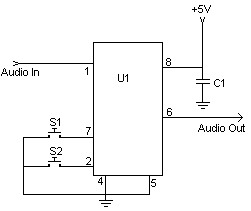
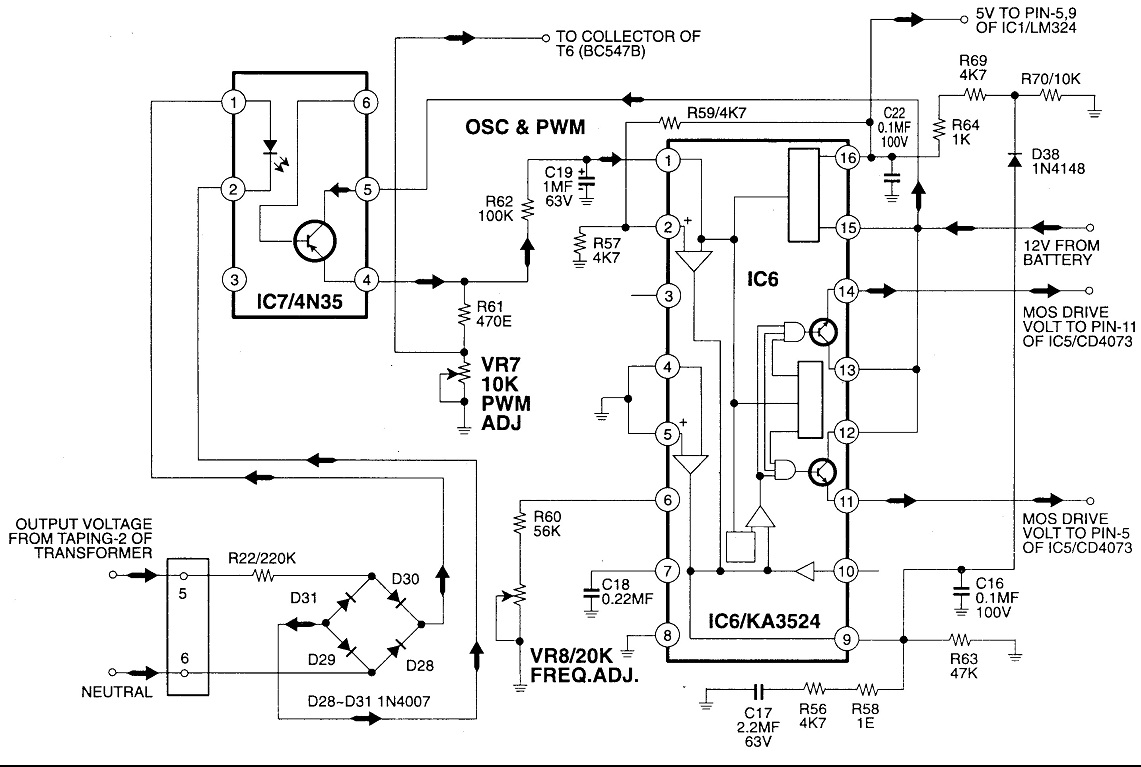
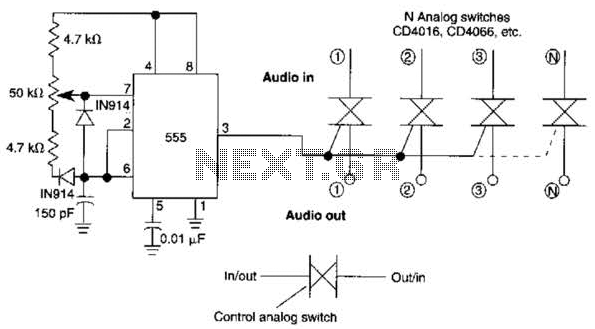
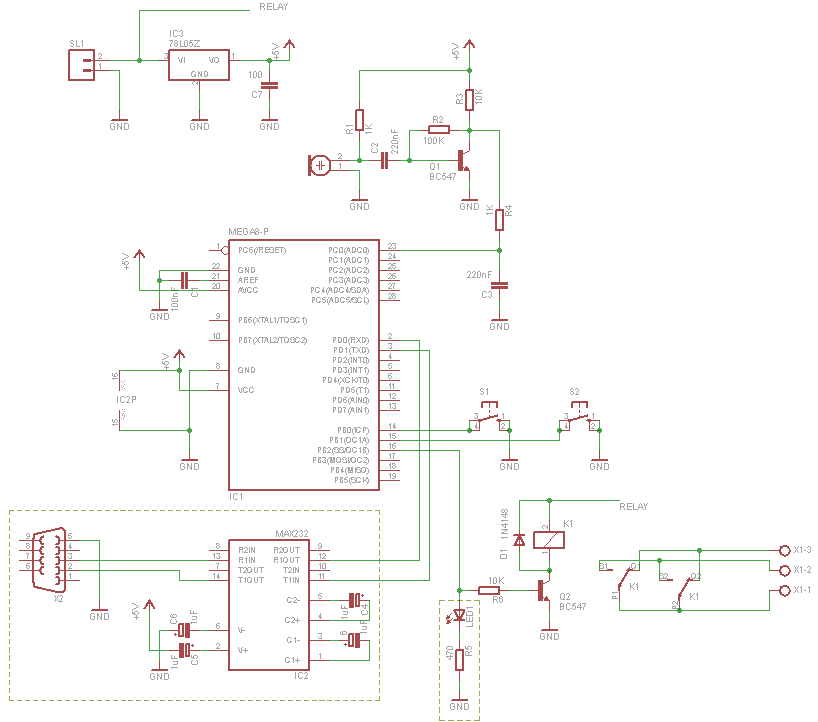
Electronic Gain Control in Quartz-Stabilized Oscillator
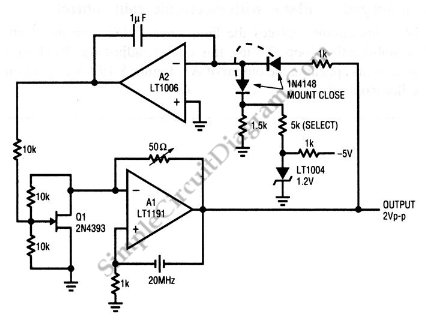
This is a quartz-stabilized oscillator circuit with electronic gain control. Replacing the common filament lamp for amplitude stabilization, this circuit uses...
This circuit represents a quartz-stabilized oscillator featuring electronic gain control, which enhances the stability and precision of the output frequency. The utilization of a quartz crystal allows for high-frequency accuracy, making this oscillator suitable for various applications requiring stable signal generation.
In this design, the traditional filament lamp, often employed for amplitude stabilization, has been replaced with a more efficient electronic gain control mechanism. This substitution not only improves the reliability of the circuit but also reduces power consumption and increases the overall lifespan of the oscillator.
The circuit typically includes a quartz crystal oscillator, which sets the fundamental frequency, and an amplifier stage that provides the necessary gain. The electronic gain control is implemented using a variable resistor or a digital potentiometer, allowing for real-time adjustments to the amplitude of the output signal. Feedback loops are utilized to maintain the desired output level and to ensure that the oscillator remains stable under varying load conditions.
Power supply considerations are also crucial for the performance of this circuit. A regulated power supply is recommended to minimize noise and fluctuations that could affect the oscillator's stability. Additionally, decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power pins of the active components to filter out high-frequency noise.
In summary, this quartz-stabilized oscillator circuit with electronic gain control offers a modern solution for generating stable frequencies with enhanced performance characteristics compared to traditional methods. Its design allows for flexibility in applications, making it suitable for communication systems, signal processing, and other electronic devices requiring precise frequency generation.This is a quartz-stabilized oscillator circuit with electronic gain control. Replacing the common filament lamp for amplitude stabilization, this circuit use.