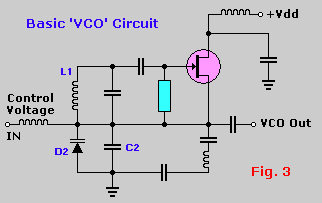
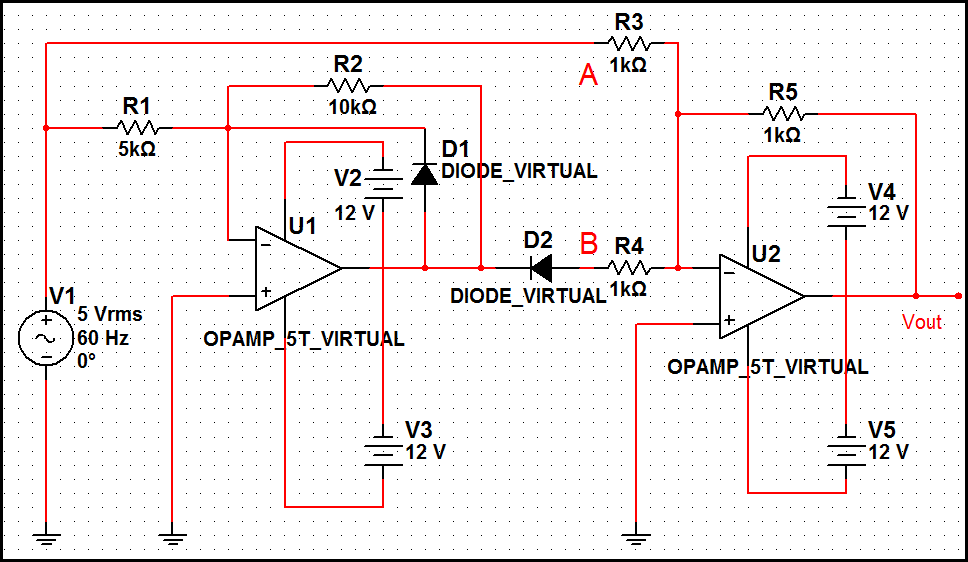
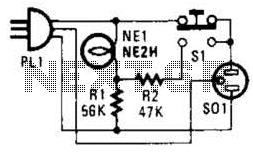
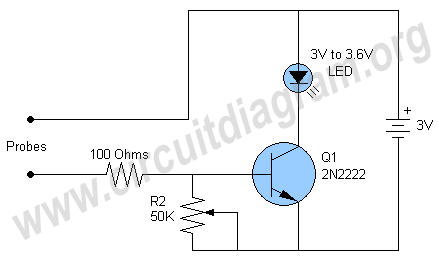
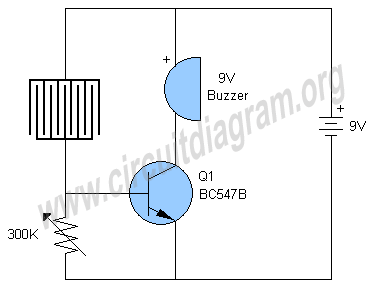
General Purpose Alarm Circuit for Resistive Sensor
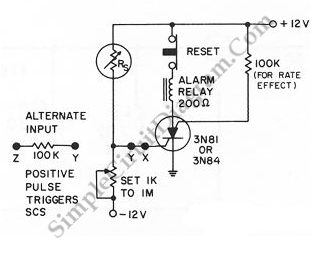
When the resistance value of temperature, light, pressure, or any other resistive sensors (Rs) drops below a certain threshold, which can be adjusted by a preset.
In electronic circuits, resistive sensors such as thermistors, photoresistors, and piezoresistors are commonly used to monitor environmental conditions. These sensors change their resistance in response to variations in temperature, light intensity, and pressure, respectively. The output from these sensors can be utilized in various applications, including environmental monitoring systems, automatic lighting controls, and pressure detection systems.
When the resistance of a sensor, denoted as Rs, falls below a predetermined threshold, it can trigger specific actions in the circuit. This threshold is typically set using a variable resistor (potentiometer) that allows for fine-tuning according to the specific application requirements.
For example, in a temperature monitoring system using a thermistor, if the temperature rises and causes Rs to drop below the preset threshold, the circuit can activate a cooling system or send an alert signal. Similarly, in a light-sensitive application, if the ambient light decreases and Rs falls below the set point, the circuit can turn on an LED or activate a relay to control other devices.
The circuit design may include an operational amplifier configured as a comparator to monitor the voltage drop across Rs. When the voltage corresponding to Rs falls below the reference voltage set by the potentiometer, the comparator output will switch states, triggering subsequent actions in the circuit. This setup allows for precise control and responsiveness to environmental changes, enhancing the functionality and automation of electronic systems.When the resistance value of a temperature, light, pressure,? or any other resistive sensors? Rs drops below a certain point? (adjusted by a preset. 🔗 External reference
In electronic circuits, resistive sensors such as thermistors, photoresistors, and piezoresistors are commonly used to monitor environmental conditions. These sensors change their resistance in response to variations in temperature, light intensity, and pressure, respectively. The output from these sensors can be utilized in various applications, including environmental monitoring systems, automatic lighting controls, and pressure detection systems.
When the resistance of a sensor, denoted as Rs, falls below a predetermined threshold, it can trigger specific actions in the circuit. This threshold is typically set using a variable resistor (potentiometer) that allows for fine-tuning according to the specific application requirements.
For example, in a temperature monitoring system using a thermistor, if the temperature rises and causes Rs to drop below the preset threshold, the circuit can activate a cooling system or send an alert signal. Similarly, in a light-sensitive application, if the ambient light decreases and Rs falls below the set point, the circuit can turn on an LED or activate a relay to control other devices.
The circuit design may include an operational amplifier configured as a comparator to monitor the voltage drop across Rs. When the voltage corresponding to Rs falls below the reference voltage set by the potentiometer, the comparator output will switch states, triggering subsequent actions in the circuit. This setup allows for precise control and responsiveness to environmental changes, enhancing the functionality and automation of electronic systems.When the resistance value of a temperature, light, pressure,? or any other resistive sensors? Rs drops below a certain point? (adjusted by a preset. 🔗 External reference