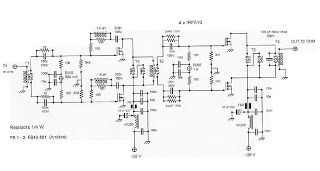
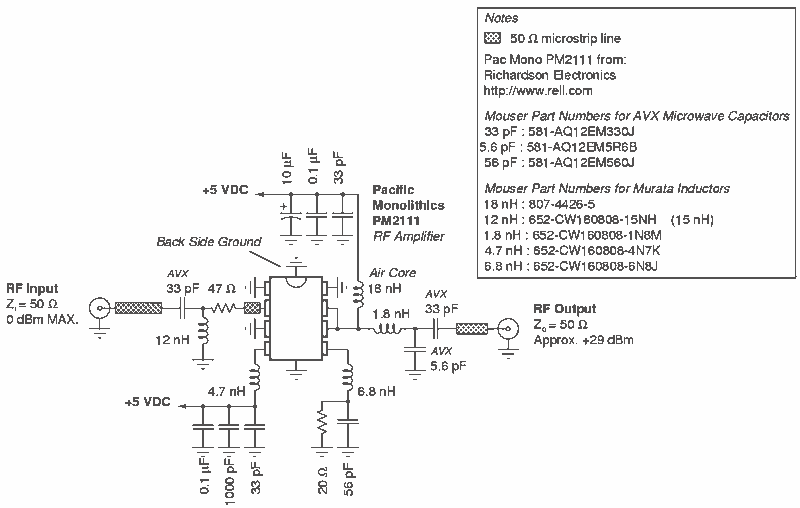
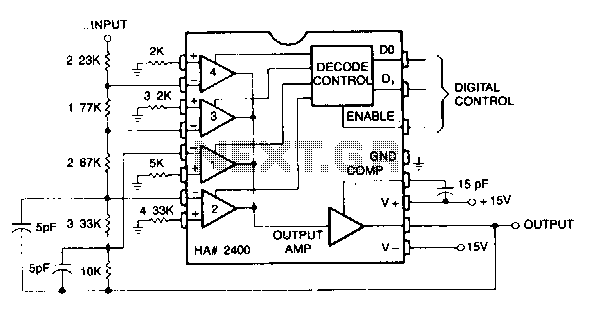
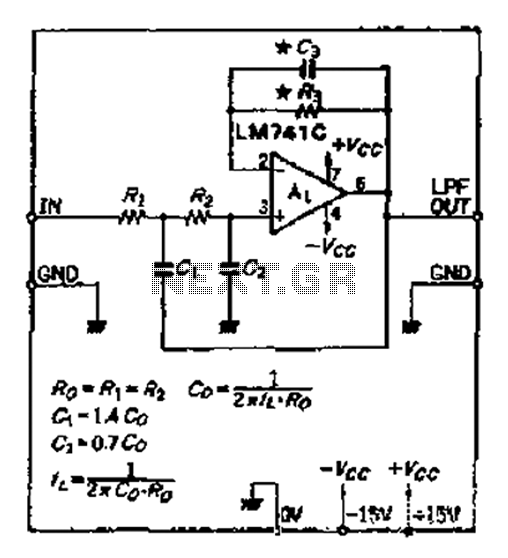
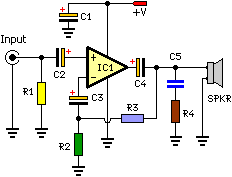
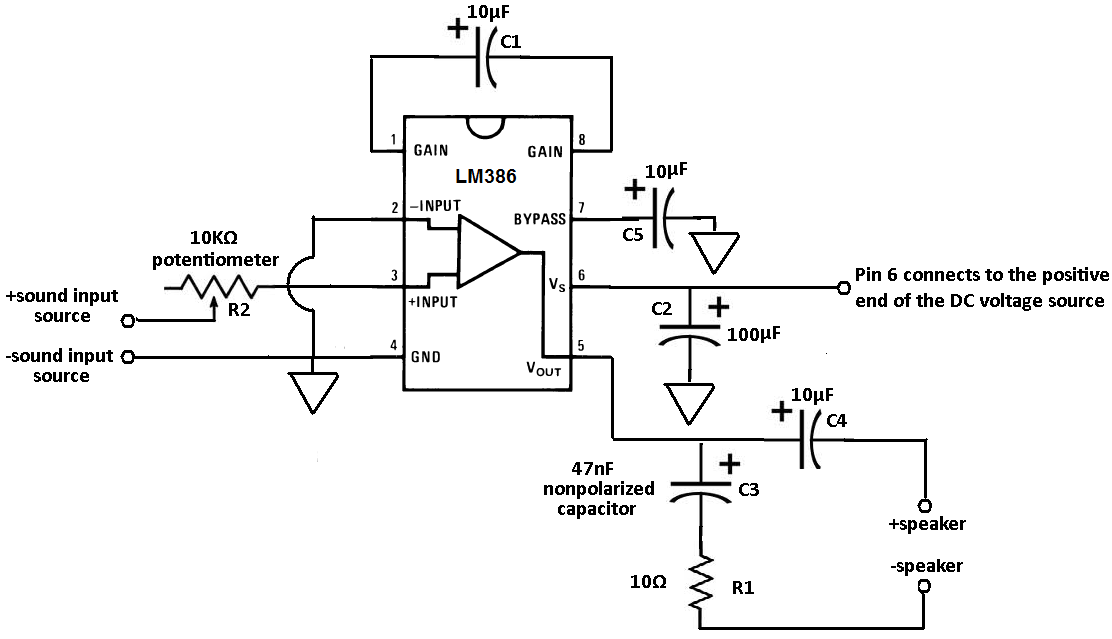
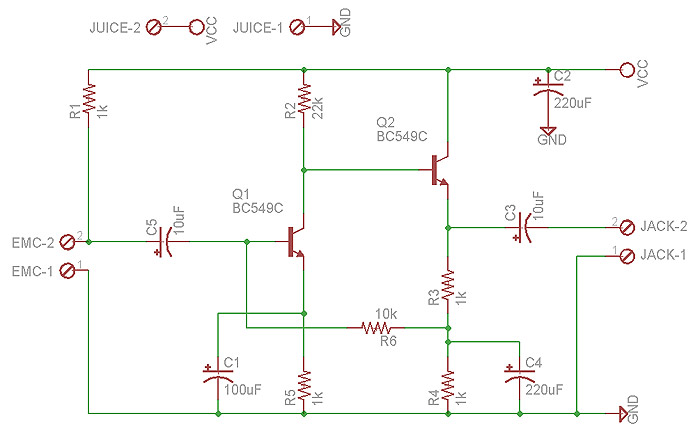
electret microphone amplifier
Level refers to the relative strength of the signal and is measured in decibels. LINE level sources are much-amplified signals compared to MIC (microphone) level signals. Line level typically ranges from -10 to +4 dBm in strength, while MIC levels are generally around -60 dBm. The line output standard is designed to drive a load of 600 ohms or greater, with a mean signal level of 0.775V RMS. An exception exists for compact disc players, where the output level is most commonly 2V RMS.
The concept of signal levels is crucial in audio engineering, particularly when designing circuits that interface different types of audio equipment. LINE level signals are significantly stronger than MIC level signals, necessitating careful consideration when connecting devices to avoid distortion or damage.
In practical applications, LINE level signals are often used in professional audio equipment such as mixers, amplifiers, and recording devices. The standard output impedance of 600 ohms is important to ensure compatibility with a wide range of audio equipment, allowing for optimal signal transfer and minimizing loss.
When designing circuits that incorporate both LINE and MIC level inputs, it is essential to include appropriate preamplification stages for MIC signals to boost their levels to match LINE levels. This can be achieved using operational amplifiers configured as non-inverting amplifiers, which can provide the necessary gain while maintaining low noise characteristics.
Additionally, when dealing with compact disc players, which output at a higher level of 2V RMS, it is important to implement attenuation circuits if interfacing with equipment designed for standard LINE levels. This can be accomplished through passive voltage dividers or active circuits that adjust the signal level to prevent clipping and ensure a clean audio signal throughout the system.
