Electronic Selector for 10 sources with Display-Relay Drive circuit
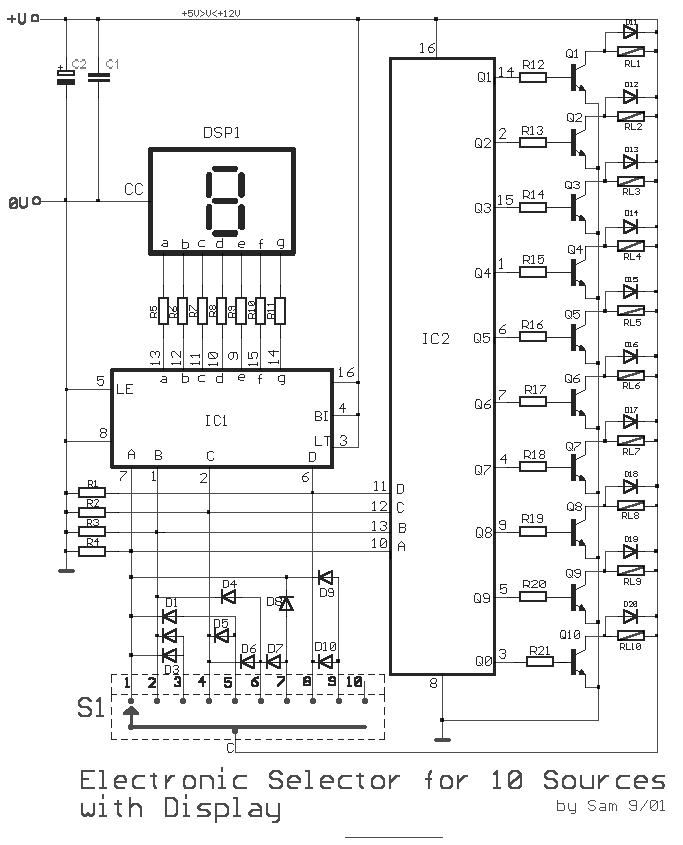
This circuit is designed for the selection of alternative sources. It integrates mechanical selection through a rotating switch S1, electronic control of relays RL1 to RL10, and optical indication of the selection via the display DSP1.
The circuit operates by allowing the user to select between multiple power sources or signal inputs through a mechanical rotating switch (S1). This switch is connected to a series of relays (RL1 to RL10), which are electronically driven to switch the selected source to the output. Each relay corresponds to a specific input or source, enabling the circuit to handle various operational requirements.
The electronic drive for the relays is typically implemented using a microcontroller or a dedicated relay driver IC, which receives input from the rotating switch. This design ensures that the selected relay is activated while others remain deactivated, preventing cross-talk between sources. The relays are chosen based on their switching capacity to handle the required voltage and current levels of the signals being managed.
To provide visual feedback to the user, an optical indication is achieved through the display (DSP1). This display can be an LED array, LCD, or other types of visual indicators that illuminate or change state to reflect the current selection made via the switch. The display is updated in real-time as the switch is rotated, ensuring the user is always aware of which source is currently active.
The overall design emphasizes reliability and user-friendliness, making it suitable for applications where multiple sources need to be managed efficiently, such as in audio systems, power distribution systems, or laboratory setups. Proper consideration should be given to the layout of the circuit to minimize noise and interference, particularly in sensitive applications. Additionally, the selection mechanism should be robust to ensure longevity and consistent performance over time.This is a circuit for alternative sources selection. It combines mechanical selection using a rotating switch S1, the electronic drive of the relays RL 1-10 and also the optical indication of the selection by the Display DSP1.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by allowing the user to select between multiple power sources or signal inputs through a mechanical rotating switch (S1). This switch is connected to a series of relays (RL1 to RL10), which are electronically driven to switch the selected source to the output. Each relay corresponds to a specific input or source, enabling the circuit to handle various operational requirements.
The electronic drive for the relays is typically implemented using a microcontroller or a dedicated relay driver IC, which receives input from the rotating switch. This design ensures that the selected relay is activated while others remain deactivated, preventing cross-talk between sources. The relays are chosen based on their switching capacity to handle the required voltage and current levels of the signals being managed.
To provide visual feedback to the user, an optical indication is achieved through the display (DSP1). This display can be an LED array, LCD, or other types of visual indicators that illuminate or change state to reflect the current selection made via the switch. The display is updated in real-time as the switch is rotated, ensuring the user is always aware of which source is currently active.
The overall design emphasizes reliability and user-friendliness, making it suitable for applications where multiple sources need to be managed efficiently, such as in audio systems, power distribution systems, or laboratory setups. Proper consideration should be given to the layout of the circuit to minimize noise and interference, particularly in sensitive applications. Additionally, the selection mechanism should be robust to ensure longevity and consistent performance over time.This is a circuit for alternative sources selection. It combines mechanical selection using a rotating switch S1, the electronic drive of the relays RL 1-10 and also the optical indication of the selection by the Display DSP1.. 🔗 External reference