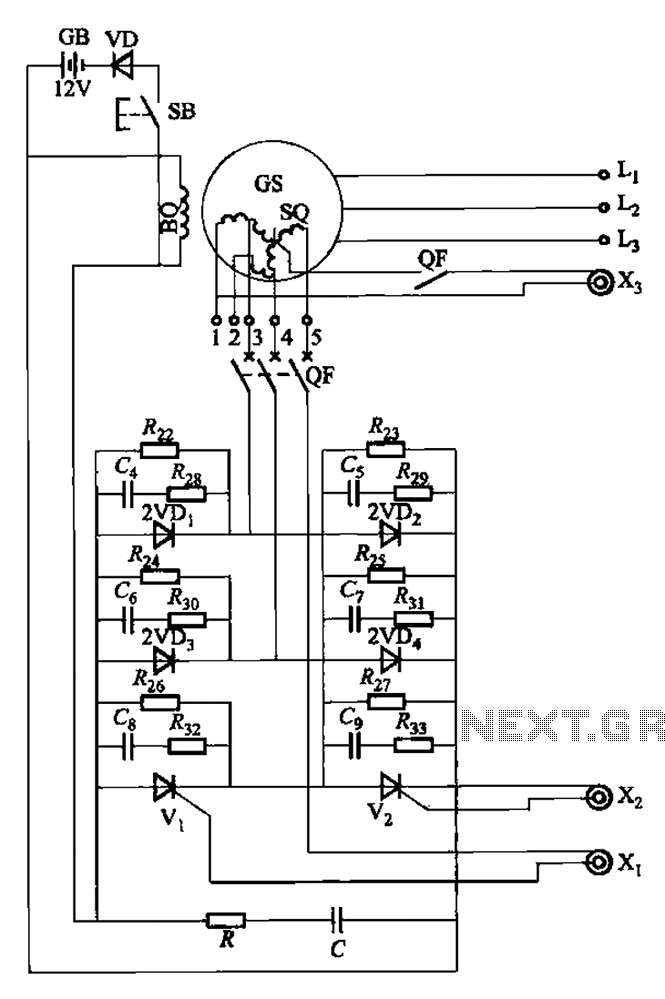
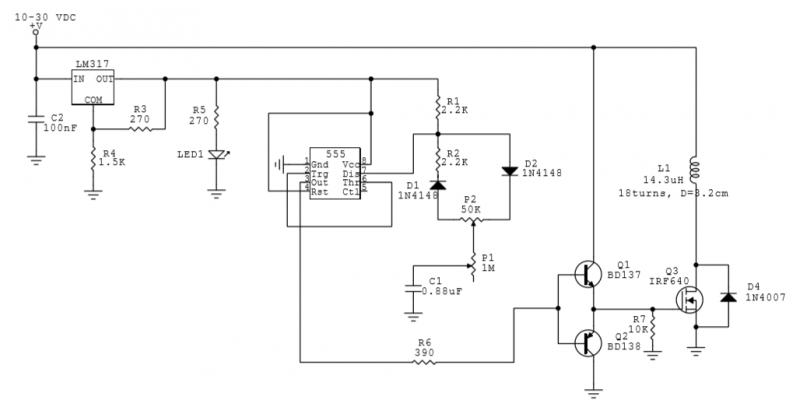
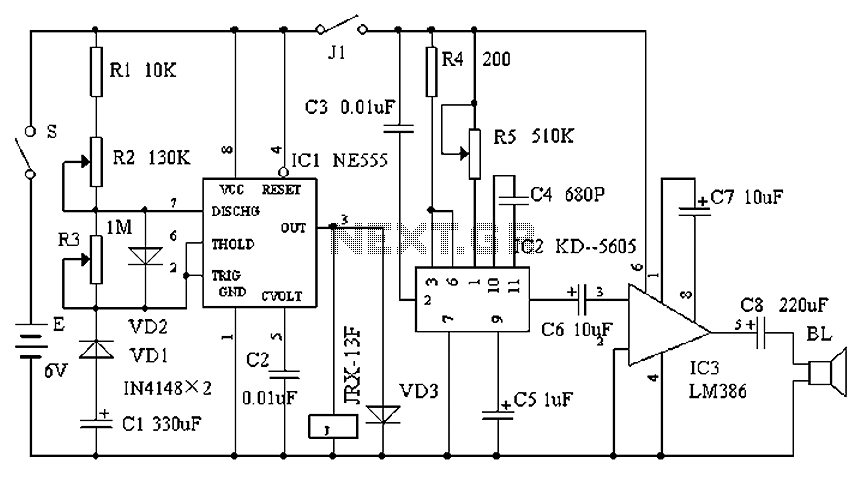
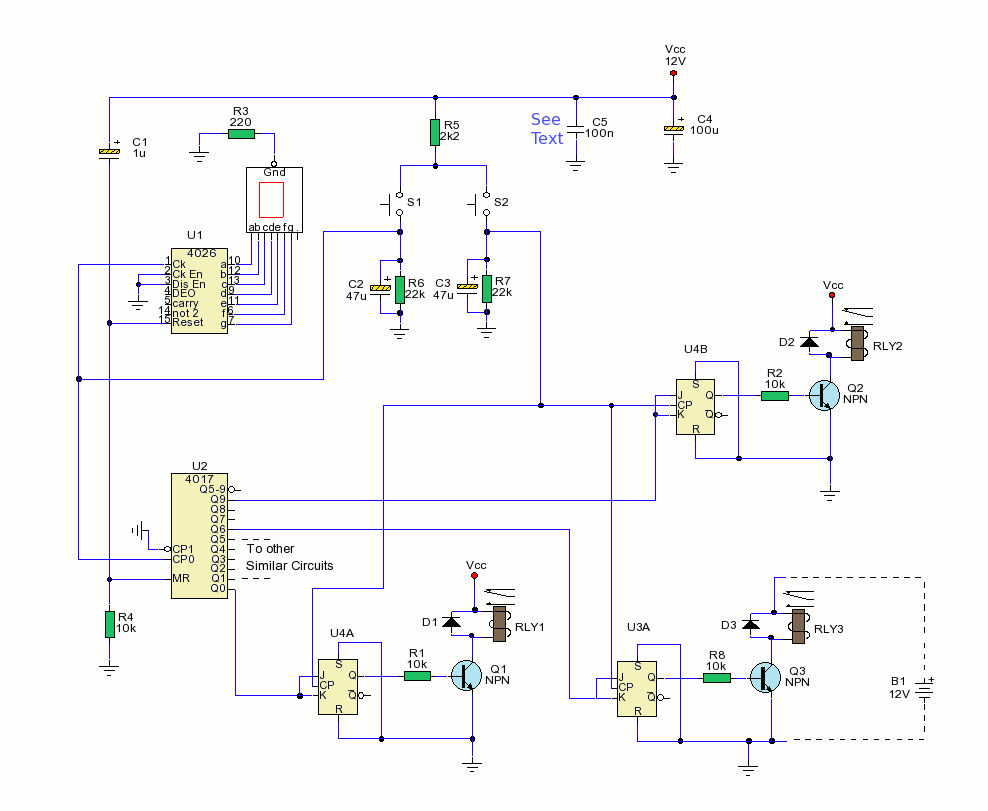
Electronic bio-wave therapy device
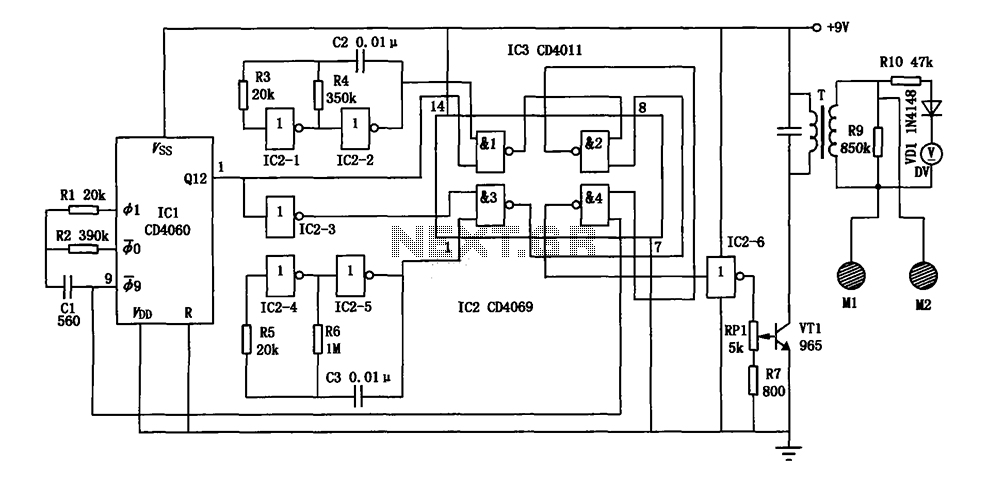
The electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit is designed to generate a variety of complex frequency electrical signals. These signals can enhance the absorption of medication and provide direct therapeutic effects on specific body points.
The electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit operates on the principle of applying electrical signals to the body to stimulate healing and improve drug absorption. The circuit typically includes several key components: a microcontroller or signal generator, which produces the desired frequency signals; an amplifier to boost these signals; and electrodes that interface with the patient's skin.
The microcontroller is programmed to generate a range of frequencies, which can be adjusted based on the specific treatment protocol. These frequencies may vary widely, allowing for customization depending on the patient's condition and the intended therapeutic effect. The amplifier ensures that the signals are strong enough to penetrate the skin and reach the underlying tissues effectively.
Electrodes are strategically placed on the body to target specific acupoints or areas of pain. The design of these electrodes may vary, with some being adhesive pads and others being more specialized for particular applications. The placement and type of electrodes used can significantly influence the treatment's effectiveness.