In summary, understanding the differences between LINE and MIC level signals, as well as their respective output characteristics, is essential for the design and implementation of reliable audio circuits that maintain signal integrity across various devices.Level refers to the relative strength of the signal and is measured in decibels. LINE level sources are much-amplified signals over MIC (microphone) level signals. Line level is usually between -10 to +4 dbm in strength while MIC levels are normally -60 dbm. The line output standard designed to drive a load of 600 ohms or greater, at a mean signal level of 0. 775V RMS. An exception exists in respect of compact disc players, where the output level is most commonly 2V RMS. 🔗 External reference
The concept of signal levels is crucial in audio engineering, particularly when designing circuits that interface different types of audio equipment. LINE level signals are significantly stronger than MIC level signals, necessitating careful consideration when connecting devices to avoid distortion or damage.
In practical applications, LINE level signals are often used in professional audio equipment such as mixers, amplifiers, and recording devices. The standard output impedance of 600 ohms is important to ensure compatibility with a wide range of audio equipment, allowing for optimal signal transfer and minimizing loss.
When designing circuits that incorporate both LINE and MIC level inputs, it is essential to include appropriate preamplification stages for MIC signals to boost their levels to match LINE levels. This can be achieved using operational amplifiers configured as non-inverting amplifiers, which can provide the necessary gain while maintaining low noise characteristics.
Additionally, when dealing with compact disc players, which output at a higher level of 2V RMS, it is important to implement attenuation circuits if interfacing with equipment designed for standard LINE levels. This can be accomplished through passive voltage dividers or active circuits that adjust the signal level to prevent clipping and ensure a clean audio signal throughout the system.
In summary, understanding the differences between LINE and MIC level signals, as well as their respective output characteristics, is essential for the design and implementation of reliable audio circuits that maintain signal integrity across various devices.Level refers to the relative strength of the signal and is measured in decibels. LINE level sources are much-amplified signals over MIC (microphone) level signals. Line level is usually between -10 to +4 dbm in strength while MIC levels are normally -60 dbm. The line output standard designed to drive a load of 600 ohms or greater, at a mean signal level of 0. 775V RMS. An exception exists in respect of compact disc players, where the output level is most commonly 2V RMS. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713