system. The Z1 filter plays a pivotal role in mitigating electrical noise and transients, which can adversely affect the rectifier's performance. By using capacitors and inductors in the Z1 filter, both common mode and differential mode noise are effectively attenuated, leading to improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference.
The relay K2 operates as a protective mechanism, monitoring the AC voltage levels. In the event of over-voltage or under-voltage conditions, K2 disconnects the load, preventing potential damage to downstream components. The use of a current-limiting resistor R4 is crucial for managing inrush currents during startup, ensuring that the system operates within safe limits.
The bridge rectifier is designed to convert the AC voltage to a stable DC output. The choice of diodes within the rectifier is essential, as they must withstand the peak inverse voltage and provide efficient conduction to minimize power losses. The output capacitor bank, connected in parallel, smooths the rectified voltage, reducing ripple and providing a stable DC supply for further processing.
R2, as a leakage resistance, serves to discharge the capacitor bank during shutdown, ensuring safety and preventing capacitor damage from residual charge. The AC current limiting delay circuit is engineered with precision to allow for a controlled startup sequence. This is critical in applications where sudden surges in current can lead to circuit damage or operational instability.
Overall, this circuit schematic illustrates a robust design tailored for AC to DC conversion with integrated protective features, ensuring both operational reliability and safety in various electrical applications.220V (5Hz) alternating voltagepass Z1 circuit filter filtering, then it will send to the connect point of AC over voltage, under voltage protect relay K2. When normal working, K2 connect point should up-close, connect AC 220V voltage to AC current-limiting resistance R4 (after starting up, delay period of time, R1 is short-circuit by K1 connec
t point), send to power frequency bridge rectifier rectifying, get DC 300V output voltage through parallel connection condenser bank smoothed filtering, finish power frequency AC/DV transform. R2 is leak resistance. (2) Z1 circuit filter is used for suppressing and absorbing obstruction of strong pulse to rectifier on electric network, increasing the reliability of rectifier.
At the same time, the good common mode and difference module insertion loss of circuit filter can effectively inhibit inverted output high frequency interfering signal generated by high frequency switching converter, it canisolate rectifier and electric fence, avoid mutual interference. (3) AC over voltage, under voltage protection circuit, AC 220V voltage sended to reducing transformer after through circuit filter filtering.
(4)AC current limiting delay circuit, AC voltage can switch-in machine in normal work range, build time at auxiliary power supply after AC power supply switch-in, andby a period of time delay after auxiliary power supply build, it can make AC current-limiting resistance short-circuit, this period time is AC current limiting delay, it is finish by AC current limiting delay circuit. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713