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit represents a quartz-stabilized oscillator featuring electronic gain control, which enhances the stability and precision of the output frequency. The utilization of a quartz crystal allows for high-frequency accuracy, making this oscillator suitable for various applications requiring stable signal generation.
In this design, the traditional filament lamp, often employed for amplitude stabilization, has been replaced with a more efficient electronic gain control mechanism. This substitution not only improves the reliability of the circuit but also reduces power consumption and increases the overall lifespan of the oscillator.
The circuit typically includes a quartz crystal oscillator, which sets the fundamental frequency, and an amplifier stage that provides the necessary gain. The electronic gain control is implemented using a variable resistor or a digital potentiometer, allowing for real-time adjustments to the amplitude of the output signal. Feedback loops are utilized to maintain the desired output level and to ensure that the oscillator remains stable under varying load conditions.
Power supply considerations are also crucial for the performance of this circuit. A regulated power supply is recommended to minimize noise and fluctuations that could affect the oscillator's stability. Additionally, decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power pins of the active components to filter out high-frequency noise.
In summary, this quartz-stabilized oscillator circuit with electronic gain control offers a modern solution for generating stable frequencies with enhanced performance characteristics compared to traditional methods. Its design allows for flexibility in applications, making it suitable for communication systems, signal processing, and other electronic devices requiring precise frequency generation.This is a quartz-stabilized oscillator circuit with electronic gain control. Replacing the common filament lamp for amplitude stabilization, this circuit use.. 🔗 External reference