Safety features are also an essential aspect of the circuit design. Overcurrent protection, isolation mechanisms, and user interface controls are implemented to ensure that the device operates within safe parameters. Additionally, the circuit may include a feedback system to monitor the response of the patient, adjusting the frequency or intensity of the signals in real time for optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Overall, the electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit represents a sophisticated approach to non-invasive treatment modalities, leveraging the principles of bioelectromagnetics to enhance patient care.Electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit as shown, it can produce a variety of complex frequency electrical signals, the absorption of the drug can help patients affected area can also be a direct effect of treatment on the body points.
The electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit operates on the principle of applying electrical signals to the body to stimulate healing and improve drug absorption. The circuit typically includes several key components: a microcontroller or signal generator, which produces the desired frequency signals; an amplifier to boost these signals; and electrodes that interface with the patient's skin.
The microcontroller is programmed to generate a range of frequencies, which can be adjusted based on the specific treatment protocol. These frequencies may vary widely, allowing for customization depending on the patient's condition and the intended therapeutic effect. The amplifier ensures that the signals are strong enough to penetrate the skin and reach the underlying tissues effectively.
Electrodes are strategically placed on the body to target specific acupoints or areas of pain. The design of these electrodes may vary, with some being adhesive pads and others being more specialized for particular applications. The placement and type of electrodes used can significantly influence the treatment's effectiveness.
Safety features are also an essential aspect of the circuit design. Overcurrent protection, isolation mechanisms, and user interface controls are implemented to ensure that the device operates within safe parameters. Additionally, the circuit may include a feedback system to monitor the response of the patient, adjusting the frequency or intensity of the signals in real time for optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Overall, the electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit represents a sophisticated approach to non-invasive treatment modalities, leveraging the principles of bioelectromagnetics to enhance patient care.Electronic bio wave therapy instrument circuit as shown, it can produce a variety of complex frequency electrical signals, the absorption of the drug can help patients affected area can also be a direct effect of treatment on the body points.