Easy exchange of magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit
Easy exchange of magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit
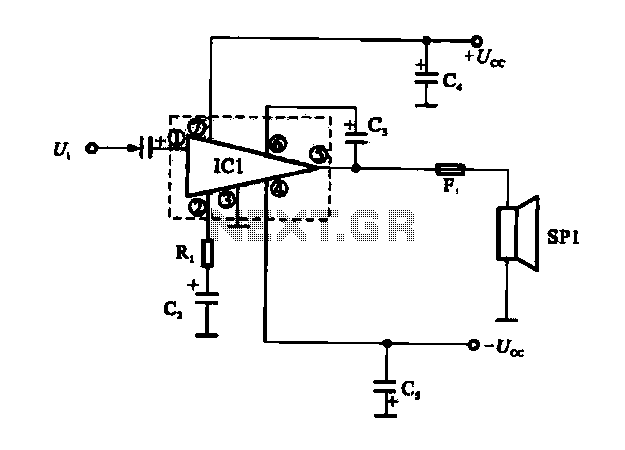
The magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit is designed to stabilize output voltage levels by utilizing magnetic saturation principles. This circuit typically employs a magnetic core, which operates in saturation to regulate voltage, ensuring minimal fluctuations in output despite variations in load or input voltage. The primary components of this circuit include a transformer, diodes, and a feedback mechanism that monitors the output voltage.
The transformer is crucial in stepping down the input voltage to a manageable level before it is rectified by the diodes. The diodes convert the AC voltage from the transformer into DC voltage, which is then smoothed using capacitors to reduce ripple. The feedback mechanism is essential for maintaining voltage stability; it continuously compares the output voltage to a reference voltage and adjusts the control signal accordingly.
When the output voltage rises above the desired level, the feedback loop reduces the current flowing through the transformer, effectively bringing the output voltage back into the acceptable range. Conversely, if the output voltage drops, the feedback loop increases the current to compensate. This dynamic adjustment allows the magnetic saturation voltage regulator to maintain a constant output voltage even under varying load conditions.
The design of this circuit can be optimized for efficiency by selecting appropriate components and tuning the feedback loop for quick response times. Additionally, considerations for thermal management should be made, as components may generate heat during operation. Overall, the magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit presents a reliable solution for applications requiring stable voltage regulation.Easy exchange of magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit
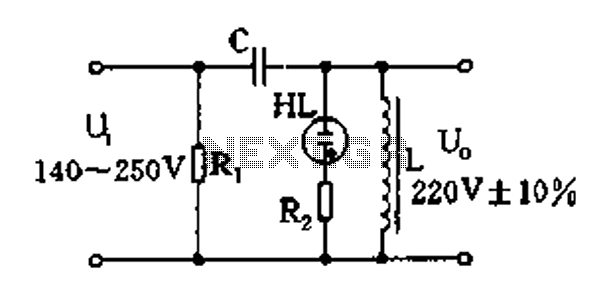
The magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit is designed to stabilize output voltage levels by utilizing magnetic saturation principles. This circuit typically employs a magnetic core, which operates in saturation to regulate voltage, ensuring minimal fluctuations in output despite variations in load or input voltage. The primary components of this circuit include a transformer, diodes, and a feedback mechanism that monitors the output voltage.
The transformer is crucial in stepping down the input voltage to a manageable level before it is rectified by the diodes. The diodes convert the AC voltage from the transformer into DC voltage, which is then smoothed using capacitors to reduce ripple. The feedback mechanism is essential for maintaining voltage stability; it continuously compares the output voltage to a reference voltage and adjusts the control signal accordingly.
When the output voltage rises above the desired level, the feedback loop reduces the current flowing through the transformer, effectively bringing the output voltage back into the acceptable range. Conversely, if the output voltage drops, the feedback loop increases the current to compensate. This dynamic adjustment allows the magnetic saturation voltage regulator to maintain a constant output voltage even under varying load conditions.
The design of this circuit can be optimized for efficiency by selecting appropriate components and tuning the feedback loop for quick response times. Additionally, considerations for thermal management should be made, as components may generate heat during operation. Overall, the magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit presents a reliable solution for applications requiring stable voltage regulation.Easy exchange of magnetic saturation voltage regulator circuit