Electronic Circuit Schematic DC Motor Driver using L293D Dual H-Bridge
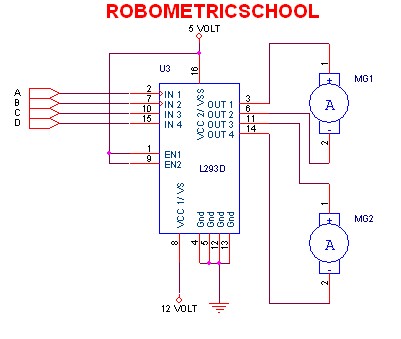
The electronic schematic of a DC motor driver using the L293D, as illustrated in Figure 2, enables the control of two DC motors continuously. It allows for one motor to rotate clockwise while the other rotates counterclockwise. Additionally, all motors can be controlled to rotate either clockwise, counterclockwise, or to stop entirely. Control is achieved through input signals to the L293D.
According to the guidance provided in Figure 3, the motor will rotate clockwise when a logic high (1) is applied to input A and a logic low (0) is applied to input B. Conversely, the motor will rotate counterclockwise when input A receives a logic low (0) and input B is set to a logic high (1). To stop all motors, a logic high (1) must be applied to all input pins. It is crucial to avoid applying a logic low (0) to all inputs simultaneously, as this can lead to errors or damage to the L293D, potentially resulting in overheating or short circuits.
The L293D is a dual H-bridge motor driver capable of controlling the direction and speed of DC motors. Each H-bridge can control one motor, allowing for independent operation of two motors. The device features built-in diodes for back EMF protection, which is essential for safeguarding the circuit from voltage spikes generated by the motors during operation.
To implement the circuit, the L293D is connected to the power supply, motors, and a microcontroller or other control logic. The control signals from the microcontroller dictate the state of the inputs A and B for each motor. By using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) on the enable pins of the L293D, speed control can also be achieved, allowing for variable motor speeds in addition to directional control.
Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered, as the L293D can generate heat during operation, especially under high load conditions. Heat sinks may be necessary to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent thermal shutdown. Overall, the L293D motor driver is a versatile component for robotics and automation applications, providing efficient control of DC motors in various configurations.According electronic schematic of DC driver motor using L293D in figure 2, we can use it to control two DC motor continuously. We can control DC motor one to rotate clock wise and DC motor two to rotate anti clock wise. We also can control all motor to rotate clock wise, anti click wise, or stop all. We can control it with give control in input of L293D. You can use guidance like in figure 3 bellow: From figure 3 above, we can make motor rotate clock wise when in input we give 1 logic in A and 0 logic in B. Also we can make motor rotate anti clock wise when input we give 0 logic in A and 1 logic in B. We can stop all motor with give in all input 1 logic. Attention you don`t give in all input with 0 logic, because it can make L293D error or damage like burn or shot circuit.
So careful when you set it. Thank you very much for your visiting in Robometricschool blog, We hope you will get more information about Robotic, Mechatronic, and Electronic. And don`t forget to give us your comment about this article. Let keep for building comment. 🔗 External reference
According to the guidance provided in Figure 3, the motor will rotate clockwise when a logic high (1) is applied to input A and a logic low (0) is applied to input B. Conversely, the motor will rotate counterclockwise when input A receives a logic low (0) and input B is set to a logic high (1). To stop all motors, a logic high (1) must be applied to all input pins. It is crucial to avoid applying a logic low (0) to all inputs simultaneously, as this can lead to errors or damage to the L293D, potentially resulting in overheating or short circuits.
The L293D is a dual H-bridge motor driver capable of controlling the direction and speed of DC motors. Each H-bridge can control one motor, allowing for independent operation of two motors. The device features built-in diodes for back EMF protection, which is essential for safeguarding the circuit from voltage spikes generated by the motors during operation.
To implement the circuit, the L293D is connected to the power supply, motors, and a microcontroller or other control logic. The control signals from the microcontroller dictate the state of the inputs A and B for each motor. By using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) on the enable pins of the L293D, speed control can also be achieved, allowing for variable motor speeds in addition to directional control.
Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered, as the L293D can generate heat during operation, especially under high load conditions. Heat sinks may be necessary to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent thermal shutdown. Overall, the L293D motor driver is a versatile component for robotics and automation applications, providing efficient control of DC motors in various configurations.According electronic schematic of DC driver motor using L293D in figure 2, we can use it to control two DC motor continuously. We can control DC motor one to rotate clock wise and DC motor two to rotate anti clock wise. We also can control all motor to rotate clock wise, anti click wise, or stop all. We can control it with give control in input of L293D. You can use guidance like in figure 3 bellow: From figure 3 above, we can make motor rotate clock wise when in input we give 1 logic in A and 0 logic in B. Also we can make motor rotate anti clock wise when input we give 0 logic in A and 1 logic in B. We can stop all motor with give in all input 1 logic. Attention you don`t give in all input with 0 logic, because it can make L293D error or damage like burn or shot circuit.
So careful when you set it. Thank you very much for your visiting in Robometricschool blog, We hope you will get more information about Robotic, Mechatronic, and Electronic. And don`t forget to give us your comment about this article. Let keep for building comment. 🔗 External reference